Objective
This article provides instructions on how to assign a port to one or more VLANs in the Cisco Business 250 or 350 series switch.
Applicable Devices | Software Version
Introduction
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) allows you to logically segment a Local Area Network (LAN) into different broadcast domains. In scenarios where sensitive data may be broadcast on a network, VLANs can be created to enhance security by designating a broadcast to a specific VLAN. Only users that belong to a VLAN are able to access and manipulate the data on that VLAN. VLANs can also be used to enhance performance by reducing the need to send broadcasts and multicasts to unnecessary destinations.
A VLAN allows a group of hosts that are not connected to the same switch to communicate as if they were on the same broadcast domain. An interface that has VLAN traffic needs to have the VLANs assigned to that interface, or packets may be dropped. When Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP) VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) is enabled for an interface, then VLANs can be dynamically assigned and it is not necessary to manually assign them.
This article provides instructions on how to assign a port to one or more VLANs in the Cisco Business 250 or 350 series switch.
Configure VLAN Membership of an Interface
Step 1. Log in to the web-based utility of your switch then choose VLAN Management > Port VLAN Membership.

Step 2. Choose the interface type (Port or LAG) and click Go.

The following fields are displayed for all interfaces of the selected type:
- Interface - Port or LAG ID.
- Mode - Interface VLAN mode that was selected in the Interface Settings page.
- Administrative VLANs - Drop-down list that displays all VLANs of which the interface might be a member.
- Operational VLANs - Drop-down list that displays all VLANs of which the interface is currently a member.
- LAG - If the interface selected is Port, it will display the LAG in which it is a member.
Note: In this example, Port is chosen.
Step 3. Click the radio button of a port that you want to configure.
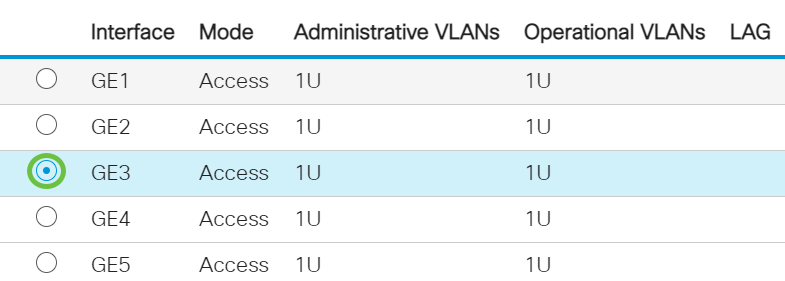
Note: In this example, GE3 is chosen.
Step 4. Click the Join VLAN button.
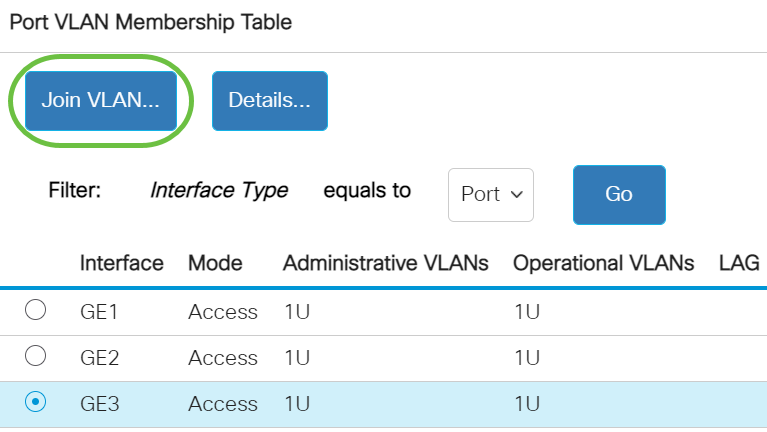
Step 5. Make sure the correct Port or LAG is chosen in the Interface area.

Note: The Current VLAN Mode displays the port VLAN mode that was chosen in the Interface Settings page. In this example, the mode is set to Access. To learn more about how to configure this feature, click here for instructions.
Step 6. Choose an access VLAN ID from the drop-down list. When the port is in Access mode, it will be a member of the Access VLAN. The default value is 1.

Note: In this example, VLAN 20 is chosen.
Step 7. Choose a multicast TV VLAN from the drop-down list. When the port is in Access mode, it will be a member of the Multicast TV VLAN. The default value is None.
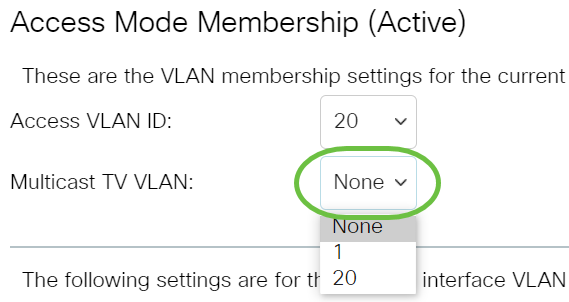
The following settings are for the inactive interface VLAN modes. These effects will be saved, but will not take effect until the interface VLAN mode is changed in the VLAN Interface Settings page. To learn more about how to configure this feature, click here for instructions.
Step 8. Choose a native VLAN ID from the drop-down list. When the port is in Trunk mode, it will be a member of the Native VLAN. The default value is 1.
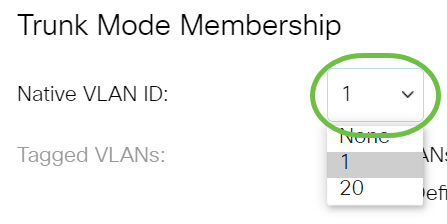
Step 9. When the port is in Trunk mode, it will be a member of the Tagged VLANs. Choose from the following options:
- All VLANs - When the port is in Trunk mode, it will be a member of all VLANs.
- User Defined - When the port is in Trunk mode, it will be a member of the VLANs that are entered in this field.

Note: In this example, User Defined is chosen and VLANs 30-40 are used.
Step 10. Enter the VLAN ID in the Untagged VLANs field. When the port is in General mode, it will be an untagged member of this VLAN.

Note: In this example, VLAN 1 is used.
Step 11. Enter the VLAN ID in the Tagged VLANs field. When the port is in General mode, it will be a tagged member of this VLAN.

Note: In this example, VLAN 30 is used.
Step 12. Enter the VLAN ID in the Forbidden VLANs field. When the port is in General mode, the interface is not allowed to join the VLAN even from GVRP registration. When a port is not a member of any other VLAN, enabling this option on the port makes the port part of internal VLAN 4095 which is a reserved VLAN ID (VID).
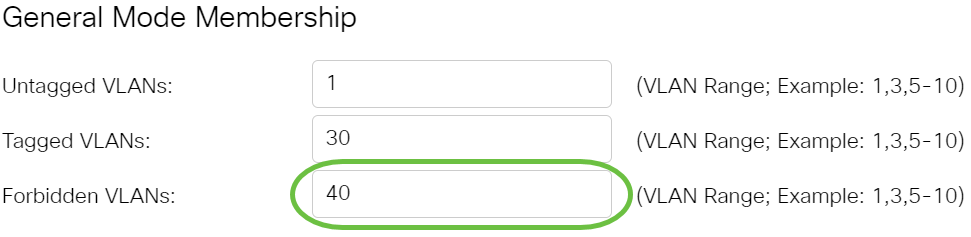
Note: In this example, VLAN 40 is used.
Step 13. Choose a VLAN ID from the General PVID drop-down list. When the port is in General mode, it will be a member of these VLANs. The default value is 1.

Step 14. (Optional) Choose a VLAN ID from the Customer VLAN ID drop-down list. When the port is in Customer mode, it will be a member of this VLAN.

Note: In this example, VLAN 20 is chosen.
Step 15. (Optional) Enter the VLAN ID in the Customer Multicast VLANs field. When the port is in Customer mode, it will be a member of this Multicast TV VLAN.
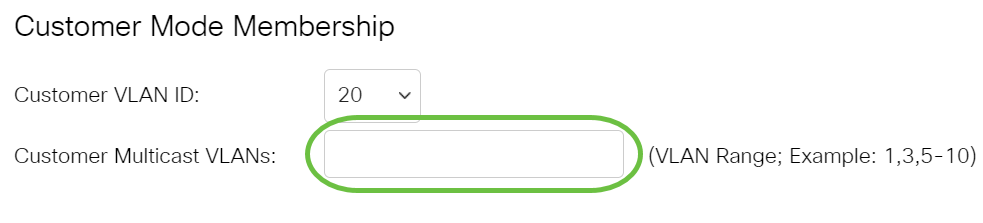
Note: In this example, no VLAN ID is entered.
Step 16. Click Apply then click Close.

Step 17. (Optional) Click Save to save settings to the startup configuration file.
You have now successfully assigned a port to one or more VLANs in the switch.
Looking for more information on VLANs for your Cisco Business Switches? Check out any of the following links for more information.
Article Skeleton w/ Content
Objective
This article provides instructions on how to configure an interface VLAN as an access or trunk
port on your Cisco Business 350 series switch through the Command Line Interface (CLI).
Introduction
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) allows you to logically segment a Local Area Network (LAN) into different broadcast domains. In scenarios where sensitive data
may be broadcast on a network, VLANs can be created to enhance security by designating a broadcast to a specific
VLAN. Only users that belong to a VLAN are able to access and manipulate the data on that VLAN.
You can configure the ports and specify whether the port should be in access or trunk mode, and assign specific
ports to VLANs.
VLAN is a network that is usually segmented by function or application. VLANs
behave much like physical LANs, but you can group hosts even if they are not physically
co-located. A switch port can belong to a VLAN. Unicast, broadcast, and multicast packets are forwarded and
flooded out ports in the same VLAN.
VLANs can also be used to enhance performance by reducing the need to send broadcasts and multicasts to
unnecessary destinations. It also eases network configuration by logically connecting devices without physically
relocating those devices.
To learn how to configure the VLAN settings on your switch through the web-based utility, click here. For CLI-based instructions, click here.
The image below displays a CBS350 switch that is configured with the following VLANs:

- VLAN1 - This is the default VLAN. The switch is connected to the router through this VLAN. This can be used
but cannot be modified or deleted.
- VLAN10 - Virtual network for the Admin department. The network address is 192.168.10.1 with subnet mask
255.255.255.0 or /24.
- VLAN20 - Virtual network for the Finance department. The network address is 192.168.20.1 with subnet mask
255.255.255.0 or /24.
- VLAN30 - Virtual network for the Operations department. The network address is 192.168.30.1 with subnet mask
255.255.255.0 or /24.
In a bigger network, the configured VLANs with interfaces assigned as access and trunk ports on switches could
look like this:
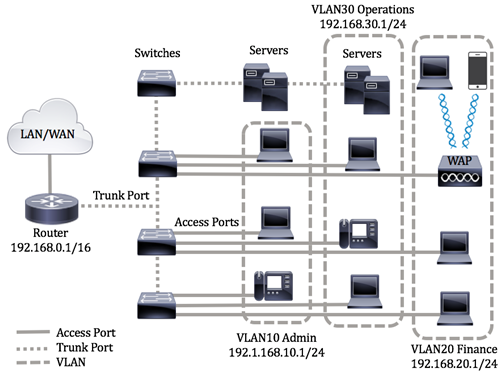
The port modes are defined as follows:
- Access Port - The frames received on the interface are assumed to not have a VLAN tag and are assigned to
the specified VLAN. Access ports are used primarily for hosts and can only carry traffic for a single VLAN.
- Trunk Port - The frames received on the interface are assumed to have VLAN tags. Trunk ports are for links
between switches or other network devices and are capable of carrying traffic for multiple VLANs.
Note: By default, all interfaces are in trunk mode, which means they can carry traffic for all VLANs. To
know how to assign an interface VLAN as an Access or Trunk port through the web-based utility of the switch,
click here.
To configure VLANs, follow these guidelines:
1. Create the VLANs. To learn how to configure the VLAN settings on your switch through the web-based utility,
click here. For CLI-based instructions, click here.
2. (Optional) Set the desired VLAN-related configuration for ports. For instructions on how to configure the VLAN
interface settings on your switch through the web-based utility, click here. For CLI-based instructions, click here.
3. Assign interfaces to VLANs. For instructions on how to assign interfaces to VLANs through the web-based
utility of your switch, click here.
4. (Optional) Configure VLAN groups on your switch. You can configure any of the following:
- MAC-based VLAN Group Overview - For instructions on how to configure MAC-based VLAN Groups through the
web-based utility of your switch, click here. For CLI-based instructions, click here.
- Subnet-based VLAN Groups Overview - For instructions on how to configure subnet-based VLAN Groups through
the web-based utility of your switch, click here. For CLI-based instructions, click here.
- Protocol-based VLAN Groups Overview - For instructions on how to configure Protocol-based VLAN Groups
through the web-based utility of your switch, click here. For CLI-based instructions, click here.
5. (Optional) Configure TV VLAN settings on your switch. You can configure any of the following:
- Access Port Multicast TV VLAN - For instructions on how to configure Access Port Multicast TV VLAN through
the web-based utility of your switch, click here.
- Customer Port Multicast TV VLAN - For instructions on how to configure Customer Port Multicast TV VLAN
through the web-based utility of your switch, click here.
Applicable Devices | Software Version
Configure VLAN Interface Settings on the Switch through the CLI
Configure Interface as Access Port and Assign to VLAN
Step 1. Log in to the switch console. The default username and password is cisco/cisco. If you have configured a
new username or password, enter the credentials instead.
The commands may vary depending on the exact model of your switch.
Step 2. To display the current VLAN on the switch, enter the following:
CBS350#show vlan
Step 3. From the Privileged EXEC mode of the switch, enter the Global Configuration mode by entering the
following:
CBS350#configure terminal
Step 4. In the Global Configuration mode, enter the Interface Configuration context by entering the following:
CBS350(config)#interface [interface-id | range vlan vlan-range]
The options are:
- interface-id - Specifies an interface ID to be configured.
- range vlan vlan-range - Specifies a list of VLANs. Separate nonconsecutive VLANs with a comma and no spaces.
Use a hyphen to designate a range of VLANs.
Step 5. In the Interface Configuration context, use the switchport mode command to configure the VLAN
membership mode.
CBS350(config-if-range)#switchport mode access
Step 6. Use the switchport access vlan command to assign the port or range of ports into access ports. A
port in access mode can have only one VLAN configured on the interface which can carry traffic for only one
VLAN.
CBS350(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan [vlan-id | none]
The options are:
- vlan-id - Specifies the VLAN to which the port is configured.
- none - Specifies that the access port cannot belong to any VLAN.
Step 7. (Optional) To return the port or range of ports to the default VLAN, enter the following:
CBS350(config-if-range)#no switchport access vlan
Step 8. To exit the Interface Configuration context, enter the following:
CBS350(config-if-range)#exit
Step 9. (Optional) Repeat steps 4 to 6 to configure more access ports and assign to the corresponding VLANs.
Step 10. Enter the end command to go back to the Privileged EXEC mode:
CBS350(config-if)#end
Step 11. (Optional) To display the configured ports on the VLANs, enter the following:
CBS350#show vlan
The configured ports should be displayed according to the assigned VLANs.
Step 12. (Optional) In the Privileged EXEC mode of the switch, save the configured settings to the startup
configuration file, by entering the following:
CBS350#copy running-config startup-config
Step 13. (Optional) Press Y for Yes or N for No on your keyboard once the Overwrite file
[startup-config]… prompt appears.
You should now have configured the interfaces on your switch as access ports and assigned to their corresponding
VLANs.
Configure Interface as Trunk Port and Assign to VLAN
Step 1. In the Privileged EXEC mode of the switch, enter the Global Configuration mode by entering the following:
CBS350#configure terminal
Step 2. In the Global Configuration mode, enter the Interface Configuration context by entering the following:
CBS350#interface [interface-id | range vlan vlan-range]
The options are:
- interface-id - Specifies an interface ID to be configured.
- range vlan vlan-range - Specifies a list of VLANs. Separate nonconsecutive VLANs with a comma and no spaces.
Use a hyphen to designate a range of VLANs.
Step 3. In the Interface Configuration context, use the switchport mode command to configure the VLAN
membership mode.
CBS350(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
Step 4. (Optional) To return the port to the default VLAN, enter the following:
CBS350(config-if)#no switchport mode trunk
Step 5. Use the switchport trunk allowed vlan command to specify which VLANs the port belongs to when its
mode is configured as trunk.
CBS350(config-if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan [all | none | add vlan-list | remove vlan-list | except vlan-list]
The options are:
- all - Specifies all VLANs from 1 to 4094. At any time, the port belongs to all VLANs existing at the
time.
- none - Specifies an empty VLAN list. The port does not belong to any VLAN.
- add vlan-list - List of VLAN IDs to add to the port. Separate nonconsecutive VLAN IDs with a comma
and no spaces. Use a hyphen to designate a range of IDs.
- remove vlan-list - List of VLAN IDs to remove from a port. Separate nonconsecutive VLAN IDs with a
comma and no spaces. Use a hyphen to designate a range of IDs.
- except vlan-list - List of VLAN IDs including all VLANs from range 1-4094 except VLANs belonging to
vlan-list.
Step 6. To exit the Interface Configuration context, enter the following:
CBS350(config-if)#exit
Step 7. (Optional) To return the port or range of ports to the default VLAN, enter the following:
CBS350(config-if)#no switchport trunk allowed vlan
Step 8. (Optional) Repeat steps 2 to 6 to configure more trunk ports and assign to the corresponding VLANs.
Step 9. Enter the end command to go back to the Privileged EXEC mode:
CBS350(config-if)#end
Step 10. (Optional) To display the configured ports on the VLANs, enter the following:
CBS350#show vlan
Note: The configured ports should be displayed according to the assigned VLANs.
Step 11. (Optional) In the Privileged EXEC mode of the switch, save the configured settings to the startup
configuration file, by entering the following:
CBS350#copy running-config startup-config
Step 12. (Optional) Press Y for Yes or N for No on your keyboard once the Overwrite file
[startup-config]… prompt appears.
You have now configured the interfaces on your Cisco Business 350 series switch as trunk ports and assigned to their corresponding
VLANs.
Important: To proceed with configuring the VLAN group settings on your switch, follow the guidelines above.
Looking for more information on VLANs for your Cisco Business Switches? Check out any of the following links for more information.



















