Best Practices for Setting Static IP Addresses on Cisco Business Hardware
Available Languages
Introduction
A Local Area Network (LAN) might be as big as several buildings or as small as a home. Everyone connected to the LAN is in the same physical location.
In a LAN, the router assigns each device its own unique internal IP address. They follow a pattern as follows:
- 10.0.0.0 /8 (10.x.x.x)
- 172.16.0.0 /12 (172.16.x.x - 172.31.x.x)
- 192.168.0.0 /16 (192.168.x.x)
These addresses are only visible inside a network, between devices, and are considered private from outside networks. There are potentially millions of locations that might have the same pool of internal IP addresses as your business. It doesn't negatively affect your addressing scheme, as they are only used within their own private network, and hence, there is no conflict.
There are special configurations that can be done, but there are some standard things to keep in mind. In order for the devices in the network to communicate with each other, they should all follow the same pattern as the other devices. They should also be on the same subnet, which is the organizational method within the IP addressing scheme. Each IP address must also be unique. You should never see any of these addresses in this pattern as a public IP address, as they are reserved for private LAN addresses only.
All of these devices send data through a default gateway (a router) to move data out to the Internet. When the default gateway receives the information, it needs to do Network Address Translation (NAT), which encapsulates the IP address to be publicly facing. Since anything going out across the Internet needs a public IP address, this encapsulation ensures the data can find its way back to the requestor.
Manually assigning IP addresses can be a secure method of IP addressing, being a manual process, there are network scaling issues that can occur. To solve manual assignment, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a protocol that automatically assigns IP addresses to devices in a network. Devices that use DHCP are automatically given a dynamic IP address in the proper subnet mask. This pool of available IP address can change over time as addresses are assigned or abandoned.
You can configure the internal IP address to stay the same by configuring static DHCP on the router or assign a static IP address on the device itself. From that point forward, that device will keep the same IP address unless manually changed or if the router is reset to factory default.
Note: Public IP addresses are not guaranteed to stay the same either, unless you pay to have a static public IP address through your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Many companies pay for this service so their employees and customers have a more reliable connection to their servers (web, mail, VPN, etc.) but it can be expensive.
Some small businesses can leave all their IP addresses dynamic. With DHCP, devices can be added or removed without any issues. DHCP assigns each device a local IP address that is unique from all others and in the same subnet so there are no conflicts and they can all communicate with each other.
Objective
This article gives the reader general information about static IP addresses and some recommended best practices when using Cisco Business hardware.
When Should a Device have a Static IP Address?
If you need constant access to a device, or server, in the network it would be beneficial for that address not to change. Here are some examples:
- Your router. In order to access the network while you are away from the LAN, whether connecting a computer to work from home, or accessing a surveillance camera connected to the network.
- You share a printer within the network.
- You have two or more routers in the network.
- You host a file server such as a web server or File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server.
-
A DHCP server – a DHCP server is likely to automatically have a static address.
- Your network doesn’t support DHCP.
What Devices Don’t Typically Need a Static IP Address?
If you do not need constant access to a device in the network it would be beneficial and much less complicated to use DHCP. In a network, there may be hundreds of these devices and it would be very difficult to keep track of which addresses have been used. These devices may often be moved between networks and in order to connect, the IP address needs to change. With DHCP, this is done automatically. Here are some examples:
- Mobile phones
- Computers
- VoIP phones
What are the Challenges when Using Static IP addresses?
- The administrator has to keep track of all devices and the static IP addresses they have been assigned.
- If the same static IP addresses are assigned to two different devices they will both be unable to communicate on the network. This can be prevented if the administrator has kept good notes on the topology of the network.
- If DHCP assigns an IP address that is already assigned as a static IP address, those devices can’t communicate. The solution for this problem is to assign blocks of IP addresses for DHCP and different blocks for static addressing.
Cisco Business Recommendations
- Keep good notes including each static IP and Media Access Control (MAC) address.
- Only assign a static IP address if necessary.
- Reserve a block of addresses for DHCP and a separate block for static addressing.
- Only use addresses from the 10.0.0.0 /8 (10.x.x.x), 172.16.0.0 /12 (172.16.x.x - 172.31.x.x), or 192.168.0.0 /16 (192.168.x.x) pattern.
- Do not use an address that ends in .0 as those are typically reserved for networks.
- Do not use an address that ends in .1 or .254, as those are often the default IP addresses of devices. The first or last usable IP address of a network is so common that a hacker would most likely use it to try to access the network.
- Do not use the last IP address of the IP Network pool, ending in .255, as they are reserved for the broadcast address.
- In general, it is recommended to use different LAN IP subnets (or different subnet masks) at both ends while configuring VPN between different sites. For example, if the site you connect to uses a 192.168.x.x addressing scheme, you would want to use a 10.x.x.x or 172.16.x.x - 172.31.x.x subnet. When you change your router IP address, the devices on DHCP would automatically pick up an IP address in that subnet.
How to View or Change the Pool of IP Addresses for DHCP
On your router, you can view or change the range of IP addresses that are reserved for DHCP. If you would like some help logging in, click here.
Instructions for the RV160, RV260 or RV34x Series Routers
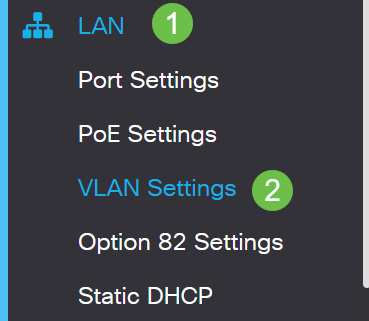
Step 1. Navigate to LAN > VLAN Settings.
Note: If you are using a RV160, RV260, or RV34x router and are not seeing the Graphical User Interface (GUI) shown in the previous section, it is highly recommended that you upgrade to the latest firmware. This should update your router to the new GUI. Check to see the latest firmware by clicking here.
If you would like instructions on how to upgrade firmware on an RV34x router, click here.
If you would like instructions on how to upgrade firmware on an RV160 or RV260 router, click here.
Step 2. Click the checkbox for the VLAN ID, the default is VLAN 1. Cisco Business routers automatically reserve 50 IP addresses for DHCP. You can change the range here to whatever you prefer, but this is usually sufficient for smaller networks. Be sure to take note of this so that you do not assign any static IP addresses in this range.

Instructions for All Other Routers
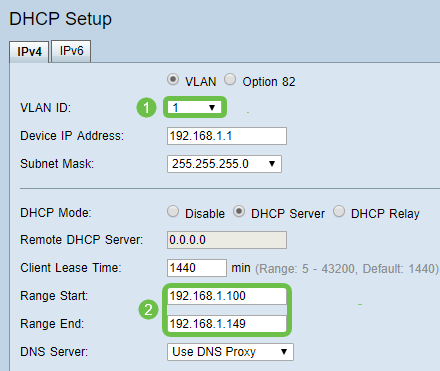
Step 1. Navigate to DHCP >DHCP Setup.

Step 2. Select the VLAN ID, the default is VLAN 1. Cisco Business routers automatically reserve 50 IP addresses for DHCP. You can change the range here to whatever you prefer, but this is usually sufficient for smaller networks. Be sure to take note of this so that you do not assign any static IP addresses in this range.
How to Assign Static IP Addresses
There are a few options for assigning a static IP address to a device. The first option is to configure all static IP addresses on the main router. This is an easy way to have all of the static IP addresses in one location. However, if you reset the router to factory settings, all configured static IP addresses will be deleted.
The second option is to configure it directly on each device. If a static IP address is configured directly on a device, and it gets reset, it will likely revert to DHCP and pick up a different IP address.
Configuring Static DHCP on a Router
To configure static DHCP on the router, you will need to know the MAC address for each device. This is the unique identifier for each device that consists of letters and numbers. The MAC address does not change. It can be found on the body of the Cisco device. It is labeled MAC and is typically shown with a white background.
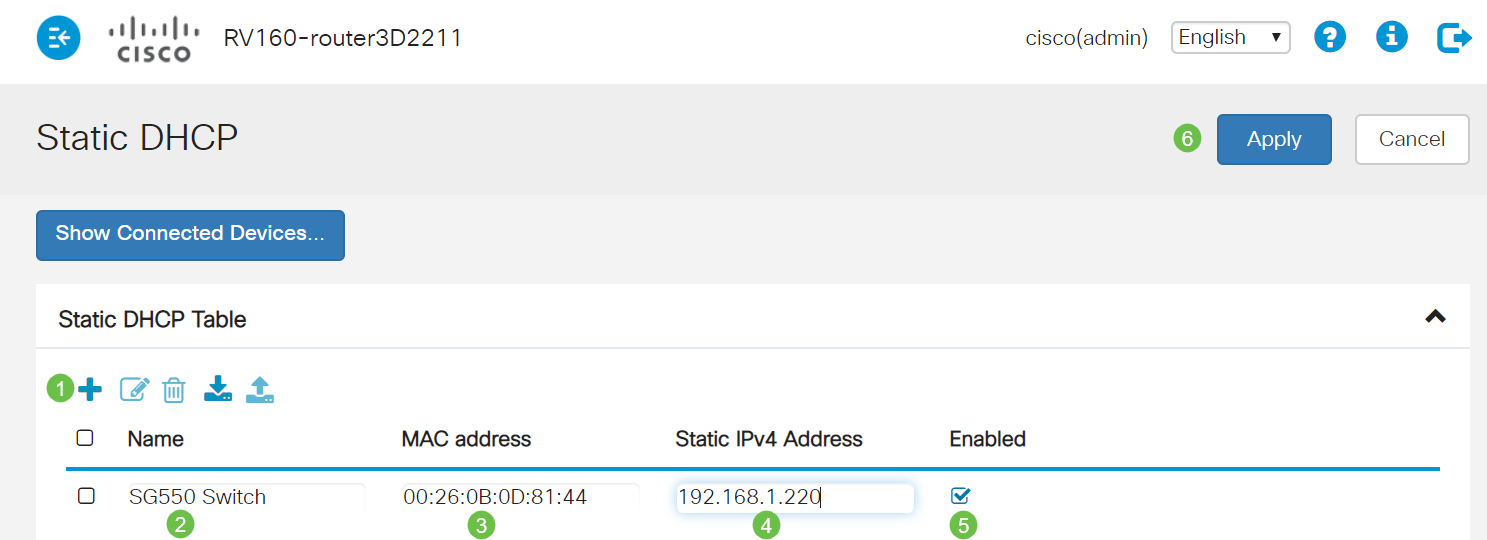
Step 1. Log into the router. Navigate to LAN > Static DHCP.

Step 2. Complete the following steps to assign a static IP.
- Click the plus icon.
- Create a Name that will help you associate the device that is listed, such as SG550 Switch.
- Enter the MAC address of the device.
- Enter the Static IPv4 Address. Make sure you use an address that is not in the DHCP pool.
- Make sure the Enabled box is checked.
- Click Apply.
You will need to repeat this process for each device you would like to assign a static IP address.
Configuring Static IP Address on a Switch
Step 1. Log in to the switch. Navigate to IP Configuration > IPv4 Interface.

Step 2. Click Add.
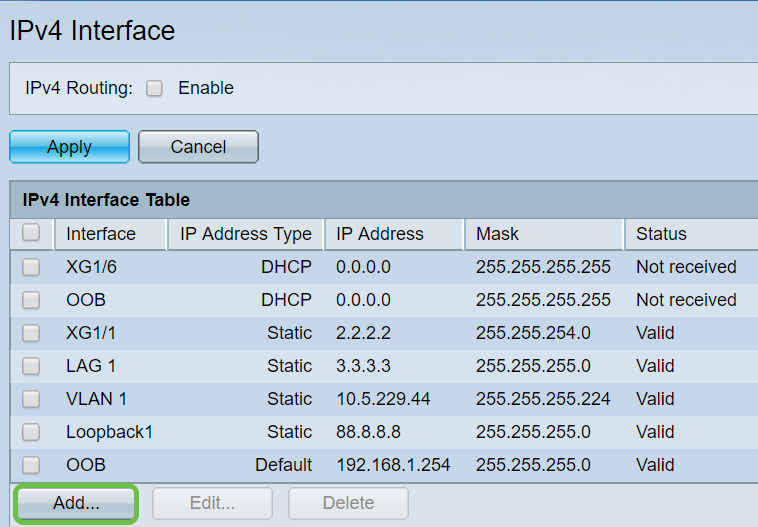
Step 3. Select the Static IP Address radio button. Enter the desired Static IP address and Subnet Mask. Click Apply.

Configuring Static IP Address on a Wireless Access Point (WAP)
Step 1. Log into the WAP. Navigate to LAN > VLAN and IPv4 Address.
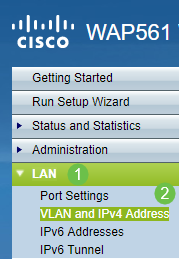
Step 2. Select the Static IP radio button. Enter the desired Static IP address and Subnet Mask. You also need to specify Default Gateway and Domain Name Servers (DNS) server address. Click Save.
Note: Usually both the default gateway and the DNS server are the LAN IP address of the router; however the DNS server for Google, 8.8.8.8, is sometimes utilized here.

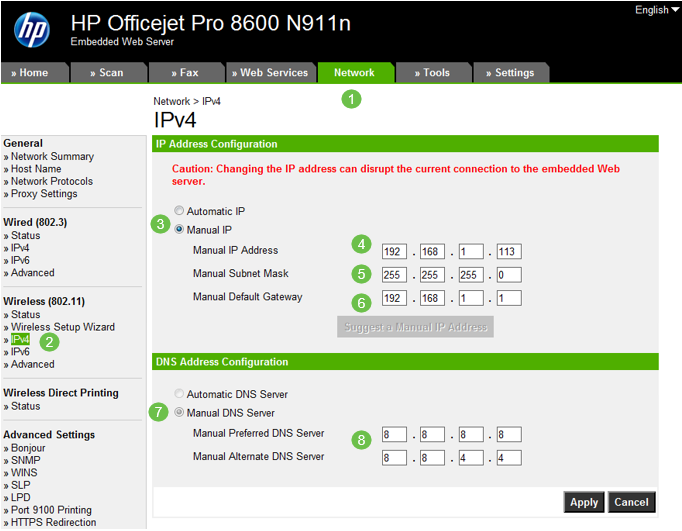
Configuring Static IP Address on a Printer
In this example, you would select Network > IPv4. You would then select the Manual IP radio button, fill in the Manual IP Address, Manual Subnet Mask, and Manual Default Gateway. You would also assign a DNS server. Click Apply.
Note: This printer is not a Cisco product and is not supported by Cisco. These instructions are only provided for general illustration purposes.
Conclusion
There you have it! Now you have a starting off point for IP addressing in your network.
Click on the hyperlinks for more information on the following topics:
- Configure Static Internet Protocol (IP) Address Settings on a Cisco IP Phone 6800, 7800, or 8800 Series Multiplatform Phone
- Setting a Static IPv4 Address on a Switch using the Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- Setting Static IPv4 Addesses on a Switch via Command Line Interface (CLI)
- Creating a Text File to Adjust IP Settings on a Switch