Basic Firewall Configuration on RV320 and RV325 Routers
Available Languages
Objective
This article explains how to configure basic firewall settings on the RV32x VPN Router Series.
A firewall is a set of features designed to keep a network secure. A router is considered a strong hardware firewall. This is due to the fact that routers are able to inspect all inbound traffic and drop any unwanted packets. Network firewalls guard an internal computer network (home, school, business intranet) against malicious access from the outside. Network firewalls may also be configured to limit access to the outside from internal users.
Applicable Devices
- RV320 Dual WAN VPN Router
- RV325 Gigabit Dual WAN VPN Router
Software Version
- v1.1.0.09
Basic Settings
Step 1. Log in to the web configuration utility and choose Firewall > General. The General page opens:

Step 2. Based on your requirements, check the Enable check box that corresponds to the features that you wish to enable.
- Firewall — Router firewalls can be turned off (disabled), or they can be enabled to filter certain types of network traffic through so called firewall rules, A firewall can be used to filter all the incoming and outgoing traffic and based.
- SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection) — Monitors the state of network connections such as TCP streams and UDP communication The firewall distinguishes legitimate packets for different types of connections. Only packets that match a known active connection are allowed by the firewall, all the others are rejected.
- DoS (Denial of Service) — Used to protect a network from a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack. DDoS attacks are meant to flood a network to the point where the resources of the network become unavailable. The RV320 uses DoS protection to protect the network through the restriction and removal of unwanted packets.
- Block WAN Request — Blocks all ping requests to the router from the WAN port.
- Remote Management — Allows access to the router from a remote WAN network.
- Port — Enter a port number to remotely manage.
- Multicast Pass Through — Allows IP multicast messages to pass through the device.
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) — Is a communications protocol for secure communication over a computer network. It provides bidirectional encryption from client and server.
- SSL VPN — Allows an SSL VPN connection made through the router.
- SIP ALG — SIP ALG offers functionality that allows Voice-over-IP traffic that goes both from the private to public and public to private side of the firewall when network address and port translation (NAPT) are used. NAPT is the most common type of network address translation.
- UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) — Allows for automatic discovery of devices that can communicate with the router.
Step 3. Based on your requirements, check the Enable check box that corresponds to the features that you wish to block.
- Java — Checking this box blocks Java applets from being downloaded and executed. Java is a common programming language used by many websites. However, java applets that are made for malicious intent can pose a security threat to a network. Once downloaded, a hostile java applet can exploit network resources.
- Cookies — Cookies are created by websites to store information about users. Cookies can track the web history of the user which may lead to an invasion of privacy.
- ActiveX — ActiveX is a type of applet that is used by many websites. Though generally safe, once a malicious ActiveX applet is installed on a computer, it can do anything a user can do. It may insert harmful code into the operating system, surf a secure intranet, change a password, or retrieve and send documents.
- Access to HTTP Proxy Servers — Proxy servers are servers that provide a link between two separate networks. Malicious proxy servers can record any unencrypted data that is sent to them such as logins or passwords.
- Exception — Allows the selected features (Java, Cookies, ActiveX, or Access to HTTP Proxy Servers), but restricts all non-selected features on configured trusted domains. A domain that is trusted and has access to the trusted network. You can set up a trusted domain that allows users of an external domain to access your network resources. If this option is disabled, a trusted domain allows all the features.
Note: Time Saver: If you have not checked the Exception check box then skip step 4 .
Step 4. Click Add, enter a new Trusted domain, and click Save to create a trusted domain.

Step 5. Click Save to update the changes.

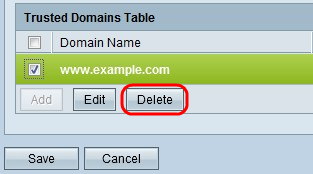
Step 6. (Optional) To Edit the name of the Trusted Domain, check the check box of the trusted domain that you want to edit, click Edit, edit the domain name, and click Save.

Step 7. (Optional) To Delete a domain in the Trusted Domain list, check the check box of the trusted domain that you want to delete and click Delete.
 Feedback
Feedback