Clone the MAC Address of a Third-Party Router to an RV160 or RV260 Router
Available Languages
Objective
This article explains how to configure MAC Address Clone using an RV160 or RV260 router.
Introduction
Every device has its own Media Access Control (MAC) address. Each MAC address is unique to every device. It is good to know your MAC address when setting up a network and troubleshooting. It is physically located on the device and contains 12 hexadecimal numbers.
When a network device is configured, it is common to utilize Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for both Local Area Network (LAN) and Wide Area Network (WAN) IP addresses. DHCP manages a pool of available IP addresses, assigning them to hosts as they join the network. It is a simple way to maintain a network, as it is all done automatically, without intervention from an administrator. DHCP is also used to configure the correct subnet mask, default gateway, and Domain Name System (DNS) information on the device.
At some point, you may observe that the WAN interface of an RV160 or RV260 router is configured to DHCP. However, for some reason, the WAN interface is unable to get an IP from their Internet Service Provider (ISP). Most likely, the ISP has configured MAC address binding on their side for the known devices. Due to that, the ISP will not assign any DHCP IP to the unknown devices.
If rebooting the router doesn’t work, and your network contains a separate, pre-configured third-party router, such as D-Link, check that router out. Can that router get a DHCP IP on the WAN interface using the same ISP link?
If it can, the RV160 or RV260 can clone the MAC address of that third-party router. In this example, the MAC address of the WAN interface of the D-Link will be cloned. Then the RV160 or RV260, showing the cloned MAC address on its WAN interface, will be able to get a DHCP IP address and resume the connection.
Applicable Devices
- RV160 series routers
- RV260 series routers
Software Version
- 1.0.00.15
Verification of the Basic Settings
Step 1. Log into the router to access the Graphical User Interface (GUI). For information on how to access the GUI of Cisco VPN router, click here.

Note: Enter the username and password as cisco if the router is in default configuration. Otherwise use your pre-configured username and password to log in to the router.
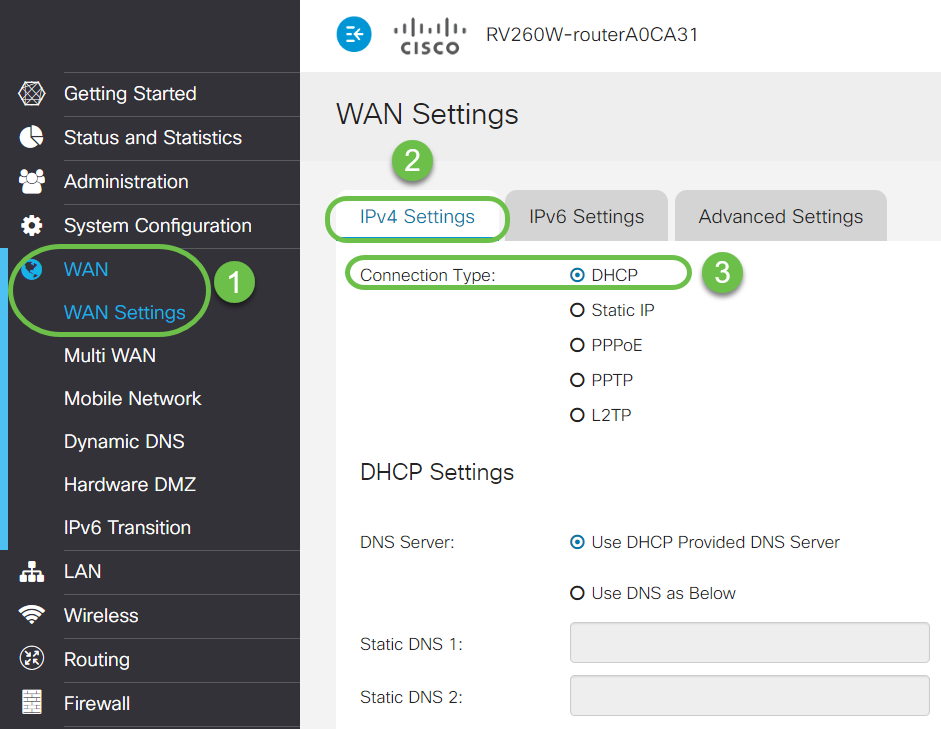
Step 2. Navigate to WAN > WAN Settings. Select IPv4 Settings. Make sure the Connection Type on the WAN interface is configured as DHCP.
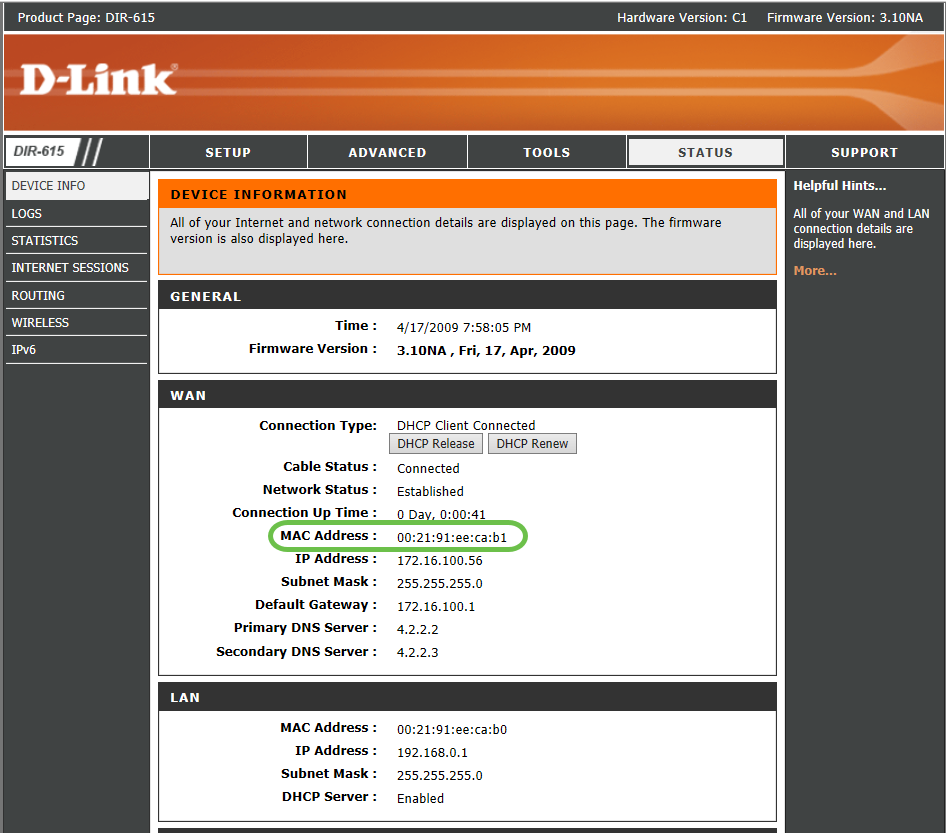
Step 3. Note the MAC address details of the WAN interface for the known working third-party router.
Note: In this example, a D-Link router is selected.
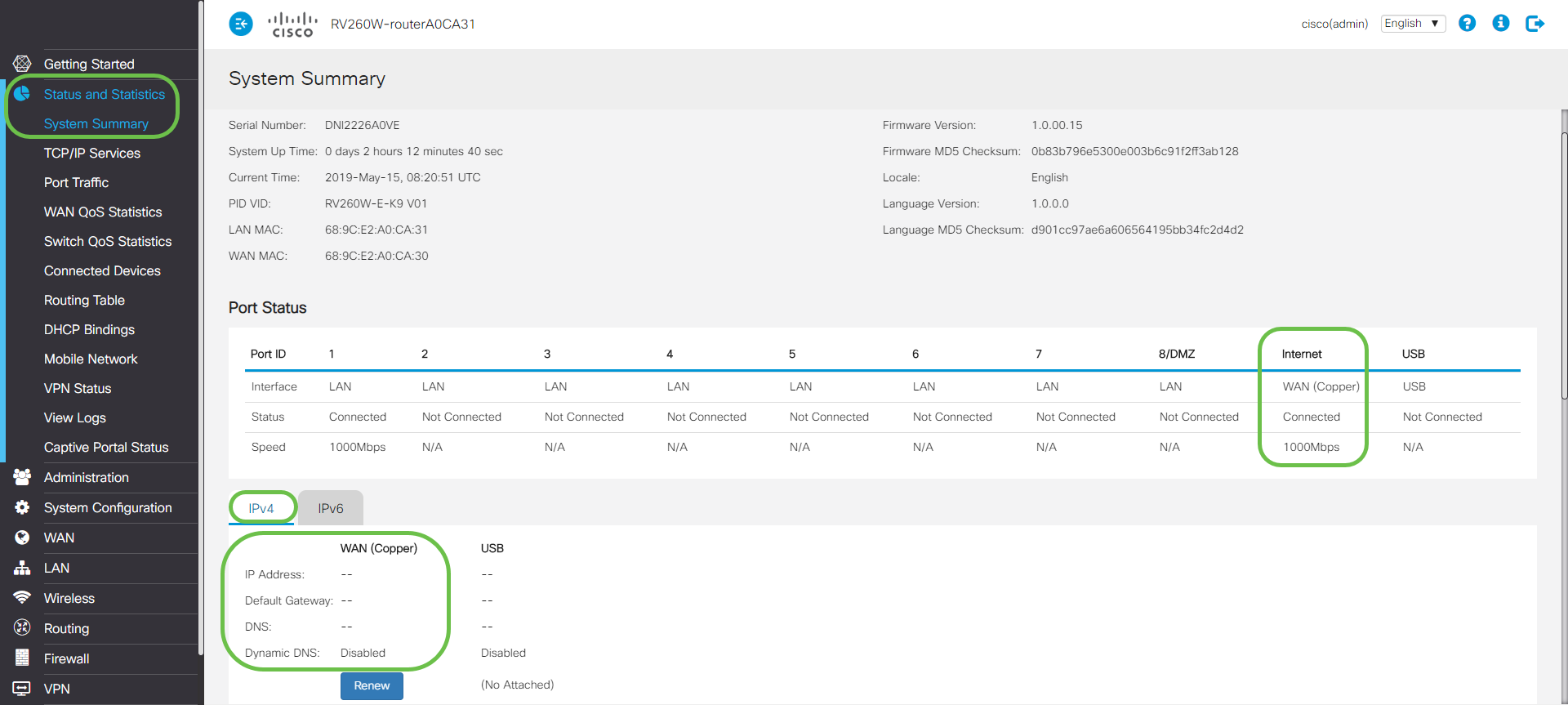
Step 4. Navigate to Status and Statistics > System Summary. Most likely, you will see the WAN interface status is showing connected. You will also notice there is no IP, Default Gateway, or DNS server listed on the WAN interface.
Configuring MAC Address Clone on an RV160 or RV260 Router
Step 1. Navigate to WAN > WAN Settings. Click Advanced Settings and click on the MAC Address Clone check box to enable that option. Enter the MAC Address of the known working third-party router WAN MAC address and click Apply.

Verification
To verify the newly configured MAC address is reflected on the WAN interface of the RV160 or RV260 router, select Status and Statistics > System Summary. Verify the WAN MAC address.
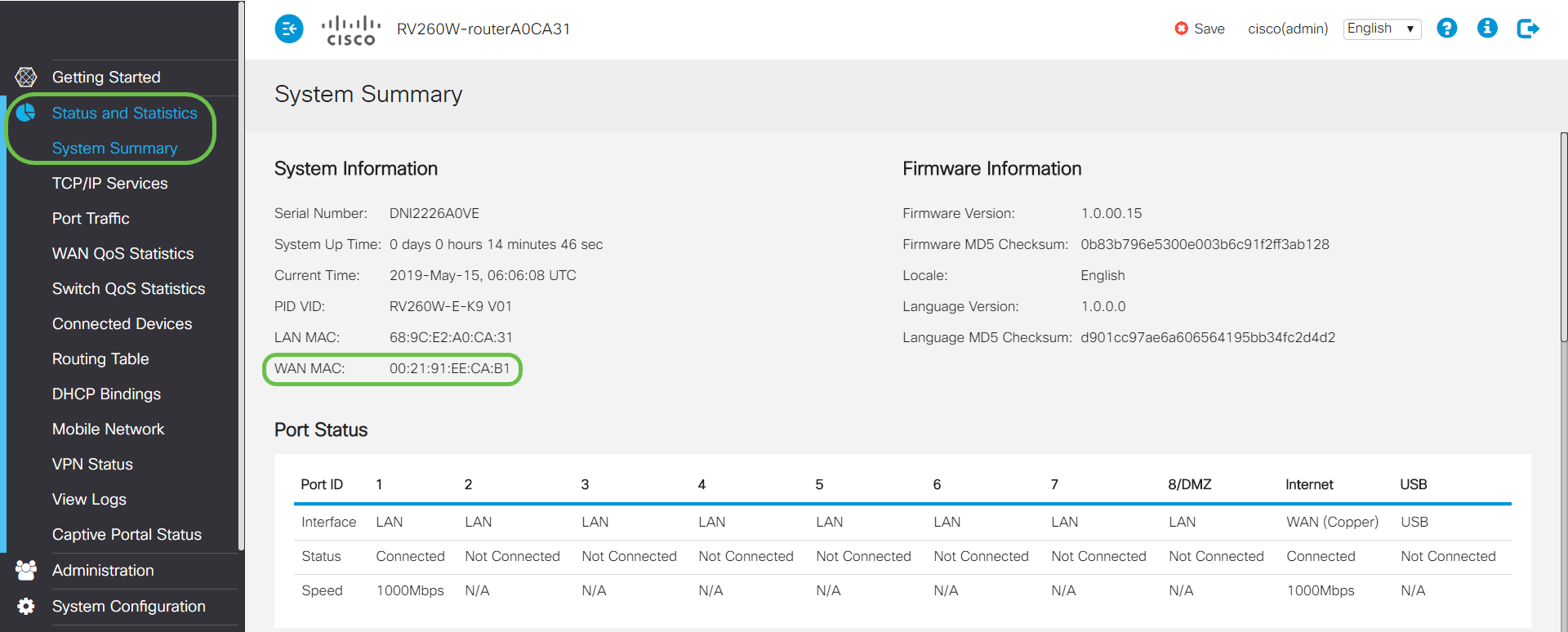
Note: You can also verify that the IP address on the WAN interface of the RV160 or RV260 router will be displayed. This IP will be different for different users based on the ISP link.
Conclusion
You have now completed and confirmed a MAC Address Clone and verified that an IP address has been assigned on your RV160 or RV260 series router.