Site-to-Site VPN with Amazon Web Services
Available Languages
Objective
The objective of this article is to guide you through setting up a Site-to-Site VPN between Cisco RV Series routers and Amazon Web Services.
Applicable Devices | Software Version
Introduction
A Site-to-Site VPN allows a connection to two or more networks, which gives businesses and general users the ability to connect to different networks. Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides many on demand cloud computing platforms including site to site VPNS that allow you to access your AWS platforms. This guide will help you configure the site to site VPN on both the RV16X, RV26X, RV34X router to the Amazon Web Services.
The two parts are as follows:
Setting up Site-to-Site VPN on Amazon Web Services
Setting up Site-to-Site VPN on an RV16X/RV26X, RV34X Router
Setting up a Site-to-Site VPN on Amazon Web Services
Step 1
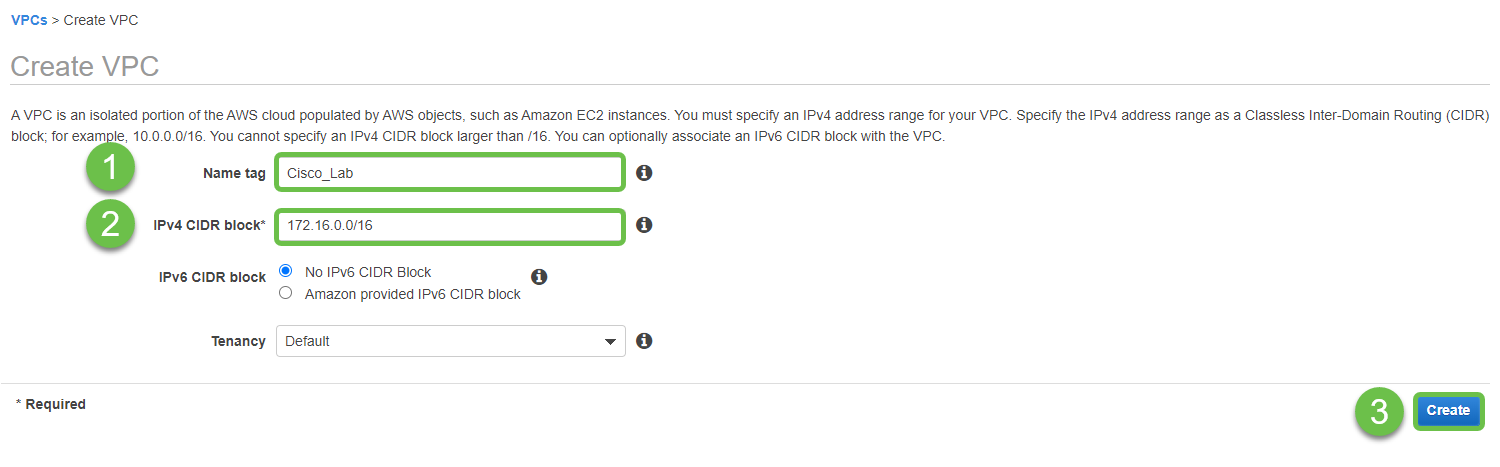
Create a new VPC, defining an IPv4 CIDR block, in which we will later define the LAN used as our AWS LAN. Select Create.
Step 2
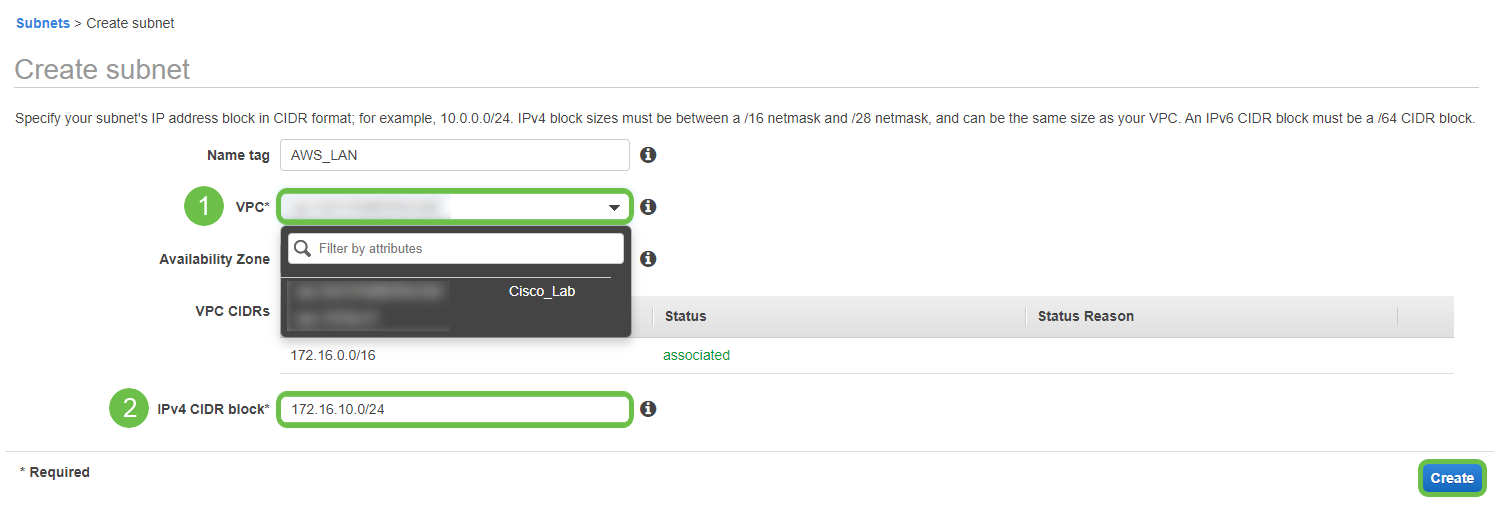
When creating the subnet, ensure that you have selected the VPC created previously. Define a subnet within the existing /16 network created previously. In this example, 172.16.10.0/24 is used.
Step 3
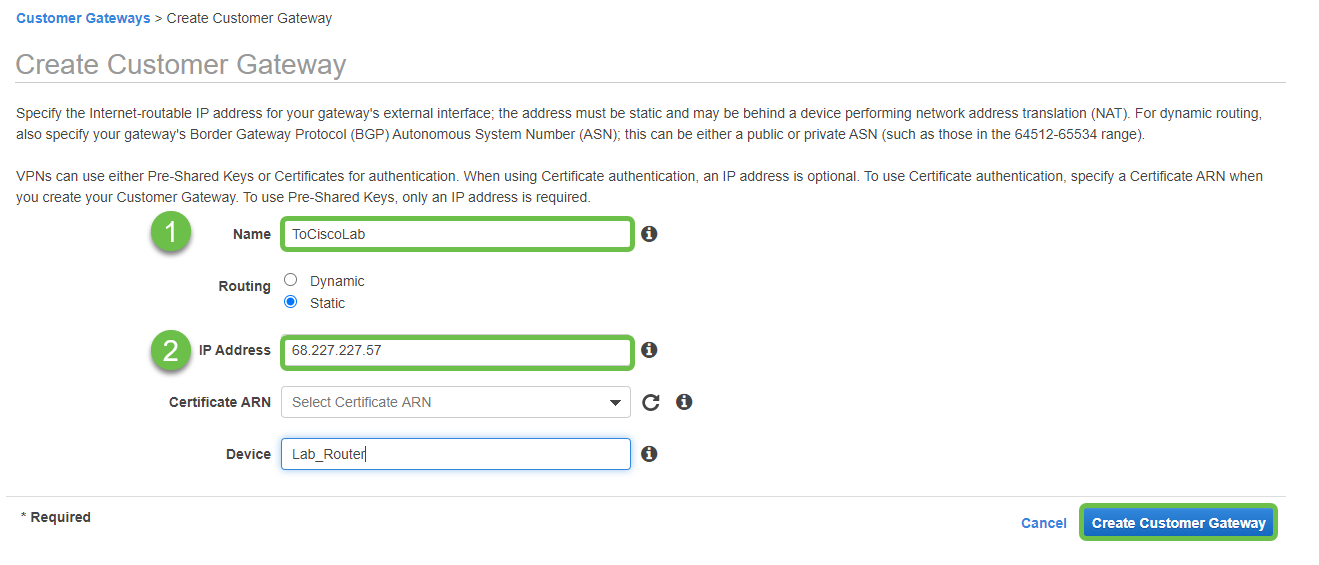
Create a Customer Gateway, defining the IP Address as the Public IP Address of your Cisco RV Router.
Step 4
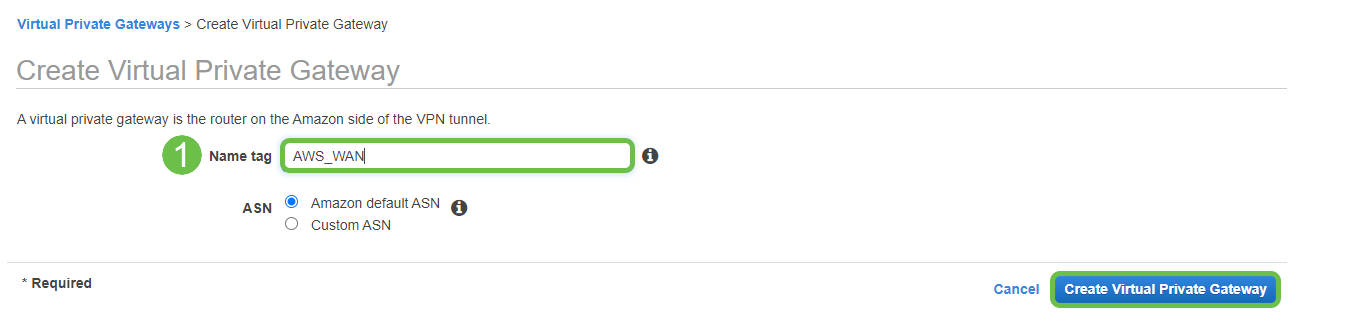
Create a Virtual Private Gateway – creating a Name tag to help identify later.
Step 5
Attach the Virtual Private Gateway to the VPC created previously.
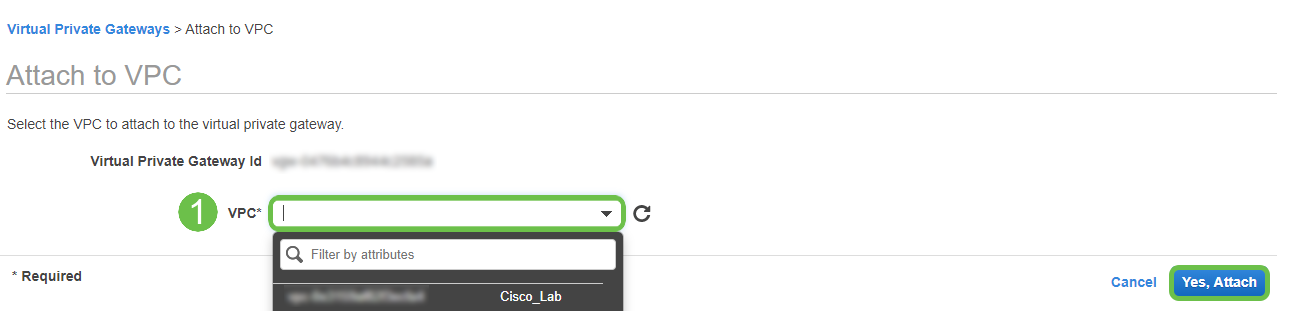
step 6
Create a new VPN Connection, selecting the Target Gateway Type Virtual Private Gateway. Associate the VPN Connection with the Virtual Private Gateway created previously.
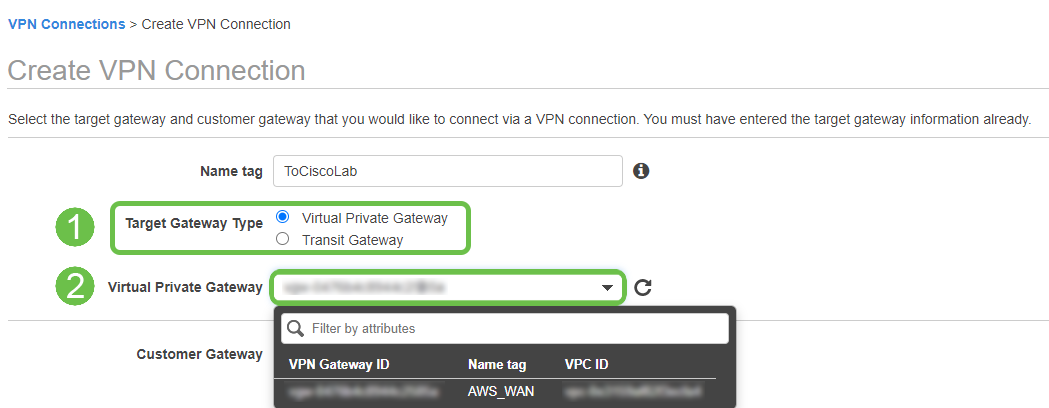
Step 7
Select Existing Customer Gateway. Select the Customer Gateway created previously.
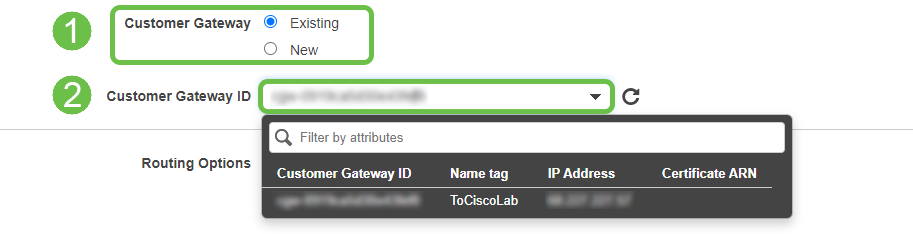
Step 8
For Routing Options, ensure to select Static. Enter any IP Prefixes including CIDR notation for any remote networks you expect to traverse the VPN. [These are the networks that exist on your Cisco Router.]
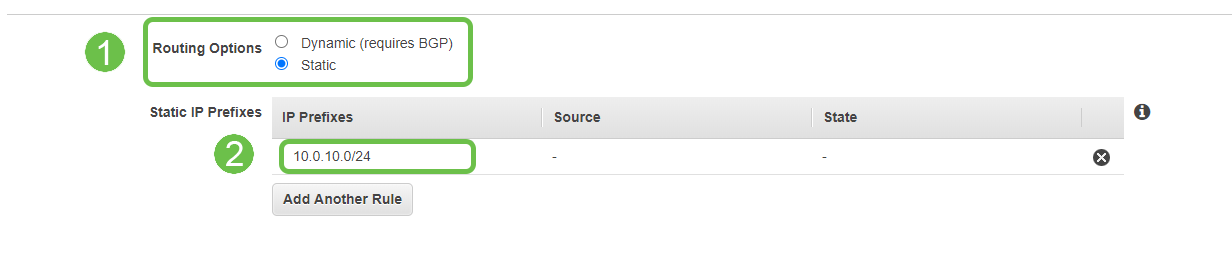
Step 9
We will not cover any of the Tunnel Options in this guide - select Create VPN Connection.
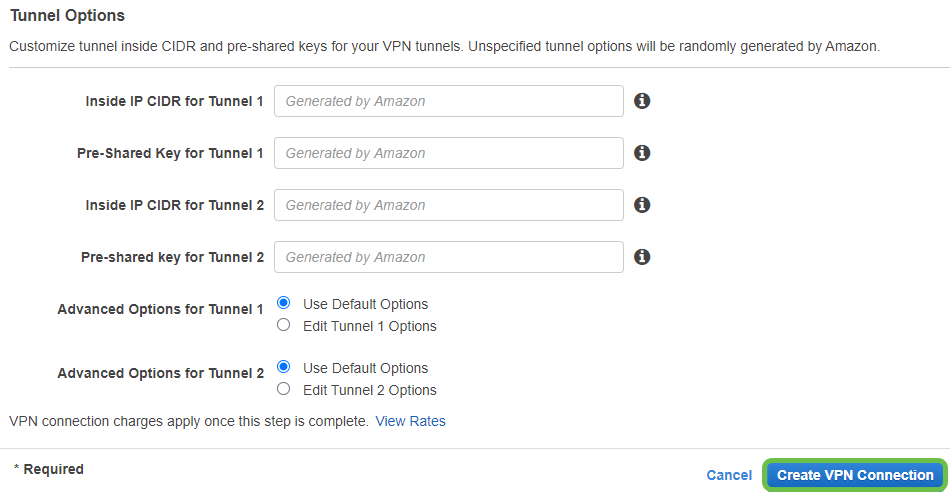
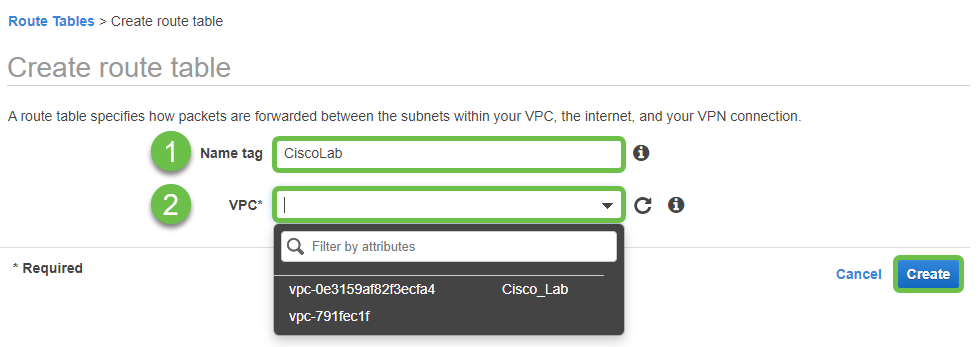
Step 10
Create a Route Table and associate the VPC created previously. Press Create.
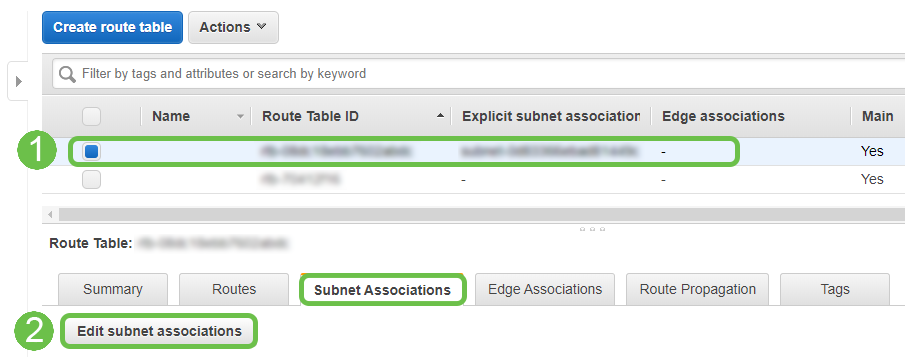
Step 11
Select the Route Table created previously. From the Subnet Associations tab, choose Edit subnet associations.
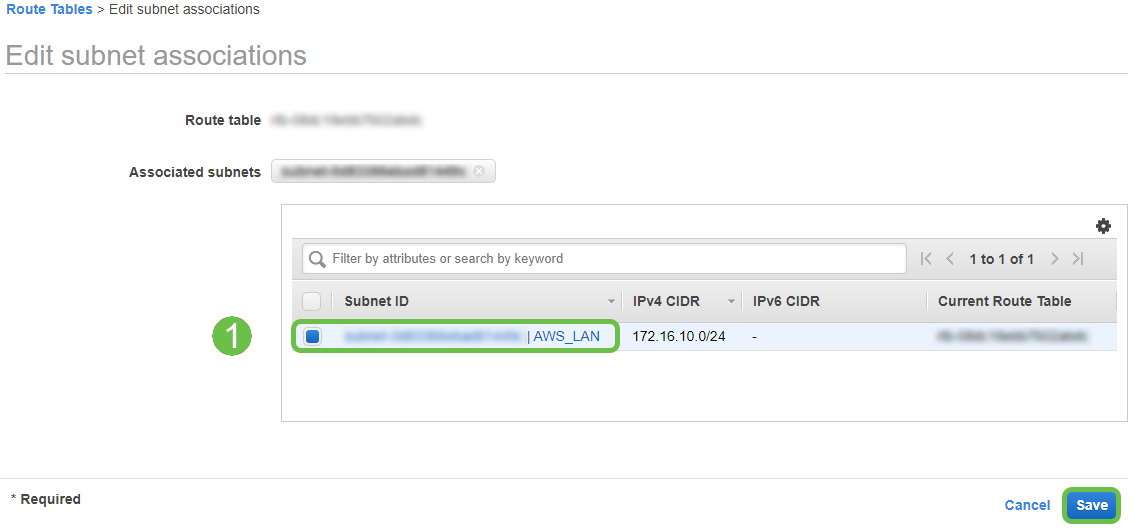
Step 12
From the Edit subnet associations page, select the subnet created previously. Select the Route Table created previously. Then select save.
Step 13
From the Route Propagation tab, choose Edit route propagation.
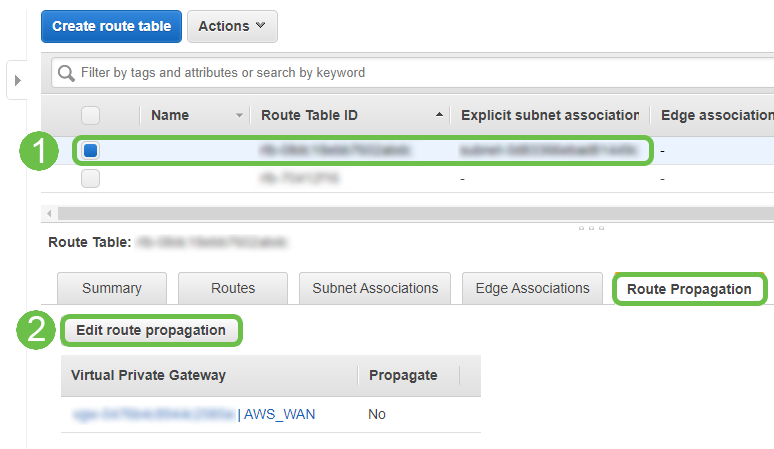
Step 14
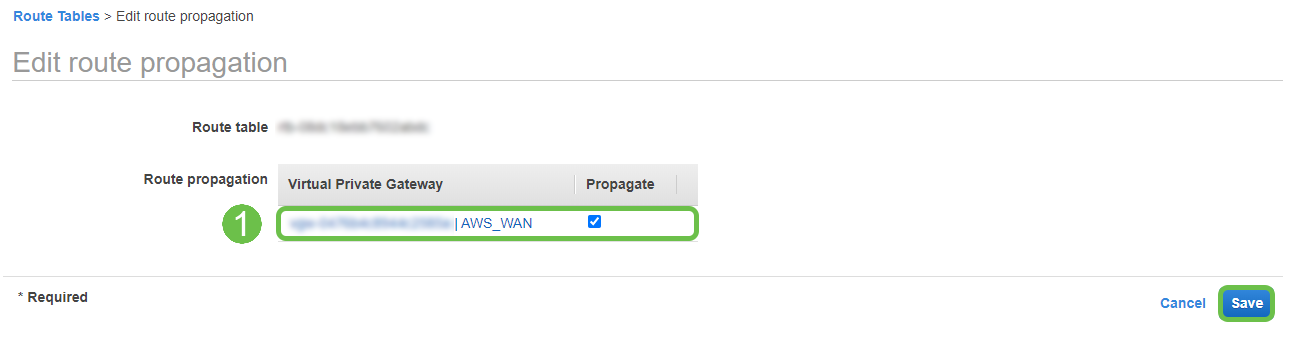
Select the Virtual Private Gateway created previously.
Step 15
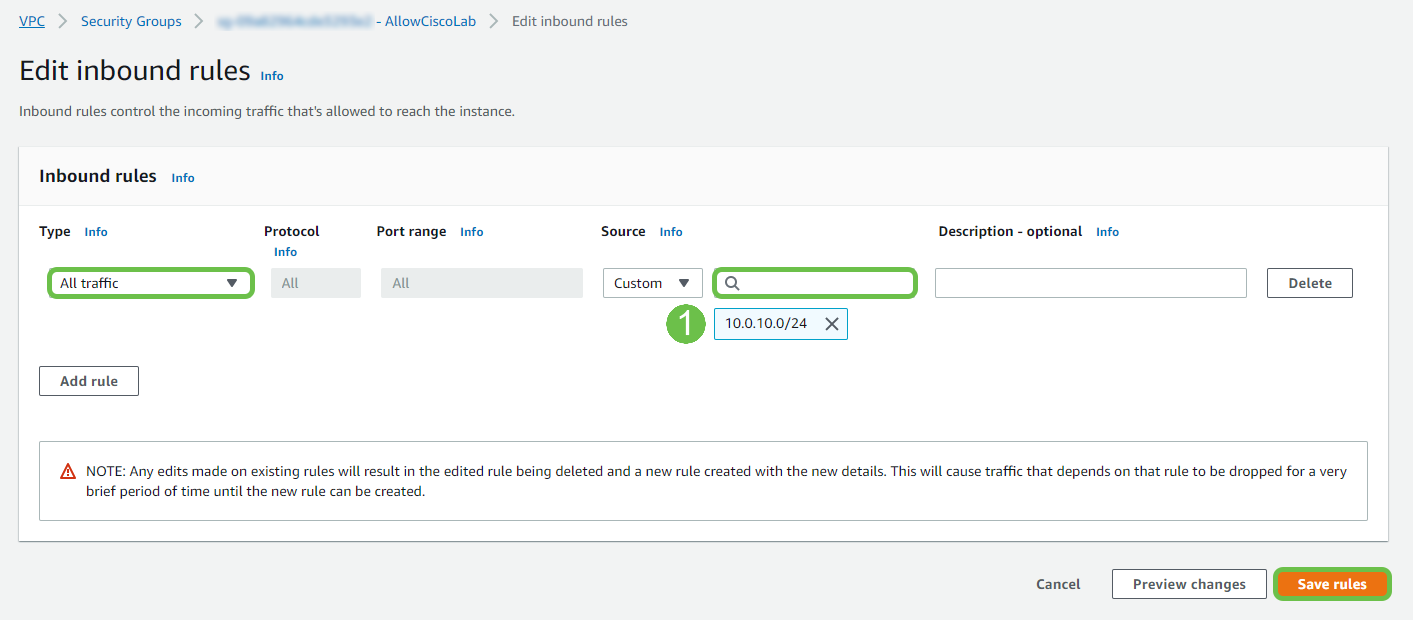
From VPC > Security Groups, ensure that you have a policy created to allow the desired traffic.
Note: In this example, we are using a source of 10.0.10.0/24 – which corresponds to the subnet in use on our example RV router.
Step 16
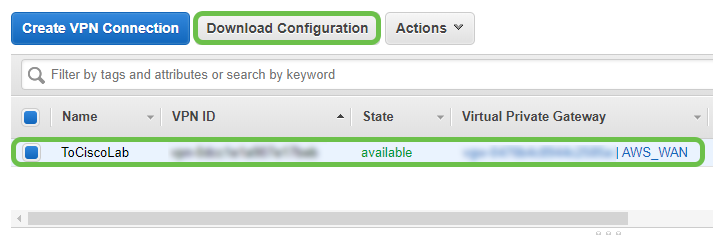
Select the VPN Connection that you have created previously and choose Download Configuration.
Setting up Site-to-Site on an RV16X/RV26X, RV34X Router
Step 1
Log in to the router using valid credentials.

Step 2
Navigate to VPN > Ipsec Profiles. This will take you to the Ipsec profile page, press the add icon (+).
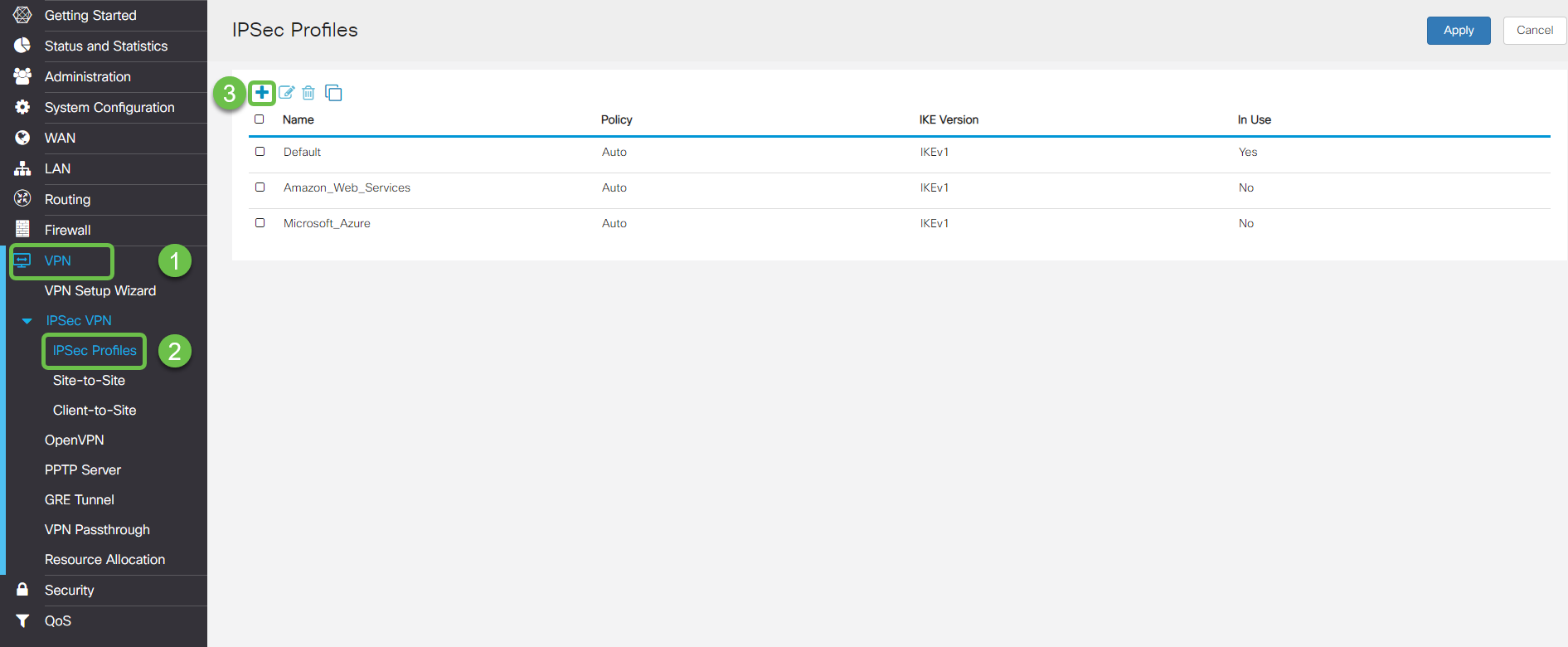
Step 3
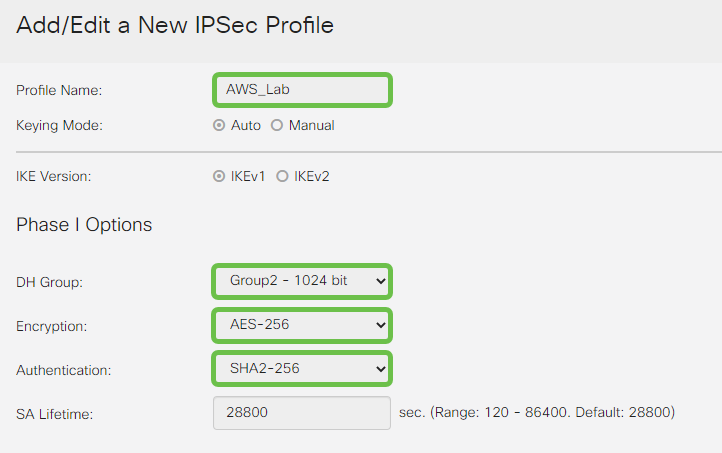
We will now create our IPSEC profile. When creating the IPsec Profile on your Small Business router, ensure that DH Group 2 is selected for Phase 1.
Note: AWS will support lower levels of encryption and authentication – in this example, AES-256 and SHA2-256 are used.
Step 4
Ensure that your Phase two options match those made in phase one. For AWS DH Group 2 must be used.
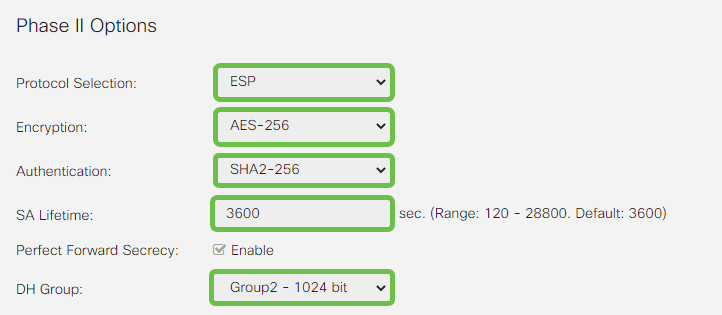
Step 5
Press Apply and you will be navigated to the IPSEC page, be sure to press Apply once again.
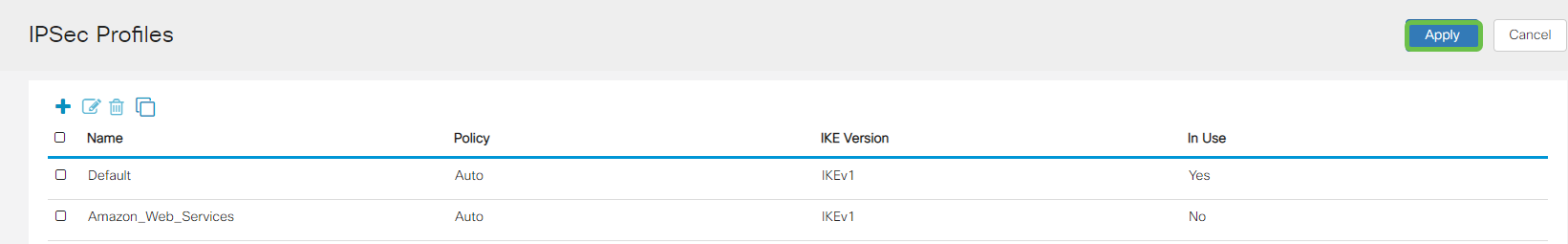
Step 6
Navigate to VPN< Client to site and on the client to site page press the plus icon (+).
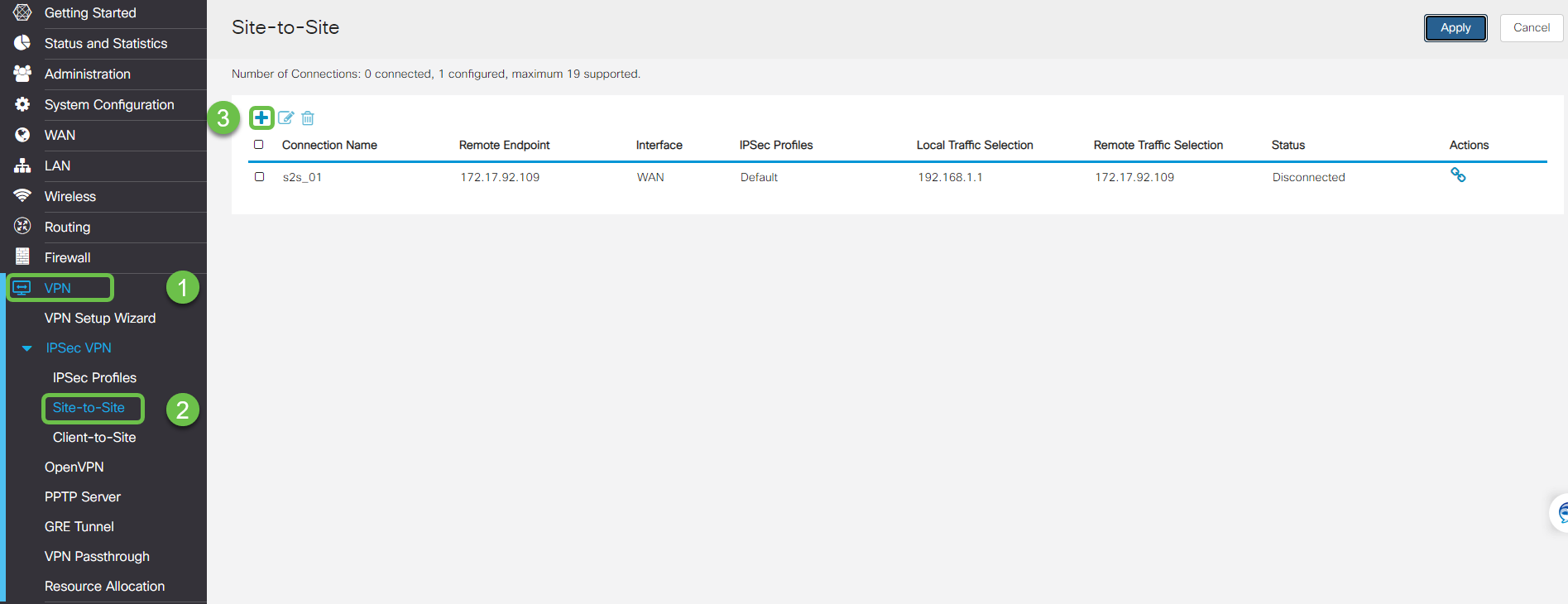
Step 7
When creating the IPsec Site-to-Site Connection, ensure to select the IPsec Profile created in the previous steps. Use the Remote Endpoint type of Static IP and enter the address provided in the exported AWS configuration. Enter the Pre-Shared Key provided in the exported configuration from AWS.
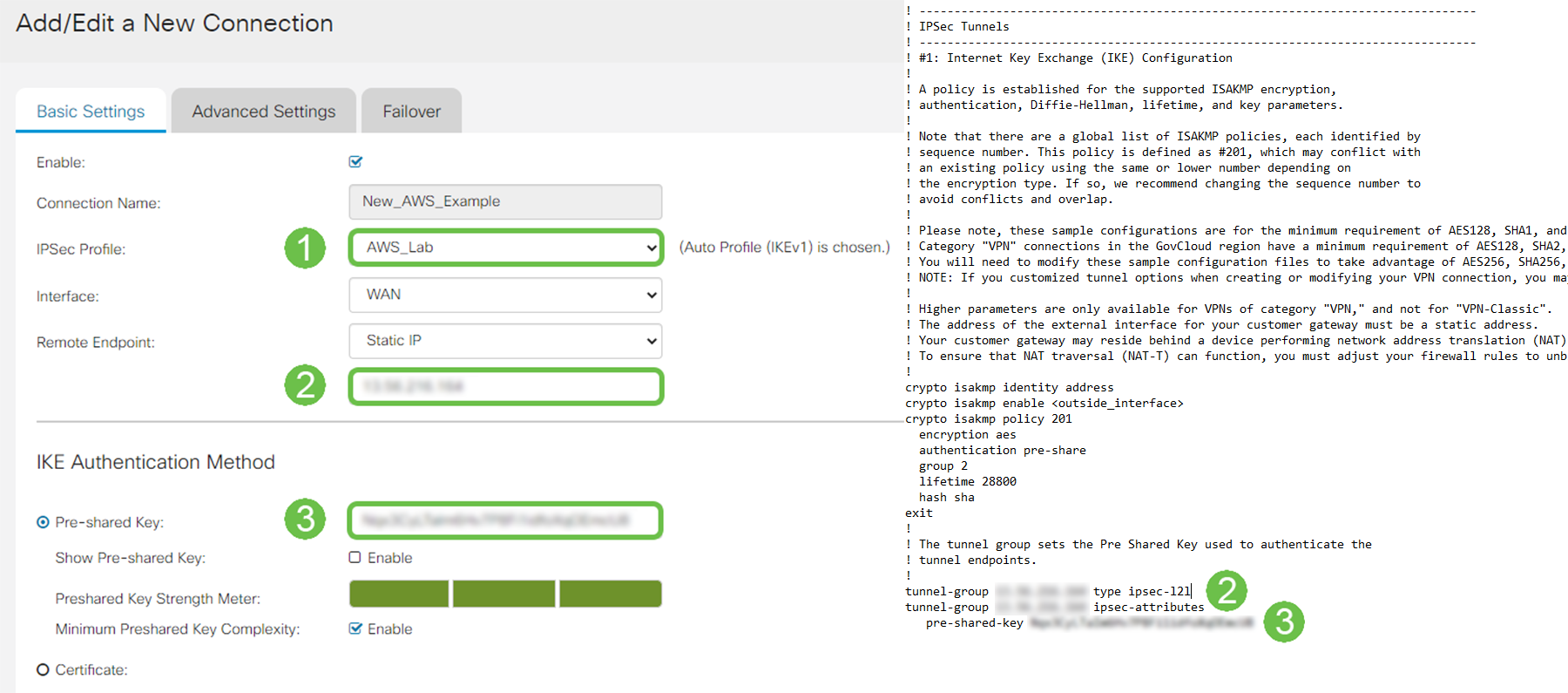
Step 8
Enter the Local Identifier for your Small Business router – this entry should match the Customer Gateway created in AWS. Enter the IP Address and Subnet Mask for your Small Business router – this entry should match the Static IP Prefix added to the VPN Connection in AWS. Enter the IP Address and Subnet Mask for your Small Business router – this entry should match the Static IP Prefix added to the VPN Connection in AWS.
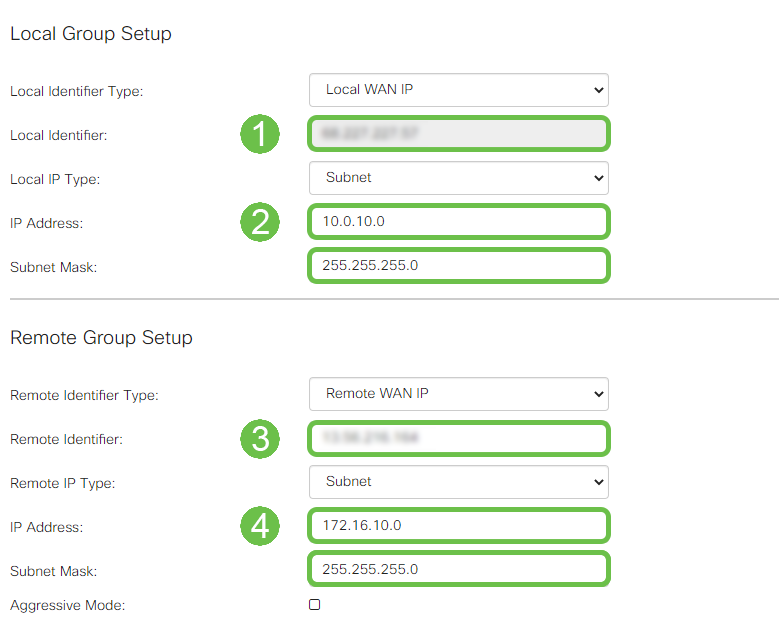
Step 9
Enter the Remote Identifier for your AWS connection – this will be listed under Tunnel Details of the AWS Site-to-Site VPN Connection . Enter the IP Address and Subnet Mask for your AWS connection – which was defined during the AWS configuration. Then press Apply .
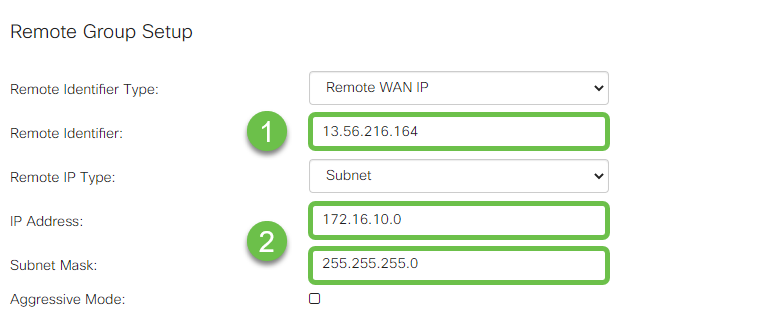
Step 10
Once on the Ip Site to Site page press Apply.
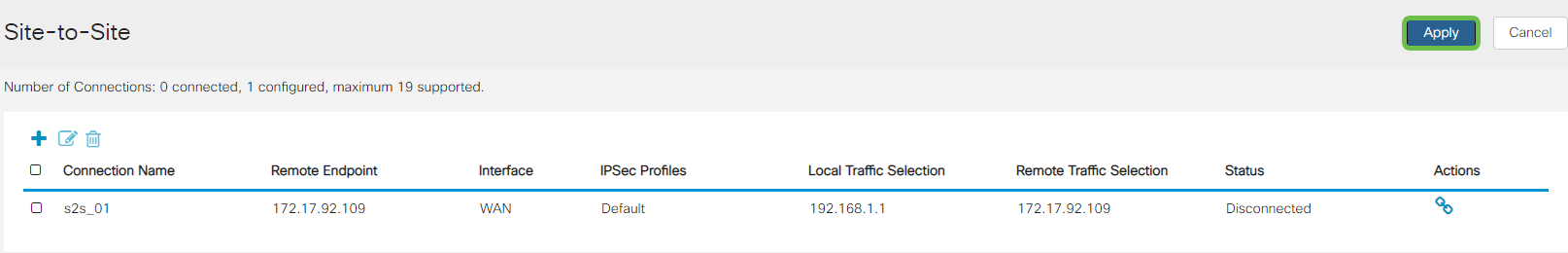
Conclusion
You have now successfully created a Site to Site VPN between your RV series router and your AWS. For community discussions on Site-to-Site VPN, go to the Cisco Small Business Support Community page and do a search for Site-to-Site VPN.