Configure Basic Wireless Settings on an RV Series Router
Available Languages
Objective
Wireless networking operates by sending information over radio waves, which can be more vulnerable to intruders than a wired network. You can take these steps to keep your network more secure by configuring the basic wireless settings of the router. The RV Series Routers provide you with four default Service Set Identifiers (SSIDs) that use the same default passwords which can be customized to increase network security.
This article aims to show you how to configure the basic wireless settings of your RV Series Router.
Applicable Devices
- RV Series
Software Version
- 1.0.3.16 — RV130W
- 1.0.0.17 — RV132W
- 1.0.0.21 — RV134W
Configure Basic Wireless Settings
Step 1. Log in to the web-based utility and choose Wireless > Basic Settings.
Note: The images on this article are taken from the RV130W Router. Menu options may vary per device.
Step 2. Ensure that the Enable Radio check box is checked to activate wireless networks. This option is checked by default however, the Radio on the 5G Basic Settings area of the RV134W is not. Checking the Enable Radio check box on the 5G Basic Settings of the RV134W can be done to allow Wireless-AC connectivity with your Wireless-AC compatible client device. Also, the RV132W and the RV134W are equipped with a physical switch for the wireless radio located between the USB port and the Reset button at the back of the router. It must be in the ON position to be able to manipulate this page.

Step 3. In the Wireless Network Mode drop-down list, choose a wireless network mode.
The options are:
- B/G/N-Mixed — Allows Wireless-B, Wireless-G, and Wireless-N devices to connect to the network. Choosing B/G/N-Mixed will allow a range of devices to connect to your wireless network.
- B-Only — Allows devices that support only the 802.11b standard to connect to the network. Wireless-B has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s. Devices on this wireless band often experience interference from other products operating in the 2.4 GHz frequency range.
- G-Only — Allows devices that support only the Wireless-G standard to connect to the network. The 802.11g standard operates at a maximum rate of 54 Mbit/s at the 2.4 GHz frequency range.
- N-Only — Allows devices that support only the Wireless-N standard to connect to the network. The 802.11n standard operates in both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency band.
- B/G-Mixed — Allows devices that support the 802.11b and 802.11g standards to connect to the network.
- G/N-Mixed — Allows devices that support the 802.11g and 802.11n standards to connect to the network.
Note: If your wireless client devices operate on a specific wireless network mode, it is best to choose that network mode. For example, if your wireless devices only support the 802.11N standard, then you should choose N-Only from the Wireless Network Mode drop-down list. Subsequently, if you have a range of devices that operate on different wireless network modes, it is best to choose one of the mixed network mode options. In this example, B/G/N-Mixed is chosen.

If you are using the RV134W, additional wireless settings may be configured on the 5G Basic Settings area for Wireless-AC connectivity with your Wireless-AC compatible wireless client device. This option is only available on the RV134W.
The options are:
- A-Only — Operates between 5.725 GHz to 5.850 GHz and supports up to 54 Mbps. Choose this option if you have only Wireless-A devices in your network.
- N/AC-Mixed — Choose this option if you have a mix of Wireless-N and Wireless-AC devices in your network.
- A/N/AC-Mixed — Choose this option if you have a mix of Wireless-A, Wireless-N, and Wireless-AC devices in your network. This is the default 5G setting for the RV134W.

Step 4. If you selected B/G/N-Mixed, N-Only, or G/N-Mixed in Step 3, choose the wireless bandwidth on your network. Otherwise, proceed to Step 5.
For the RV130W and the RV132W, you can choose the wireless band under Wireless Band Selection. The options are:
- 20MHz — Works with the B/G/N-Mixed, G/N-Mixed, and N-Only network mode, but may be prone to lower throughput.
- 20/40MHz — Lets the router switch between 20MHz and 40MHz automatically between 20 and 40MHz. It has better throughput but not as stable as 20MHz.
Note: In this example, 20MHz is chosen.
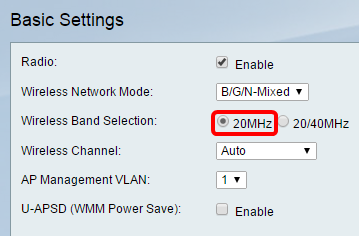
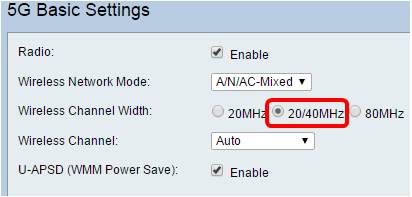
On the RV134W, you can choose the wireless band under Wireless Channel Width. The options are:
- 20MHz — Works with the B/G/N-Mixed, G/N-Mixed, and N-Only network mode, but may be prone to lower throughput.
- 20/40MHz — Lets the router switch between 20MHz and 40MHz automatically between 20 and 40MHz. It has better throughput but not as stable as 20MHz.
- 80MHz – This is the default setting for the RV134W. It is for optimum throughput for Wireless-AC mode.
Note: In this example, 20/40MHz is chosen.
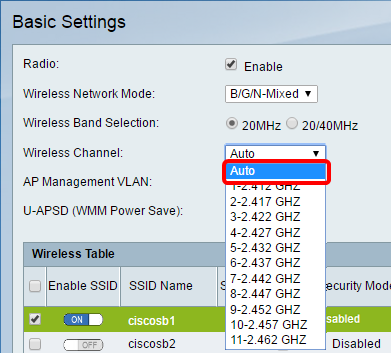
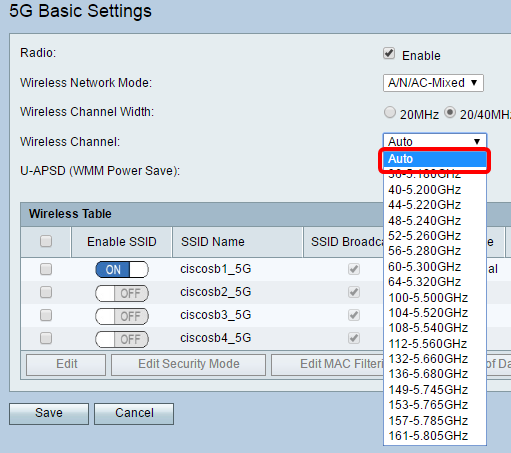
Step 5. In the Wireless Channel drop-down list, choose the wireless channel. Choose 1-2.412 GHZ or 11-2.462 GHz if you are not sure which channel to use.
Note: Choosing Auto allows the router to automatically change wireless frequency to the least congested channel. If your network has a lot of devices on the 2.4 GHz frequency, it is recommended to choose channel 1-2.412 GHz or 11-2.462 GHz. Most consumer grade access points default to channel 6. By choosing 1-2.412 GHz or 11-2.462 GHz, you eliminate potential interference between your devices. The channel varies slightly in frequency range and speed. If you choose the lower frequency, you will have a longer wireless range but slower speed. If you have a higher frequency, you will have shorter wireless range but faster speed. In this example, the wireless channel is left at Auto, which is also the default setting.
If you want to set the channel on the 5G Basic Setting of your RV134W, you can choose from 36-5.180GHz to 161-5.805GHz.
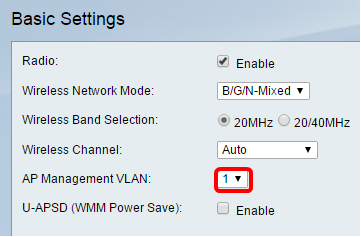
Step 6. (Optional) In the AP Management VLAN drop-down list, choose the desired Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) that will be used to access the web-based utility of the device. Only this VLAN ID will be able to manage the device.
Note: This option is available only on the RV130W.
Step 7. (Optional) Check the Enable check box in the U-APSD (WMM Power Save) area to enable the Unscheduled Automatic Power Save Delivery (U-APSD) feature. U-APSD is a power-saving scheme optimized for real-time applications such as utilizing Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and transferring full-duplex data over WLAN. By classifying outgoing IP Traffic as voice data, these types of application can increase battery life and minimize transmit delays.
Note: In this example, U-APSD (WMM Power Save) is disabled. However, this option is enabled by default.

Step 8. Click Save.
Change the Wireless Network Name or SSID
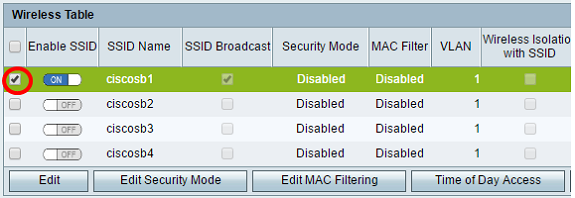
Step 9. In the Wireless Table area, check the boxes corresponding to the SSIDs you want to configure. You can edit multiple SSIDs at the same time.
Note: In this example, only the ciscosb1 SSID is edited.
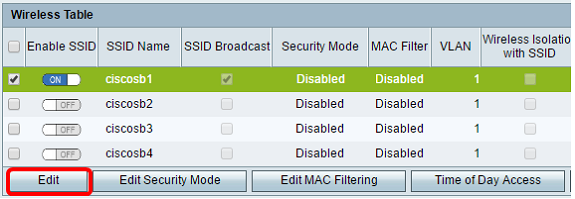
Step 10. Click Edit to modify the SSID.
Step 11. Enable or disable the desired SSID by toggling the switch to ON. The default setting of the first SSID is ON however, the default setting of the remaining SSIDs are OFF.
Note: In this example, the first SSID is used.

Step 12. Change the default name of your SSID in the SSID Name field.
Note: In this example, the SSID Name is changed to Network_Find.
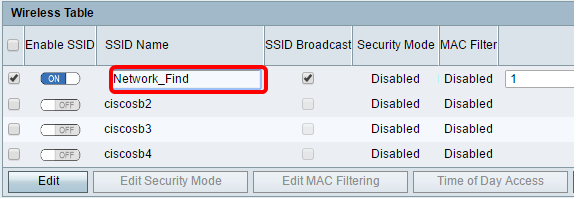
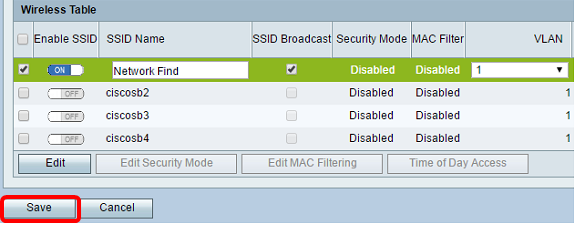
Step 13. (Optional) Check the check box under the SSID Broadcast column if you want your SSID to be visible to your wireless client devices.

Step 14. Click Save.
Configure Wireless Security
Step 15. In the Wireless Table area, check the box that corresponds to the SSID you want to configure.
Note: In this example, the Network_Find SSID is edited.
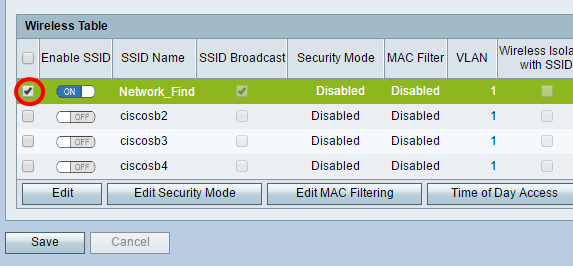
Step 16. Click Edit Security Mode.

Step 17. Choose the SSID that needs to be edited from the drop-down menu.
Note: In this example, Network_Find is chosen.
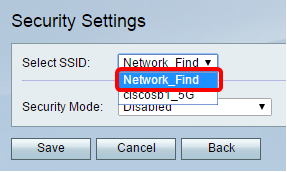
Step 18. Choose the Security Mode from the drop-down menu.

The options are:
- Disabled — This is the default setting. Choosing Disabled will leave the wireless network unsecured so anybody with a wireless client device can connect to the network easily.
- WEP —Wired Equivalent Protection (WEP) is a legacy type of security. A combination of letters from A through F and numbers 0 to 9 may be used in this type of security.
- WPA-Personal —Wi-Fi Protected Access-Personal (WPA-Personal) is a type of security is more secure than WEP, but is more suitable for a home environment. It uses the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) cypher in securing the wireless network. Although a legacy security mode, it lets you use a combination of up to 64 letters and numbers when setting up a password with WPA-Personal. This option is not available on the RV132W and RV134W.
- WPA-Enterprise — This is typically used in enterprise networks. It requires a Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) to complete this type of wireless security setup. This option is not available on the RV132W and RV134W.
- WPA2-Personal — WPA2 is the updated version of WPA. It uses Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) cipher to protect the wireless network. Like WPA-Personal, WPA2-Personal uses a combination of case-sensitive letters and numbers for the password. This security type is recommended.
- WPA2-Personal Mixed — Lets the router accommodate wireless client devices that support both WPA and WPA2.
- WPA2-Enterprise — Like WPA-Enterprise, this is typically used in enterprise networks. It requires a RADIUS to complete this type of wireless security setup.
- WPA2-Enterprise Mixed — This security type also requires a RADIUS and is typically used in an office environment.
Note: When choosing wireless security, the router automatically chooses the Encryption and generates a random alphanumeric password. In this example, WPA2-Personal is chosen.

Step 19. Check the Unmask Password check box to display the Security Key in plain text.
Note: This will be your wireless password. Take note of this password as you will need it when connecting to your network wirelessly. The password is case-sensitive. You may change the password according to your preference.
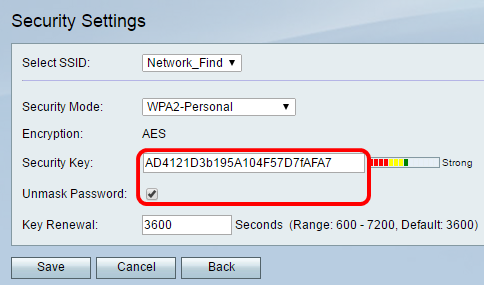
Step 20. (Optional) Set the key renewal value in the Key Renewal field. The default value is 3600.

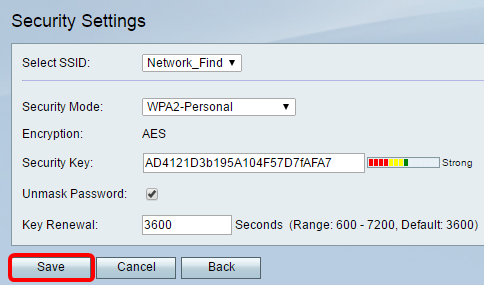
Step 21. Click Saveto save the settings and return to the Basic Settings page.
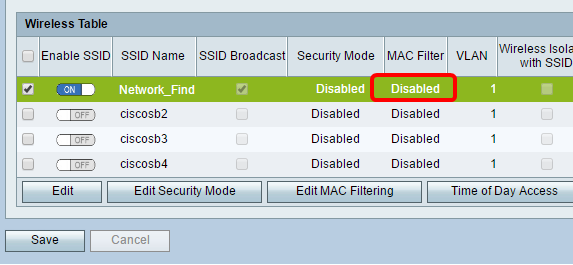
Edit MAC Filtering
Step 22. Set up Media Access Control (MAC) filtering on the RV132W or RV134W Router. For instructions, click here. If you are using the RV130W, click here to know how.
Note: In this example, MAC Filter is disabled.
Configure VLAN Membership
Step 23. In the Wireless Table area, check the box that corresponds to the SSID you want to configure.
Note: In this example, only the Network_Find SSID is edited.
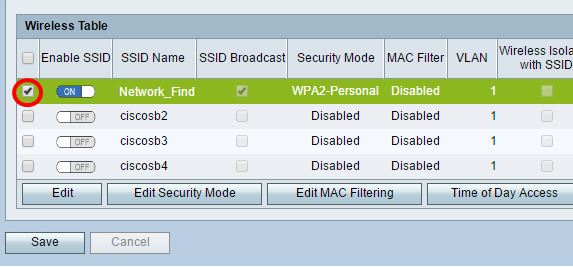
Step 24. Choose the VLAN associated with the SSID. If you want to create additional VLANs, click here.
Note: In this example, it is left at the default setting, VLAN 1.
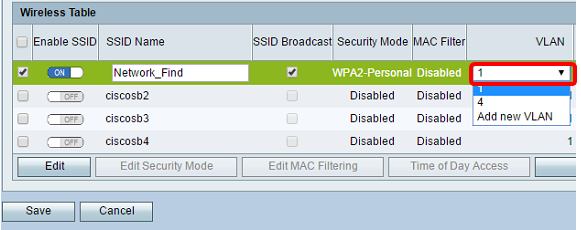
Step 25. Click Save.
Enable Wireless Isolation with SSID
Step 26. In the Wireless Table area, check the box that corresponds to the SSID you want to configure.
Step 27. (Optional) Check the check box under the Wireless Isolation with SSID column to enable the feature. With wireless isolation enabled, clients connected to the same SSID will not be able to ping each other. This feature is disabled by default. In this example, Wireless Isolation with SSID is left disabled.

Step 28. (Optional) Check the check box under the WMM column to enable Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM). This feature allows you to assign different processing priorities to different types of traffic. You can configure Quality of Service (QoS) to provide different priorities and levels of performance to different applications, users, or data flows.
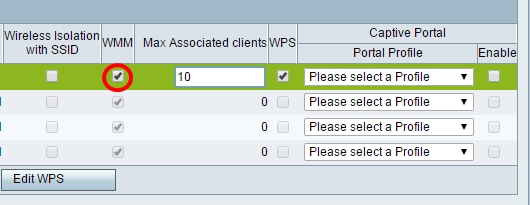
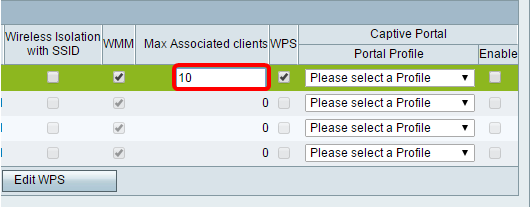
Step 29. (Optional) Choose the maximum number of clients that can connect to the selected wireless network in the Max Associated clients field. Up to 64 wireless clients are allowed on the RV130W. The RV132W supports up to 50 concurrent clients, while the RV134W supports up to 100 concurrent clients.
Note: In this example, Max Associated clients is set to 10.
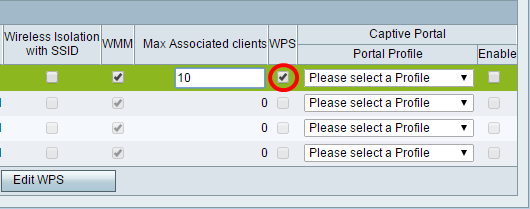
Step 30. (Optional) Check the check box under the WPS column to map the Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) information on the device to this network.
Enable Captive Portal
Step 31. (Optional) In the Captive Portal area, check the Enable check box if you want to enable the captive portal feature for the SSID. Captive Portal diverts users to a portal to log in to before they are given access. This is typically implemented in business centers, malls, coffee shops, airports, and other places that provide public wireless Internet access. This option is available only on the RV130W.
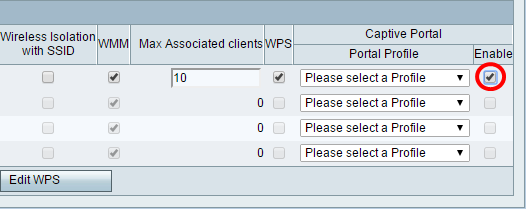
Step 32. (Optional) Choose a captive portal profile in the Portal Profile drop-down list.
Note: In this example, the PublicWebAccess portal profile is chosen.
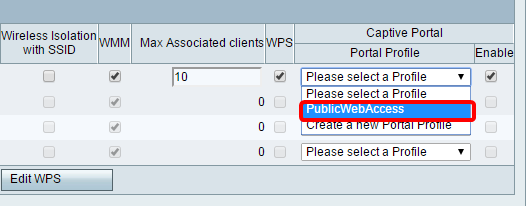
Step 33. Click Save to save your configuration.
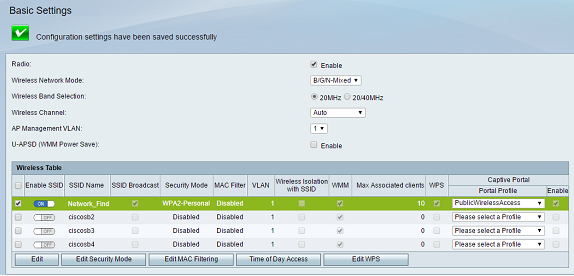
You should see the confirmation message that the configuration settings have been saved successfully. The Wireless Table is now updated with the newly configured network.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
10-Dec-2018 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback