Configure Media Access Control (MAC)-Based Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) Groups to VLAN on a Cisco Business 350 Series Switch
Available Languages
Objective
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) allows you to logically segment a Local Area Network (LAN) into different broadcast domains. In scenarios where sensitive data may be broadcast on a network, VLANs can be created to enhance security by designating a broadcast to a specific VLAN. Only users that belong to a VLAN are able to access and manipulate the data on that VLAN. VLANs can also be used to enhance performance by reducing the need to send broadcasts and multicasts to unnecessary destinations.
Networking devices on which multiple protocols are running cannot be grouped to a common VLAN. Non-standard devices are used to pass traffic between different VLANs in order to include the devices participating in a specific protocol. For this reason, the user cannot take advantage of the many features of VLAN.
VLAN groups are used to load balance the traffic on a Layer 2 network. The packets are distributed with respect to different classifications and are assigned to VLANs. Many different classifications exist, and if more than one classification scheme is defined, the packets are assigned to the VLAN in this order:
- Tag — The VLAN number is recognized from the tag.
- MAC-Based VLAN — The VLAN is recognized from the source Media Access Control (MAC)-to-VLAN mapping of the ingress interface.
- Subnet-Based VLAN — The VLAN is recognized from the source Subnet-to-VLAN mapping of the ingress interface. To learn how to configure this feature, click here for instructions.
- Protocol-Based VLAN — The VLAN is recognized from the Ethernet type Protocol-to-VLAN mapping of the ingress interface. To learn how to configure this feature, click here for instructions.
- PVID — VLAN is recognized from the port default VLAN ID.
The MAC-based VLAN classification enable packets to be classified according to their source MAC address. You can then define MAC-to-VLAN mapping per interface. You can also define several MAC-based VLAN groups, which each group containing different MAC addresses. These MAC-based groups can be assigned to specific ports or LAGs. MAC-based VLAN groups cannot contain overlapping ranges of MAC addresses on the same port.
This article provides instructions on how to configure MAC-Based groups on a Cisco Business 350 series switch.
If you are unfamiliar with terms in this document, check out Cisco Business: Glossary of New Terms.
Applicable Devices | Software Version
- CBS350 (Data Sheet) | 3.0.0.69 (Download latest)
- CBS350-2X (Data Sheet) | 3.0.0.69 (Download latest)
- CBS350-4X (Data Sheet) | 3.0.0.69 (Download latest)
Configure MAC-Based VLAN Groups to VLAN on the Switch
Map a MAC-Based VLAN Group to VLAN
Important: Before proceeding with the instructions below, make sure a MAC-Based VLAN group has already been configured. For instructions, click here.
Step 1
Log in to the web-based utility and choose Advanced from the Display Mode drop-down list.
Step 2
Click VLAN Management.
Step 3
Select VLAN Groups > MAC-Based Groups to VLAN.

Step 4
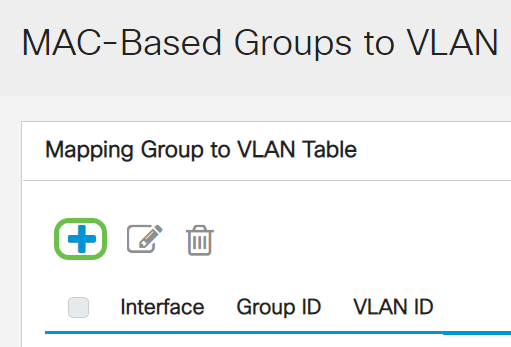
In the Mapping Group to VLAN Table, click the add icon.
Step 5
Fill out the Interface, Group ID, and VLAN IDfields.
The type of the group is displayed in the Group Type area automatically. Click one of the following interface type radio buttons in the Interface area to which the VLAN MAC-based group is assigned and choose the desired interface from the drop-down list.
The options are:
- Unit — From the Unit and Port drop-down lists choose the port to configure. The unit identifies whether the switch is the active or member in the stack.
- LAG — Choose the desired LAG from the LAG drop-down list. A Link Aggregate Group (LAG) is used to link multiple ports together. LAGs multiply bandwidth, increase port flexibility, and provide link redundancy between two devices to optimize port usage.
From the Group ID drop-down list, choose the MAC-Based VLAN Group ID to filter the traffic through the chosen port or LAG.
Enter the VLAN ID to which the traffic from the VLAN group is forwarded in the VLAN ID field.

To learn how to configure VLAN settings on your switch, click here for instructions.
Step 6
Click Apply then click Close. This mapping does not bind the interface dynamically to the VLAN; the interface must be manually added to the VLAN.

Step 7
Click the save icon in the top right corner of your screen. This will save the settings to the startup configuration file.

You should now have mapped a MAC-Based VLAN group to a VLAN on your switch.
Edit MAC-Based VLAN Group
Step 1
Choose VLAN Groups > MAC-Based Groups to VLAN.

Step 2
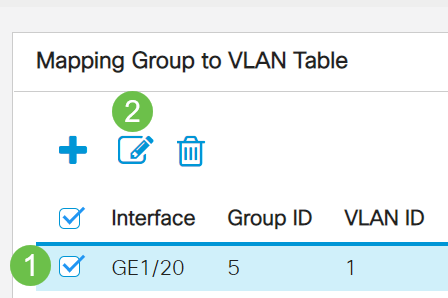
In the Mapping Group to VLAN Table, check the box next to the MAC-Based VLAN group you would like to edit. Click the edit icon button to edit a mapped MAC-Based VLAN group.
Step 3 (Optional)
Change the VLAN ID to which the traffic from the VLAN group is forwarded in the VLAN ID field.

Step 4
Click Apply then click Close.

Step 5
Click the save icon to save settings to the startup configuration file.

The MAC-Based VLAN group mapping should now have been edited from your switch.
Delete MAC-Based VLAN Group
Step 1
Choose VLAN Groups > MAC-Based Groups to VLAN.

Step 2. In the Mapping Group to VLAN Table, check the box next to the MAC-Based VLAN group you would like to delete. Click the trash icon to delete the MAC-Based VLAN group.

Step 3
Click Save to save settings to the startup configuration file.

The MAC-Based VLAN group mapping should now have been deleted from your switch.
You should now have configured MAC-Based VLAN groups to VLAN on your switch.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback