Introduction
This document describes how to install device drivers on the Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) for common operating systems.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Cisco UCS Manager
- Cisco Integrated Management Controller (CIMC)
- Virtual Machine-ware (VMware), Windows Server, or Linux Operating Systems (OS)
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these hardware platforms:
- UCS B Series
- UCS C Series
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
Driver Definition
A device driver is software that is the interface between the OS and the hardware. The device driver translates general OS commands into specialized commands for a particular device, which allows the OS to communicate with hardware devices.
Devices that Require a Driver
Here is a list of hardware devices that require device drivers:
- Ethernet Network Interface Card (ENIC)
- Fibre Channel Network Interface Card (FNIC)
- Redundant Array of Indepent Disks (RAID) Controller
- Motherboard Chipset
- Video Card
- Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
Drivers Versus Firmware
Device drivers are different from firmware. Device driver software is installed on the OS, whereas firmware is lower-level code that is installed on hardware devices. Firmware is stored in non-volatile memory, such as ROM, Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM), or flash memory.
Driver Dependence on Firmware
Device drivers have a strong dependence on the device firmware. Device drivers must be compatible with the firmware level of a hardware device, so that they properly communicate with each other; driver and firmware functionality must match for correct operation to take place.
When Drivers Must be Installed and Updated
Device drivers come pre-installed with operating systems (such as Cisco OEM VMware ESXi images), or they can be manually installed post-OS setup.
Device drivers generally need to be updated after these procedures:
- UCS firmware upgrades
- Major OS upgrades/patches
Driver Versions Required
The UCS Hardware and Software Interoperability Matrix outlines the driver versions that are required for a particular OS, device, and firmware combination.
Warning: The driver versions listed on the matrix have been tested and verified by the Cisco Engineering Quality Assurance team, and it is crucial to install the correct driver; otherwise, unexpected behavior which could lead to network outages.
This example shows that an FNIC driver version of 1.6.0.36 is required for a B200 M4 with a Virtual Interface Card (VIC) 1240 that runs ESXi 6.0 U3, on UCS Release 3.2.2.
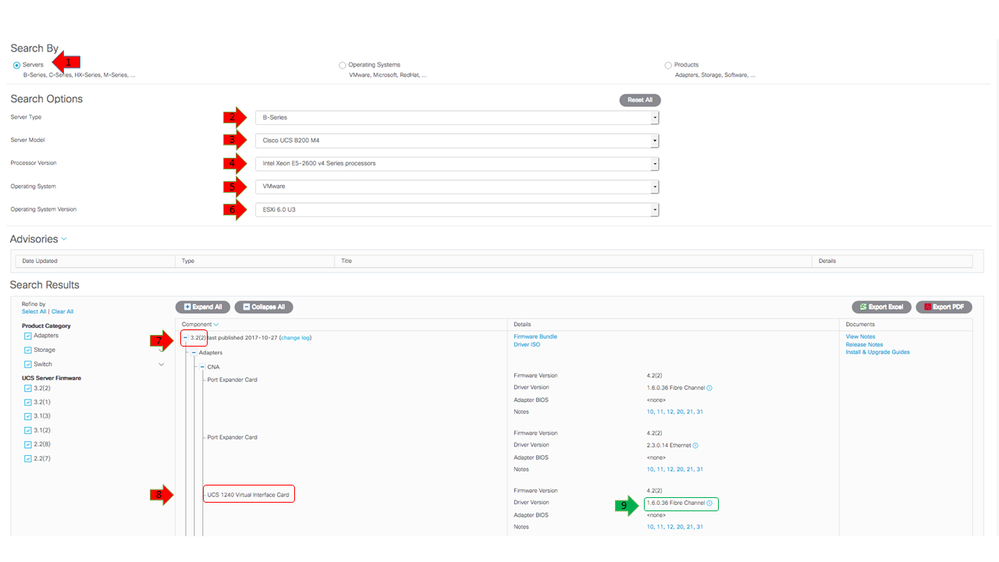
Download the Driver Bundle
Complete these steps in order to download the driver bundle:
- In a web browser, navigate to Cisco Website
- Under Support, click Download Software.
- Click Unified Computing and Servers.
- Choose your server. Cisco UCS drivers are available for both Cisco UCS B-Series Blade servers and Cisco UCS C-Series Rack-Mount.
- Click Unified Computing System (UCS) Drivers.
- Select the bundle you want to download, and click Download Now.
Tip: When you choose which driver bundle to download, it is important to select the driver bundle version that is most similar to the server firmware release. For example, if you run a UCS-B Release 3.2(2b), then VMware driver bundle ucs-bxxx-drivers-vmware.3.2.2.iso is required.
Tip: Most VMware ESXi drivers are downloaded directly from VM Ware, with a search for the driver version. This is often quicker than if you were to download the entire driver bundle.
Identify Server Hardware
Before you select the correct driver, you must identify what hardware devices are installed on the server. This section describes how to find the devices located on the UCS Manager and in the CIMC.
UCS B Series
This example shows how to find the server inventory in UCS Manager. Server 1/1 has two adapter models installed: the VIC 1240.
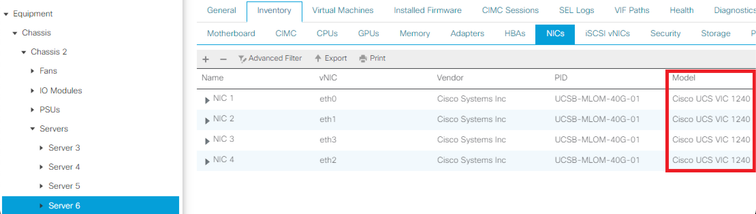
UCS C Series
This example shows how to find the server hardware devices in the CIMC. The server has a Cisco12G ModularSAS HBA RAID controller installed.
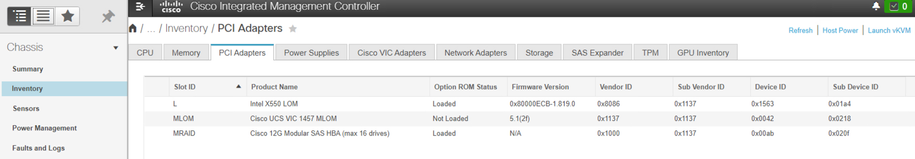
Identify the UCS Firmware Release
Before the correct driver version is selected, the UCS release must be identified. This section describes how to identify the current UCS release installed on the servers.
UCS B Series
In this example, the UCS B Series runs UCS Release 4.1(3h)
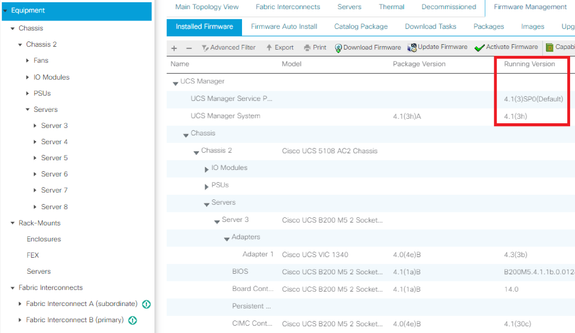
UCS C Series
In this example, the UCS C Series runs UCS Release 4.1(2f).
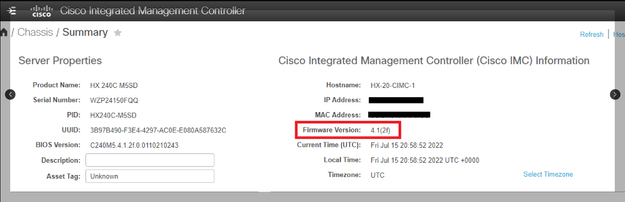
OS Specifics
This section describes how to check driver versions and how to install drivers on common OSs.
VMware ESXi
Use these commands in order to check the current driver versions and VMware build:
Tip: These commands are executed from the ESXi CLI. Secure Shell (SSH) must be enabled before an SSH session is initiated.
| Command |
Description |
| vmware -vl |
Displays the VMware build and patch level. |
| esxcli software profile get |
Displays flavor of install ISO. |
| esxcfg-scsidevs -a |
Lists the hosts HBAs and the associated driver name. |
| esxcfg-nics -l |
Lists the host vmnics and network interface card (NIC) models. |
| ethtool -i vmnicX |
Displays the Ethernet driver used by the specified vmnic. |
| esxcli network nic get -n vmnicX |
Displays the Ethernet driver used by the specified vmnic on ESXi 6.5. |
| vmkload_mod -s fnic |
Displays the host bus adapter (HBA) driver version for the Cisco VIC. |
| vmkload_mod -s enic |
Displays the Ethernet driver version for the Cisco VIC. |
| vmkload_mod -s nenic |
Displays the Ethernet driver version for the Cisco VIC for ESXi 6.5 and later releases. |
| vmkload_mod -s megaraid_sas |
Displays the LSI MegaRAID driver version. |
| vmkload_mod -s lsi_mr3 |
Displays the LSI lsi_mr3 driver version(Native driver on ESXi 6.7). |
| vmkload_mod -s driver_name |
Displays the driver version for a specified driver. |
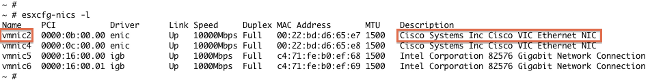
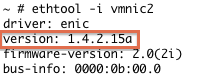
These examples show that vmnic2 uses a Cisco VIC and a driver version of 1.4.2.15a.
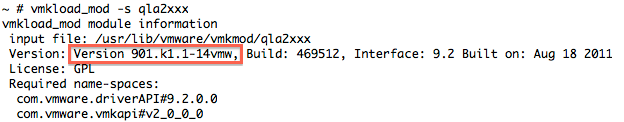
These examples show that the Qlogic Host Bus Adapter (HBA) uses driver qla2xxx Version 901.1k.1-14vmw.

Install the Driver
Complete these steps in order to install the driver:
- Extract the contents of the driver zip file, and identify the *.vib file.
- Use the Datastore Browser in order to upload the *.vib file to an ESXi host datastore.
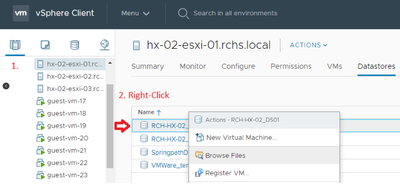
- Enter the host into Maintenance mode.
- Install the driver.
ESXi 5.x/6.x
Use this command in order to install the driver on ESXi Release 5.x/6.x:
esxcli software vib install –v /path/async-driver.vib
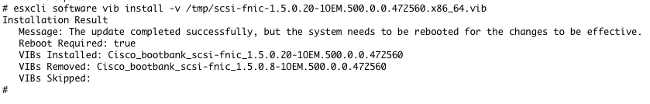
Note: If the drivers require a signature verification, run this command with the --no-sig-check switch. Ensure that you use the full path to the file.
ESXi 4.x
Use this command in order to install the driver on ESXi Release 4.x:
esxupdate --bundle=offline-bundle.zip update
Finish the Installation
After you install the driver with one of the previously mentioned commands, exit Maintenance mode and reboot the host. For more information on how to install drivers, reference the Related Information section at the end of this document.
Useful VMware CLI Commands
Here are some other useful VMware commands that you can use when you install a driver:
Check Maintenance Mode Status
vim-cmd hostsvc/hostsummary | grep -i maintenace
Check for Powered-On VMs
vim-cmd vmsvc/getallvms
Power-Off VMs
vim-cmd vmsvc/power.off <vm id>
Enter Maintenance Mode
vim-cmd hostsvc/maintenace_mode_enter
Exit Maintenance Mode
vim-cmd hostsvc/maintenace_mode_exit
Microsoft Windows Server
This section describes how to install a driver on a Microsoft Windows server.
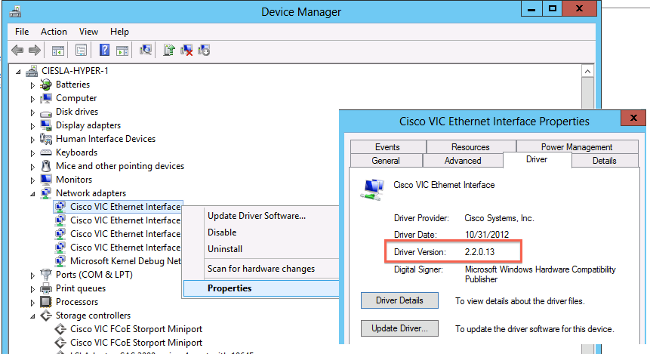
Check Current Driver Version
In order to check the device drivers in Microsoft Windows, use the Device Manager located in the Control Panel.
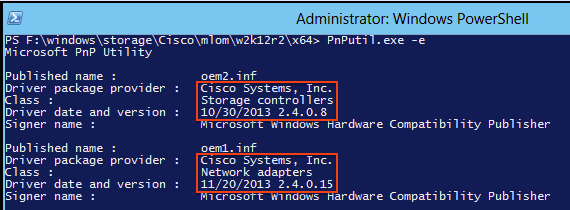
Check Current Driver Version CLI
For Windows, Server Core the Plug-and-Play (PnP) Utility (PNPUtil.exe) is used to check driver versions.
Missing Drivers
Hardware devices with missing drivers are displayed in the Device Manager with a yellow question mark. These devices must be updated with the correct driver in order to prevent unexpected behavior.

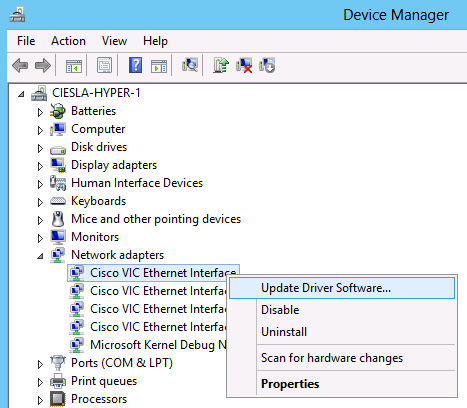
Install the Driver
In order to install or update a driver in Microsoft Windows, right-click the device, and choose Install/Update Driver in order to start the Installation Wizard.
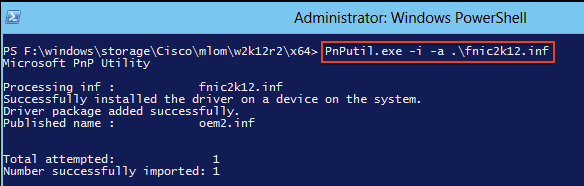
Install the Driver from CLI
The PNPUtil tool can also be used to install drivers from the CLI. The driver ISO bundle can be mounted via the UCS KVM Console Virtual Media.
Useful Windows CLI Commands
| Command |
Description |
| pnputil.exe -e |
List all installed 3rd party drivers. |
| pnputil.exe -a <INF name> |
Install driver. |
| pnputil.exe -d <INF name> |
Delete driver. |
| pnputil.exe -f -d <INF name> |
Force delete driver. |
| |
|
Red Hat and SUSE Linux
This section describes how to install and validate a driver on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES).
SUSE Background Information
Starting with SLES 12 SP1, the Cisco eNIC and usNIC drivers are bundled together into a single RPM (versus being packaged in separate RPMs, as they are for other Linux distributions). Bundling both drivers into a single RPM is required because of how kernel module dependencies are managed in SLES 12 SP1 and later. If you are not using Cisco usNIC functionality (For example, if you have not provisioned any usNIC devices in UCSM / CIMC), the usNIC driver is effectively be ignored.
The eNIC and usNIC drivers have their own distinct version numbers. If you install the cisco-enic-usnic RPM on SLES 12 SP 1 or later, once those drivers are loaded into the running kernel (For example, via rebooting), use cat /sys/module/enic/version and cat /sys/module/usnic_verbs/version to view their respective version numbers. The cisco-enic-usnic RPM has its own distinct version number as well. Because it represents the packaging of the eNIC and usNIC drivers, the RPM version number look similar, but does not reflect the specific version of either driver.
For additional information on the exact driver versions query and review the RPM description section. The query looks similar to the example below:
# rpm -qip cisco-enic-usnic-kmp-default-<RPM_VERSION>.x86_64.rpm
Name : cisco-enic-usnic-kmp-default Relocations: (not relocatable)
...
Summary : Cisco VIC Ethernet NIC drivers
Description :
This RPM contains both the Cisco VIC Linux Ethernet driver (enic.ko, version <ENIC_VERSION>) and
the Cisco Userspace NIC (usNIC) Linux Ethernet driver (usnic_verbs.ko, version <USNIC_VERSION>).
Some Linux distros require both kernel modules to be in the same RPM in order to properly test for
symbol compatibility (because usnic_verbs.ko depends on enic.ko) when installing into post-GA
upgrade kernels.
Verify Current Driver Versions and OS Release
Here is a list of commands used in order to check the current driver version and OS release:
| Command |
Description |
| modinfo driver_name |
Displays driver version for the specified driver that is loaded (by default) at next reboot. |
| modinfo /path/to/driver_name.ko |
Displays driver version for the specified driver kernel object file. |
| cat /sys/module/enic/version |
Displays the Ethernet driver version currently loaded in the running Linux kernel for the Cisco VIC adapter. |
| cat /sys/module/fnic/version |
Displays the FC NIC driver version currently loaded in the running Linux kernel for the Cisco VIC adapter. |
| cat /sys/module/megaraid_sas/version |
Displays the LSI MegaRAID driver version currently loaded in the running Linux kernel. |
| lsmod -l |
Lists currently-loaded drivers in the kernel. |
| cat /etc/redhat-release |
Shows the RHEL release (for RHEL 6.x and earlier). |
| cat /etc/SuSE-release |
Shows the SUSE release (for SLES 11 SP3 and earlier). |
| cat /etc/os-release |
Shows the RHEL release (for RHEL 7.x and later, and SLES 11 SP4 and later). |
| uname -a |
Shows kernel related information. |
Note: Be aware that the command modinfo [ driver name ] shows the module information about the driver that is loaded upon next reboot. This is not necessarily the same driver version currently loaded in the running kernel. Review cat/sys/module/DRIVER_NAME/version to validate the driver version loaded in the currently running kernel, and/or use the command modinfo [ /path/to/driver.ko ] to validate the module info for a specific driver kernel object file.
Tip: Refer to the Driver Name Reference Table located in the Appendix for examples of other common driver names.
This example shows that an ENIC driver version of 3.2.210.18-738.12 bundled in the cisco-enic-usnic RPM package 3.2.272.23 is installed on SLES 15 GA.
# cat /etc/os-release
NAME="SLES"
VERSION="15"
VERSION_ID="15"
PRETTY_NAME="SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15"
ID="sles"
ID_LIKE="suse"
ANSI_COLOR="0;32"
CPE_NAME="cpe:/o:suse:sles:15"
# rpm -qa | grep enic
cisco-enic-usnic-kmp-default-3.2.272.23_k4.12.14_23-738.12.x86_64
# modinfo enic | grep ^version
version: 3.2.210.18-738.12
# cat /sys/module/enic/version
3.2.210.18-738.12
Install the Driver
Drivers in RHEL and SLES are installed using the Redhat Package Manager (RPM). Use this command in order to install the driver:
# rpm -ihv RPM_filename.x86_64.rpm

Tip: When you install drivers in Linux, ensure that you review the README files associated with the driver if available. You can look at the contents of the RPM to see where its associated README file was installed ( rpm -qp kmod-enic). Some RPM driver packages have dependencies on other modules, and require installation of additional RPM packages. The README files contain full instructions on how to install the driver file.
Appendix
Driver Name Reference Table
This table shows the driver names or prefixes for common drivers.
| Command |
Description |
| enic |
Cisco VIC Ethernet NIC |
| fnic |
Cisco VIC FC NIC |
| qle or qla |
Qlogic adapter |
| lpfc |
Emulex HBA (light pulse) |
| be2net |
Emulex Ethernet NIC |
| igb or ixgbe |
Intel NICs |
| bnx |
Broadcom adapter |
| megaraid |
LSI MegaRAID |
| megasr |
Embedded SW RAID |
| nenic |
Cisco VIC Ethernet NIC for ESXi 6.5 |
Related Information


















 Feedback
Feedback