Enable Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Wireless Access Point
Available Languages
Objective
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol used on a Local Area Network (LAN). The purpose of STP is to allow redundant connection between devices while ensuring a loop-free topology for a LAN. STP removes loops through an algorithm that guarantees that there is only one active path between two network devices. It ensures that traffic takes the shortest path possible within the network. It can also automatically re-enable redundant paths as backup paths in case the active path fails.
STP eliminates network loops thereby optimizing the performance of the network.
This article aims to show you how to enable Spanning Tree Protocol on a wireless access point (WAP).
Applicable Devices
- WAP500 Series – WAP571, WAP571E
- WAP351
Software Version
- 1.0.0.17 — WAP571, WAP571E
- 1.0.2.2 — WAP351
Enable Spanning Tree on a WAP
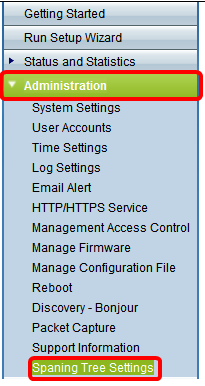
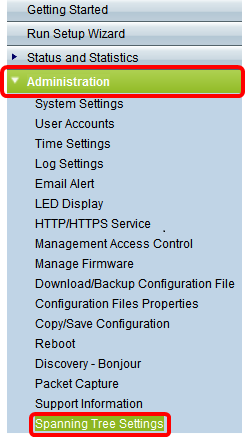
Step 1. Log in to the web-based utility of the access point and choose Administration > Spanning Tree Settings.
| WAP351 |
WAP571/WAP571E |
|
|
|
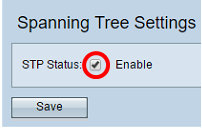
Step 2. Make sure the STP Status check box is checked to enable the feature globally. When enabled, STP helps prevent switching loops. This option is enabled by default.
| WAP571/WAP571E |
WAP351 |
|
|
|
Note: If you have a WAP571/WAP571E, skip to Step 5.
Step 3. (Optional) Check the Enable Flood BPDU if STP is disabled on port(s) check box to flood the BPDU packets received from the port or ports whose STP status is disabled, or uncheck to drop the BPDU packets received from the port or ports whose STP status is disabled. This option is enabled by default and is only found in the WAP351.

Step 4. (Optional) Under the Per Port STP Status Setting area, check the check boxes to enable STP on your preferred Ethernet/WDS port.
Note: In this example, STP is enabled on the GE1, GE3, GE4, GE5, WDS2, and WDS3 ports only.
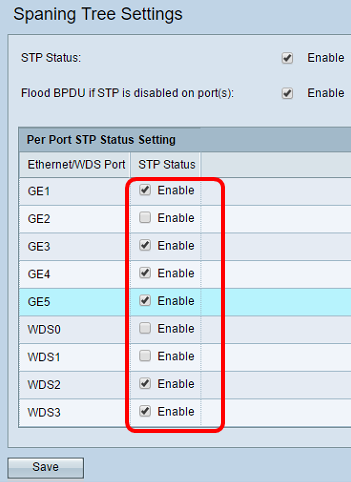
Step 5. Click Save.
You have now successfully enabled spanning tree protocol on your wireless access point.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
13-Dec-2018 |
Initial Release |

 Feedback
Feedback