Set Up a Remote Access Tunnel (Client to Gateway) for VPN Clients on RV016, RV042, RV042G and RV082 VPN Routers
Available Languages
Objective
This article explains how to configure remote access Virtual Private Network (VPN) tunnel from client to gateway on RV016, RV042, RV042G and RV082 VPN Routers with the help of third party VPN client software as The Green Bow or VPN Tracker.
Introduction
A VPN is a private network that is used to virtually connect devices of the remote user through the public network to provide security. Remote access tunnel VPN is the process used to configure a VPN between a client computer and a network. The client is configured in the desktop or laptop of the users through VPN client software. It provides the users to securely connect with the network remotely. Client to gateway VPN connection is useful for the remote employees to connect to the office network remotely and securely.
Applicable Devices
- RV016
- RV042
- RV042G
- RV082
Software Version
- v4.2.2.08
Configure a VPN Tunnel
Step 1. Log in to the web configuration utility and choose VPN > Client to Gateway. The Client to Gateway page opens:
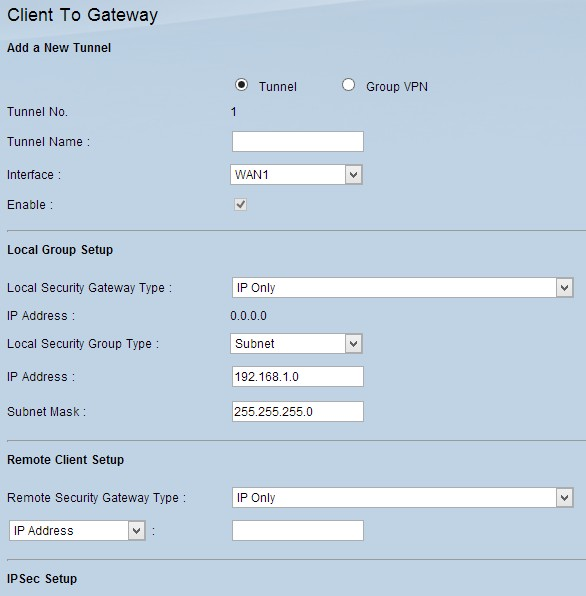
Add a New Tunnel
Step 1. Click the appropriate radio button according to what kind of tunnel you want to add.
- Tunnel - Represents a tunnel for a remote single user.
- Group VPN - Represents a tunnel for a remote group of users.
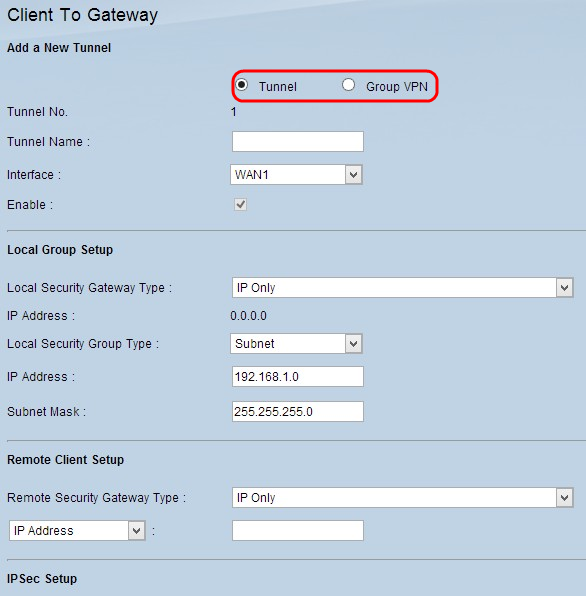
The Tunnel Number is an automatically generated field that displays the number of the tunnel.
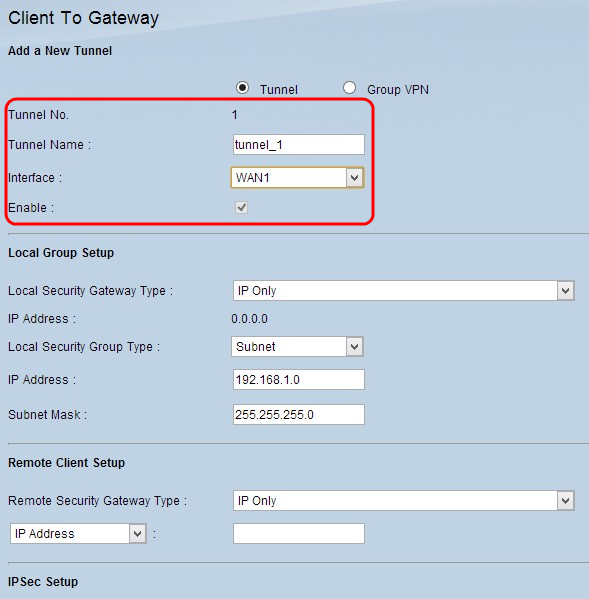
Step 2. Enter a name for the tunnel in the Tunnel Name field.
Step 3. Choose the appropriate WAN interface to use for the VPN tunnel from the Interface drop-down list.
Step 4. (Optional) To enable the VPN, check the check box in the Enable field. By default it is always checked.
Local Group Setup
Step 1. Choose the appropriate router identification method to establish a VPN tunnel from the Local Security Gateway drop-down list. Skip this step if you chose Group VPN in Step 1 of the Add A New Tunnel section.
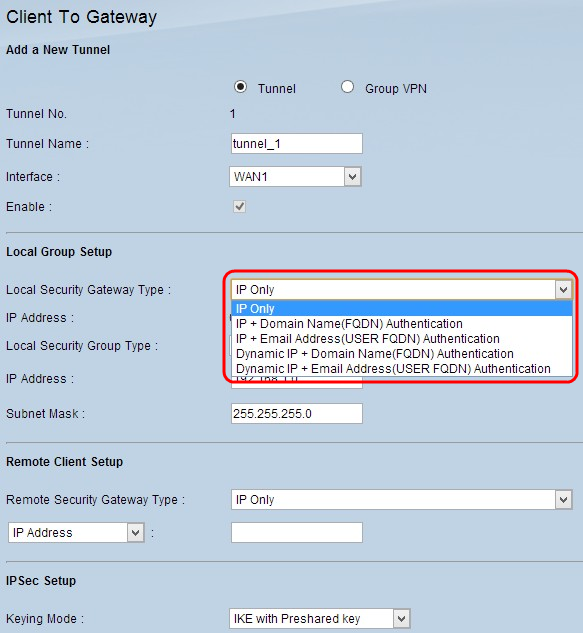
- IP Only - Access to the tunnel is possible through a static WAN IP address. You can choose this option only if the router has a static WAN IP. The static WAN IP address appears automatically.
- IP + Domain Name(FQDN) Authentication - Access to the tunnel is possible through a static IP address and a registered Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) domain. The static WAN IP address is an auto generated field.
- IP + E-mail Address(USER FQDN) Authentication - Access to the tunnel is possible through a static IP address and an email address. The static WAN IP address is an auto generated field.
- Dynamic IP + Domain Name(FQDN) Authentication - Access to the tunnel is possible through a dynamic IP address and a registered domain.
- Dynamic IP + E-mail Address(USER FQDN) Authentication — Access to the tunnel is possible through a dynamic IP address and an email address.
Step 2. Enter the name of the registered Fully Qualified Domain in the Domain Name field if you choose IP + Domain Name (FQDN) Authentication or Dynamic IP + Domain Name (FQDN) Authentication in Step 1.
Step 3. Enter the Email Address in the Email Address field if you choose IP + E-mail Address(USER FQDN) Authentication or Dynamic IP + E-mail Address(USER FQDN) Authentication in Step 1.
Step 4. Choose the appropriate local LAN user or group of users who can access the VPN tunnel from the Local Security Group drop-down list. The default is Subnet.
- IP - Only one specific LAN device can access to the tunnel. If you choose this option, enter the IP address of the LAN device in the IP Address field. The default IP is 192.168.1.0.
- Subnet - All LAN devices on a specific subnet can access to the tunnel. If you choose this option, enter the IP address and subnet mask of the LAN devices in the IP Address and Subnet Mask field respectively. The default mask is 255.255.255.0.
- IP Range - A range of LAN devices can access to the tunnel. If you choose this option, enter the starting and ending IP address in the Begin IP and End IP fields respectively. The default range is from 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.254.

Step 5. Click Save to save the settings.
Remote Client Setup
Step 1. If you choose Tunnel, choose the appropriate client identification method to establish a VPN tunnel from the Remote Security Gateway Type drop-down list. The default is IP Only. Skip this step if Group VPN in Step 1 of the Add A New Tunnel section was chosen.
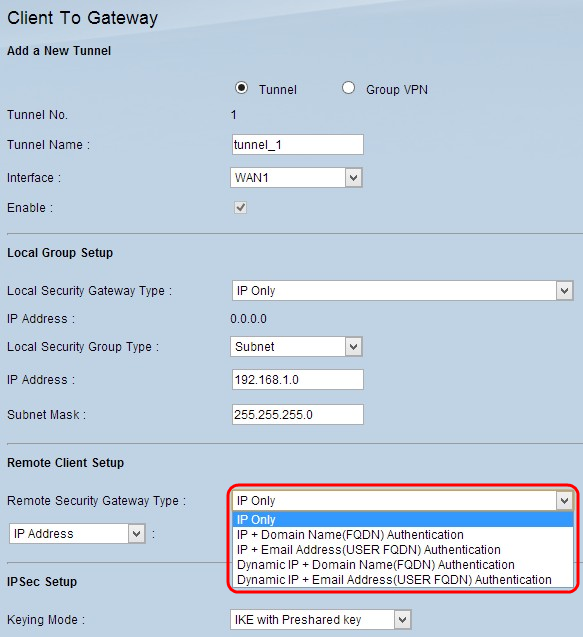
- IP Only - Access to the tunnel is possible through the static WAN IP of the client only. You must know the static WAN IP of the client to use this option.
- IP + Domain Name(FQDN) Authentication - Access to the tunnel is possible through a static IP address of the client and a registered domain.
- IP + E-mail Address(USER FQDN) Authentication - Access to the tunnel is possible through a static IP address of the client and an email address.
- Dynamic IP + Domain Name(FQDN) Authentication - Access to the tunnel is possible through a dynamic IP address of the client and a registered domain.
- Dynamic IP + E-mail Address(USER FQDN) Authentication - Access to the tunnel is possible through a dynamic IP address of the client and an email address.
Step 2. Enter the IP address of the remote client in the IP Address field if you chose IP Only, IP + Domain Name (FQDN), or IP + E-mail Address (User FQDN) Authentication in Step 1.
Step 3. Choose the appropriate option from the drop-down list to enter the IP address if you know it or resolve the IP address from the DNS server if you choose IP Only or IP + Domain Name (FQDN) Authentication or IP + E-mail Address(USER FQDN) Authentication in the Step 1.
- IP Address - Represents the static IP address of the remote client. Enter the static IP address in the field.
- IP by DNS Resolved - Represents the domain name of the IP address which retrieves the IP address automatically through the local DNS server if you do not know the static IP address of the remote client. Enter the domain name of the IP address in the field.
Step 4. Enter the domain name of the IP address in the Domain name field if you choose IP + Domain Name (FQDN) Authentication or Dynamic IP + Domain Name (FQDN) Authentication in Step 1.
Step 5. Enter the email address in the Email Address field if you choose IP + E-mail Address(USER FQDN) Authentication or Dynamic IP + E-mail Address(USER FQDN) Authentication in Step 1.
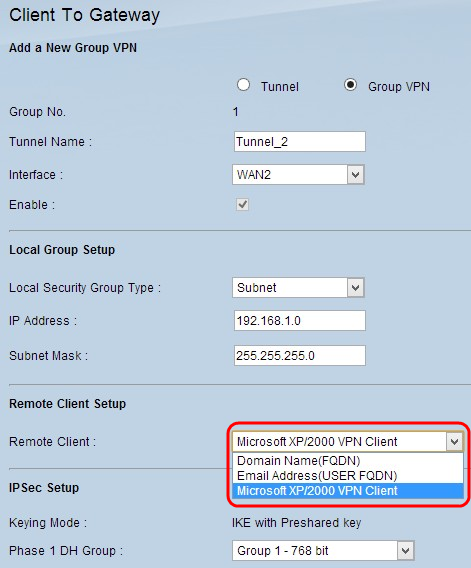
Step 6. If you choose Group, choose the appropriate remote client type from the Remote Client drop-down list. Skip this step if Tunnel VPN in Step 1 of the Add A New Tunnel section was chosen.
- Domain Name (FQDN) - Access to the tunnel is possible through a registered domain. If you choose this option, enter the name of the registered Domain in the Domain Name field.
- E-mail Addr.(USER FQDN) - Access to the tunnel is possible through an email address of the client. If you choose this option, enter the Email Address in the Email Address field.
- Microsoft XP/2000 VPN Client - Access to the tunnel is possible through Microsoft XP or Microsoft 2000 windows software. Remote users with Microsoft VPN client software can access to the tunnel through the software.
Step 7. Click Save to save the settings.
IPSec Setup
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is an internet layer security protocol which provides end-to-end security through authentication and encryption during any communication session.
Note: Two ends of the VPN need to have the same methods of encryption, decryption and authentication for the IPSec to work. Also the Perfect Forward Secrecy key must be same on the both side of the tunnel.
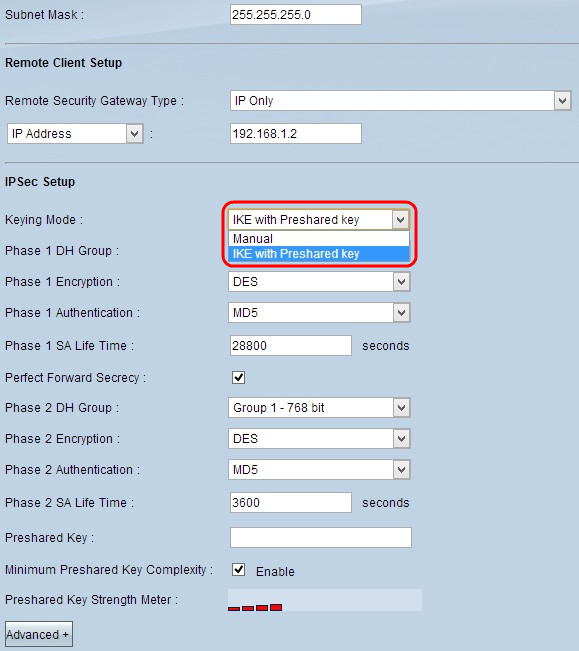
Step 1. Choose the appropriate mode of key management to ensure security from the Keying Mode drop-down list. The default mode is IKE with Preshared key.
- Manual - A custom security mode to generate a new security key by yourself and no negotiation with the key. It is the best to use during troubleshooting and small static environment. If you choose Group VPN in Step 1 in Add A New Tunnel section, this option is disabled.
- IKE with Preshared key - Internet Key Exchange (IKE) protocol is used to automatically generate and exchange a preshared key to establish authenticate communication for the tunnel.
Manual Key Mode Configuration
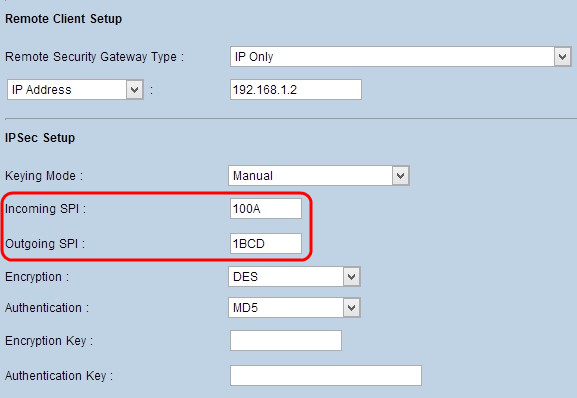
Step 1. Enter the unique hexadecimal value for incoming Security Parameter Index (SPI) in the Incoming SPI field. SPI is carried in Encapsulating Security Payload Protocol (ESP) header which together determine the protection for the incoming packet. You can enter from 100 to ffffffff. The incoming SPI of the local router need to match with the outgoing SPI of the remote router.
Step 2. Enter the unique hexadecimal value for outgoing Security Parameter Index (SPI) in the Outgoing SPI field. SPI is carried in Encapsulating Security Payload Protocol (ESP) header which together determine the protection for the outgoing packet. You can enter from 100 to ffffffff. The outgoing SPI of the remote router need to match with the incoming SPI of the local router.
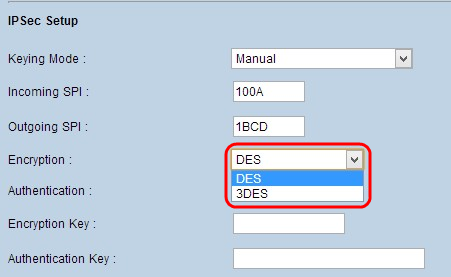
Step 3. Choose the appropriate encryption method for the data from the Encryption drop-down list. The recommended encryption is 3DES. The VPN tunnel needs to use the same encryption method for both ends.
- DES - Data Encryption Standard (DES) uses a 56-bit key size for data encryption. DES is outdated and should be only used if one endpoint only supports DES.
- 3DES - Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES) is a 168 bit, simple encryption method. 3DES encrypts the data three times, which provides more security then DES.
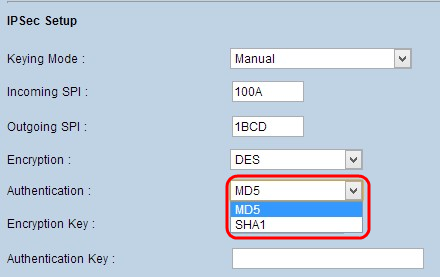
Step 4. Choose the appropriate authentication method for the data from the Authentication drop-down list. The recommended authentication is SHA1 as it is more secure than MD5. The VPN tunnel needs to use the same authentication method for both ends.
- MD5 - Message Digest Algorithm-5 (MD5) represents 32 digit hexadecimal hash function which provides protection to the data from malicious attack by the checksum calculation.
- SHA1 - Secure Hash Algorithm version 1 (SHA1) is a 160 bit hash function which is more secure than MD5 but it takes more time to compute.
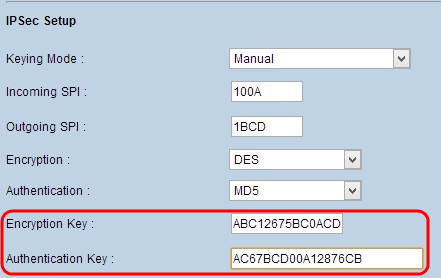
Step 5. Enter the key to encrypt and decrypt data in the Encryption Key field. If you choose DES as encryption method in Step 3, enter a 16 digit hexadecimal value. If you choose 3DES as encryption method in Step 3, enter a 40 digit hexadecimal value.
Step 6. Enter a pre-shared key to authenticate the traffic in Authentication Key field. If you choose MD5 as authentication method in step 4, enter 32 digit hexadecimal value. If you choose SHA as authentication method in Step 4, enter 40 digit hexadecimal value. The VPN tunnel needs to use the same preshared key for both of its ends.
Step 7. Click Save to save the settings.
IKE with Preshared Key Mode Configuration
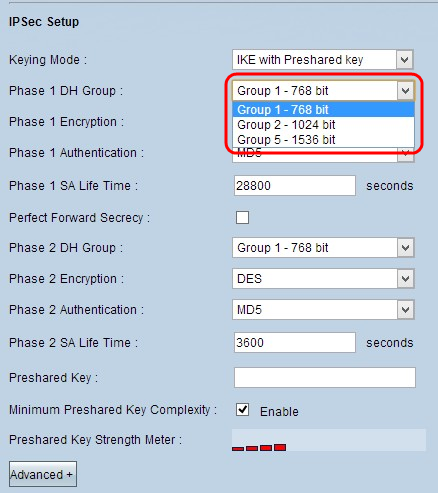
Step 1. Choose the appropriate Phase 1 DH Group from the Phase 1 DH Group drop-down list. Phase 1 is used to establish the simplex, logical security association (SA) between the two ends of the tunnel to support secure authenticate communication. Diffie-Hellman (DH) is a cryptographic key exchange protocol which is used to determine the strength of the key during Phase 1 and it also shares the secret key to authenticate the communication.
- Group 1 - 768 bit - The lowest strength key and the most insecure authentication group. But it takes less time to compute the IKE keys. This option is preferred if the speed of the network is low.
- Group 2 - 1024 bit - The higher strength key and more secure authentication group. But it needs some time to compute the IKE keys.
- Group 5 - 1536 bit - Represents the highest strength key and the most secure authentication group. It needs more time to compute the IKE keys. It is preferred if the speed of the network is high.
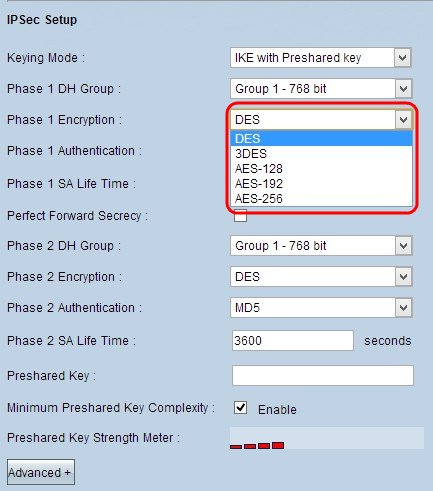
Step 2. Choose the appropriate Phase 1 Encryption to encrypt the key from the Phase 1 Encryption drop-down list. 3DES is recommended as it is the most secure encryption method. The VPN tunnel needs to use the same encryption method for both of its ends.
- DES - Data Encryption Standard (DES) uses a 56-bit key size for data encryption. DES is outdated and should be only used if one endpoint only supports DES.
- 3DES - Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES) is a 168 bit, simple encryption method. 3DES encrypts the data three times, which provides more security then DES.
- AES-128 - Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is 128 bit encryption method which transforms the plain text into cipher text through 10 cycles repetitions.
- AES-192 - Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is 192 bit encryption method which transforms the plain text into cipher text through 12 cycles repetitions. AES-192 is more secure than AES-128.
- AES-256 - Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is 256 bit encryption method which transforms the plain text into cipher text through 14 cycles repetitions. AES-256 is the most secure encryption method.
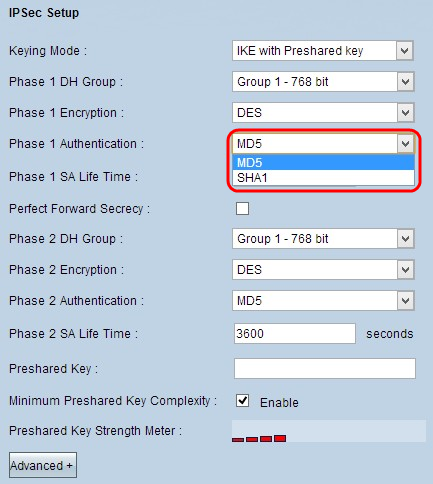
Step 3. Choose the appropriate Phase 1 authentication method from the Phase 1 Authentication drop-down list. The VPN tunnel needs to use the same authentication method for both of its ends.
- MD5 - Message Digest Algorithm-5 (MD5) represents 32 digit hexadecimal hash function which provide protection to the data from malicious attack by the checksum calculation.
- SHA1 - Secure Hash Algorithm version 1 (SHA1) is a 160 bit hash function which is more secure than MD5 but it takes more time to compute.
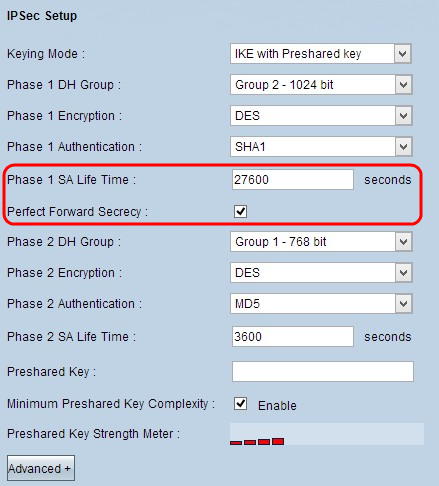
Step 4. Enter the amount of time in seconds that the Phase 1 keys are valid and the VPN tunnel remains active in the Phase 1 SA Life Time field.
Step 5. Check the Perfect Forward Secrecy check box to provide more protection to the keys. This option allows the router to generate a new key if any key is compromised. The encrypted data is only compromised through the compromised key. So it provides more secure and authenticate communication as it secures other keys though a key is compromised. This is a recommended action as it provides more security.
Step 6. Choose the appropriate Phase 2 DH Group from the Phase 2 DH Group drop-down list. Phase 2 uses security association and it is used to determine the security of the data packet during the data packets pass through the two end points.

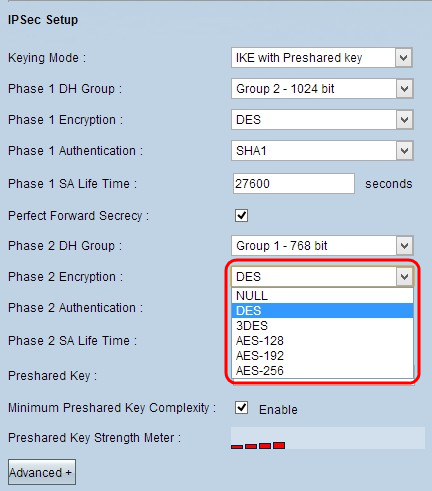
Step 7. Choose the appropriate Phase 2 Encryption to encrypt the key from the Phase 2 Encryption drop-down list. AES-256 is recommended as it is the most secure encryption method. The VPN tunnel needs to use the same encryption method for both of its ends.
- DES - Data Encryption Standard (DES) uses a 56-bit key size for data encryption. DES is outdated and should be only used if one endpoint only supports DES.
- 3DES - Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES) is a 168 bit, simple encryption method. 3DES encrypts the data three times, which provides more security then DES.
- AES-128 - Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is 128 bit encryption method which transforms the plain text into cipher text through 10 cycles repetitions.
- AES-192 - Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is 192 bit encryption method which transforms the plain text into cipher text through 12 cycles repetitions. AES-192 is more secure than AES-128.
- AES-256 - Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is 256 bit encryption method which transforms the plain text into cipher text through 14 cycles repetitions. AES-256 is the most secure encryption method.
Step 8. Choose the appropriate authentication method from the Phase 2 Authentication drop-down list. The VPN tunnel needs to use the same authentication method for both ends.
- MD5 - Message Digest Algorithm-5 (MD5) represents 32 digit hexadecimal hash function which provide protection to the data from malicious attack by the checksum calculation.
- SHA1 - Secure Hash Algorithm version 1 (SHA1) is a 160 bit hash function which is more secure than MD5 but it takes more time to compute.
- Null - No authentication method is used.
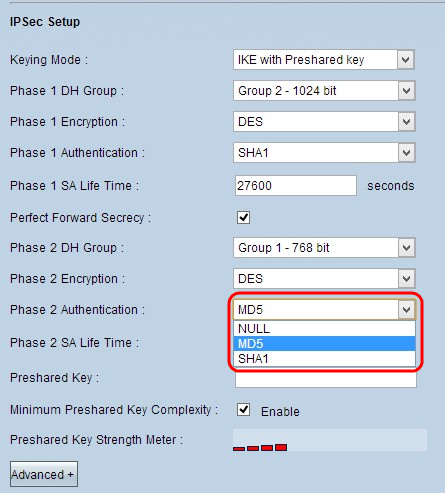
Step 9. Enter the amount of time in seconds that the Phase 2 keys are valid and the VPN tunnel remains active in the Phase 2 SA Life Time field.
Step 10. Enter a key which is shared previously between the IKE peers to authenticate the peers in the Preshared Key field. Up to 30 hexadecimal and character can be used as the preshared key. The VPN tunnel needs to use the same preshared key for both of its ends.
Note: It is strongly recommended to frequently change the preshared key between the IKE peers so the the VPN remains secured.
Step 11. Check the Minimum Preshared Key Complexity check box if you want to enable strength meter for the preshared key. It is used for determine the strength of the preshared key through color bars
Note: Preshared Key Strength Meter shows the strength of the preshared key through colored bars. Red indicates weak strength, yellow indicates acceptable strength and green indicates strong strength.

Step 12. Click Save to save the settings.
Advanced IKE with Pre-shared Key Mode Configuration
Step 1. Click Advanced to display the advanced settings for IKE with Preshared key.
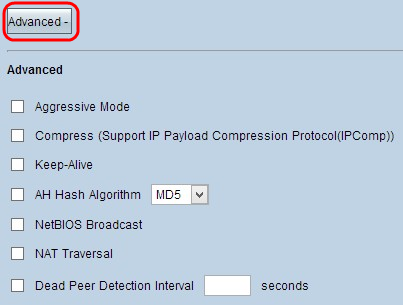
Step 2. Check the Aggressive Mode check box if your network speed is low. This exchanges the IDs of the end points of the tunnel in clear text during SA connection (Phase 1), which requires less time to exchange but is less secure.
Note: Aggressive Mode is not available for group client to gateway VPN connection.
Step 3. Check the Compress (Support IP Payload Compression Protocol (IPComp)) check box if you want to compress the size of the IP datagrams. IPComp is an IP compression protocol which is used to compress the size of IP datagram. IP compression is useful if the network speed is low and the user wants to quickly transmit the data without any loss through the slow network, but it does not provide any security.
Step 4. Check the Keep-Alive check box if you always want the connection of the VPN tunnel remain active. Keep Alive helps to re-establish the connections immediately if any connection becomes inactive.

Step 5. Check the AH Hash Algorithm check box if you want to enable Authenticate Header (AH). AH provides authentication to origin data, data integrity through checksum and protection into the IP header. The tunnel should have the same algorithm for both of its sides.
- MD5 - Message Digest Algorithm-5 (MD5) represents 128 digit hexadecimal hash function which provides protection to the data from malicious attack by the checksum calculation.
- SHA1 - Secure Hash Algorithm version 1 (SHA1) is a 160 bit hash function which is more secure than MD5 but it takes more time to compute.
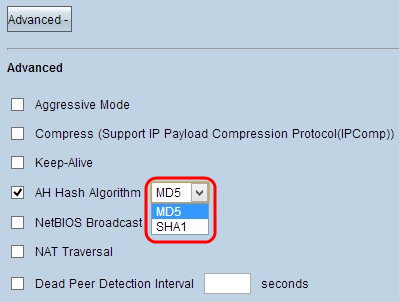
Step 6. Check NetBIOS Broadcast if you want to allow non-routable traffic through the VPN tunnel. The default is unchecked. NetBIOS is used to detect network resources like printers, computers etc. in the network through some software applications and Windows features like Network Neighborhood.
Step 7. Check NAT Traversal check box if you want to access to the internet from your private LAN through a public IP address. If your VPN router is behind a NAT gateway, check this check box to enable NAT traversal. Both ends of the tunnel must have the same settings.
Step 8. Check Dead Peer Detection Interval to check the liveliness of the VPN tunnel through hello or ACK in a periodic manner. If you check this check box, enter the desired duration or interval of the hello messages.
Note: You can configure Dead Peer Detection Interval only for single client to gateway VPN connection, not for group client to gateway VPN connection.
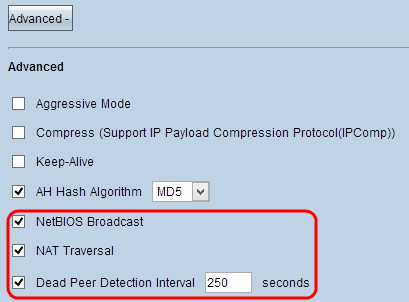
Step 9. Click Save to save the settings.
You have now learned how to configure remote access VPN tunnel from client to gateway on RV016, RV042, RV042G and RV082 VPN routers.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
10-Dec-2018 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback