VPN Client FAQ
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document answers frequently asked questions about the Cisco VPN Client.
Note: Here are the naming conventions for the various VPN clients:
-
Cisco Secure VPN Client versions 1.0 through 1.1a only
-
Cisco VPN 3000 Client versions 2.x only
-
Cisco VPN Client 3.x and later only
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Download VPN Client Software
Q. Where can I download the Cisco VPN Client software?
A. You must log in and possess a valid service contract in order to access the Cisco VPN Client software. Cisco VPN Client software can be downloaded from the Cisco Download Software ( registered customers only) page. If you do not have a valid service contract associated with your Cisco.com profile, you cannot log in and download the VPN client software.
In order to obtain a valid service contract, you can:
Contact your Cisco Account team if you have a Direct Purchase Agreement.
Contact a Cisco Partner or Reseller in order to purchase a service agreement.
Use the Profile Manager ( registered customers only) in order to update your Cisco.com profile and request association to a service agreement.
Q. The Cisco VPN Client download area appears to be empty. Why?
A. When you reach the VPN client area of the Software Center ( registered customers only) be sure that you select the downloads area for your desired operating system in the middle of the page.
Q. How can I disable the Stateful Firewall Feature during the installation of the Cisco VPN Client?
A. For VPN Client versions prior to 5.0:
Refer to the Documentation Changes section of the VPN Client Rel 4.7 Release Notes in order to learn about the two topics "Using MSI to Install the Windows VPN Client without Stateful Firewall" and "Using InstallShield to Install the Windows VPN client without Stateful Firewall".
For VPN client versions after 5.0:
Beginning with Cisco VPN Client release 5.0.3.0560, an MSI installation flag was added to avoid the installation of the guild in firewall files:
msiexec.exe /i vpnclient_setup.msi DONTINSTALLFIREWALL=1
Refer to Bypassing Installation of Firewall Files When Stateful Firewall Is Not Required section for more information regarding this.
Q. How do I uninstall or upgrade the Cisco VPN Client?
A. Refer to the Removing a VPN Client Version Installed with MSI Installer for information on how to manually uninstall (InstallShield) and then upgrade the Cisco VPN Client Version 3.5 and later for Windows 2000 and Windows XP.
The Cisco VPN Client for Windows 2000 and Windows XP software can securely download updates and new versions automatically through a tunnel from a VPN 3000 Concentrator or other VPN server that can provide notifications. The minimum prerequisite for this is remote users must have the VPN Client for Windows 4.6 or greater installed on their PCs to use the automatic update feature.
With this feature, called autoupdate, users do not need to uninstall an old version of the software, reboot, install the new version, and then reboot again. Instead, an administrator makes updates and profiles available on a web server and when a remote user starts up the VPN Client, the software detects that a download is available and automatically gets it. For more information, refer to Managing autoupdates and How Automatic Update Works.
For information about how to configure client update on a Cisco ASA Series 5500 Adaptive Security Appliance using ASDM, refer to Configuring Client Software Update Using ASDM.
Q. I want to customize the VPN clients for Vista. I realize that, with the new VPN client version for Vista, there is no file such as oem.mst. How can we customize the new VPN client versions (5.x), or where I can find this file?
A. The MST file is no longer provided with the VPN Client, but you can download it from the Download Software ( registered customers only) page:
Filename: Readme and MST for installation on the international version of Windows.
Operating System
Q. Does Cisco provide a VPN client for Windows Vista?
A. The new release Cisco VPN Client 5.0.07 supports the Windows Vista on both x86 (32-bit) and x64. Refer to the 5.0.07.0240 Release Notes for more information.
Note: Cisco VPN Client is supported only on Windows Vista clean install, which means that an upgrade of any Windows operating system to Windows Vista is not supported with the VPN client software. You must freshly install the Windows Vista and then install the Vista VPN Client software.
Note: If you do not have a valid service contract associated with your Cisco.com profile, you cannot log in and download the VPN Client software. See Download VPN Client Software for more information.
Tip: The Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client is now available for Windows operating systems, which includes Vista 32 and 64-bit. The AnyConnect client supports SSL and DTLS. It does not support IPsec at this time. Additionally, AnyConnect is available only for use with a Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance that runs version 8.0(2) or later. The client can also be used in weblaunch mode with IOS appliances running version 12.4(15)T. VPN 3000 is not supported.
The Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client and ASA 8.0 can be obtained from the Software Center ( registered customers only) . Refer to the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Release Notes for more information on the AnyConnect Client. Refer to the Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliances Release Notes for more information on ASA 8.0.
Note: If you do not have a valid service contract associated with your Cisco.com profile you cannot log in and download the AnyConnect VPN Client or ASA software. See Download VPN Client Software for more information.
Q. How do I set up a PPTP connection from a Microsoft Windows PC?
A. Setup depends on the version of Microsoft Windows that you run. You should contact Microsoft for specific information. Here are setup instructions for some of the common versions of Windows:
Windows 95
- Install Msdun13.exe.
- Choose Programs > Accessories > Dial Up Networking.
- Create a new connection named "PPTP."
- Select the VPN Adapter as the device for the connection.
- Enter the IP address of the public interface of the switch, and click Finish.
- Go back to the connection that you have just created, right-click, and choose Properties.
- Under Allowed Network Protocols, at minimum, uncheck netbeui.
- Configure the Advanced Options setting:
- Leave default settings to allow the switch and client to auto-negotiate the authentication method.
- Enable Require Encrypted Password to force Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) authentication.
- Enable Require Encrypted Password and Require Data Encryption to force MS-CHAP authentication.
Windows 98
- Complete these steps in order to install the PPTP feature:
- Choose Start > Settings > Control Panel > Add New Hardware, and click Next.
- Click Select from List, choose Network Adapter, and click Next.
- Choose Microsoft in the left panel and Microsoft VPN Adapter in the right panel.
- Complete these steps in order to configure the PPTP feature:
- Choose Start > Programs > Accessories > Communications > Dial Up Networking.
- Click Make new connection, and choose Microsoft VPN Adapter for Select a device. The VPN Server IP address= 3000 tunnel endpoint.
- Complete these steps in order to change the PC to also allow Password Authentication Protocol (PAP):
Note: The Windows 98 default authentication is to use password encryption (CHAP or MS-CHAP).
- Choose Properties > Server types.
- Uncheck Require encrypted password. You can configure data encryption (Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption [MPPE] or no MPPE) in this area.
Windows 2000
- Choose Start > Programs > Accessories > Communications > Network and Dialup connections.
- Click Make new connection, and then click Next.
- Choose Connect to a private network through the Internet and Dial a connection prior (do not select this if you have a LAN), and click Next.
- Enter the host name or IP address of tunnel endpoint (3000).
- If you need to change the password type, choose Properties > Security for the connection > Advanced. The default is MS-CHAP and MS-CHAP v2 (not CHAP or PAP). You can configure data encryption (MPPE or no MPPE) in this area.
Windows NT
Refer to Installing, Configuring, and Using PPTP with Microsoft Clients and Servers
.
Q. What operating system versions support the Cisco VPN Client?
A. Support for additional operating systems is constantly added for the VPN client. Refer to System requirements in the release notes for the VPN Client 5.0.07 to determine this, or refer to Cisco Hardware and VPN Clients Supporting IPsec/PPTP/L2TP.
Notes:
The VPN Client includes support for dual-processor and dual-core workstations for Windows XP and Windows Vista.
The Windows VPN Client Release 4.8.00.440 was the final version that officially supported the Windows 98 operating system.
The Windows VPN Client Release 4.6.04.0043 was the final version that officially supported the Windows NT operating system.
Cisco VPN Client ver 5.0.07 supports Windows Vista and Windows 7 in both the x86 (32-bit) and x64 (64-bit) editions.
Cisco VPN Client does support Windows XP 32 bit only, but Windows XP 64 bit is not supported.
Note: Windows Vista 32 bit support was available in all 5.x releases. Cisco VPN client version 5.0.07 added the 64 bit support.
Q. Do I need to be an administrator on Windows NT/2000 machines in order to load the VPN client?
A. Yes, you must have administrator privileges in order to install the VPN client on Windows NT and Windows 2000 because these operating systems require administrator privileges to bind to the existing network drivers or to install new network drivers. The VPN client software is networking software. You must have administrator privileges to install it.
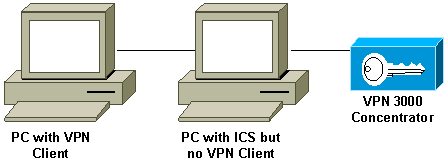
Q. Can the Cisco VPN Client work with Microsoft Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) installed on the same machine?
A. No, the Cisco VPN 3000 Client is not compatible with Microsoft ICS on the same machine. You must uninstall ICS before you can install the VPN client. Refer to Disabling ICS when Preparing to Install or Upgrade to Cisco VPN Client 3.5.x on Microsoft Windows XP for more information.
Although having the VPN client and ICS on the same PC does not work, this arrangement does work.
Q. My VPN client seems to connect only to certain addresses. I run Windows XP. What should I do?
A. Verify that the built-in firewall in Windows XP is disabled.
Q. Is the Cisco VPN Client compatible with the Windows XP stateful firewall?
A. This issue has been resolved. View Cisco Bug ID CSCdx15865 ( registered customers only) in Bug Toolkit for more details.
Q. When I install the VPN client on Windows XP and on Windows 2000, is the multi-user interface disabled?
A. The installation disables the welcome screen and the fast user switching. View Cisco Bug ID CSCdu24073 ( registered customers only) in Bug Toolkit for more details.
Q. How can I make the VPN client for Linux move to the background after execution? If I initiate a connection such as vpnclient connect foo, I get in, but the shell is returned.
A. After signing on, type:
^Z
bg
Q. When I install the Cisco VPN Client on Windows XP Home Edition, the task bar is not visible. How do I undo this?
A. Choose Control Panel > Network Connections > Remove Network Bridge to adjust this setting.
Q. When I attempt to install Linux VPN Client on RedHat 8.0, I get an error that states the module cannot be loaded because the module was compiled with GCC 2 and the kernel was compiled with GCC 3.2. What should I do?
A. This is because the new release of RedHat has a newer version of the GCC compiler (3.2+), which causes the current Cisco VPN Client to fail. This issue has been fixed and is available in Cisco VPN 3.6.2a. View Cisco Bug ID CSCdy49082 ( registered customers only) in Bug Toolkit for more details or download the software from the VPN Software Center ( registered customers only) .
Q. Why does the software disable Fast User Switching when I install VPN client 3.1 on Windows XP?
A. Microsoft automatically disables Fast User Switching in Windows XP when a GINA.dll is specified in the registry. The Cisco VPN Client installs the CSgina.dll to implement the "Start Before Login" feature. If you need Fast User Switching, then disable the "Start Before Login" feature. Registered users can get more information in Cisco Bug ID CSCdu24073 ( registered customers only) in Bug Toolkit.
Q. Does the IPsec VPN client support the Start Before Logon (SBL) feature on Windows 7?
A. The SBL feature is not supported on IPsec VPN clients on Windows7. It is supported with the AnyConnect VPN Client.
Error Messages
Q. When I install the Cisco VPN Client 4.x, I receive this error message: Warning 201: The necessary VPN sub-system is not available. You can not connect to the remote VPN server
A. This issue can be caused by firewall packages installed on your VPN client computer. In order to avoid this error message, ensure that no firewall or antivirus programs are installed or running on your PC at the time of installation.
Q. I upgraded to Mac OS X 10.3 (known as "Panther"), but now my Cisco VPN Client 4.x displays this error messages: Secure VPN Connection terminated locally by the Client Reason: Unable to contact the security gateway
A. You must add UseLegacyIKEPort=0 to the profile (.pcf file) found in the /etc/CiscoSystemsVPNClient/Profiles/ directory for the Cisco VPN Client 4.x to work with Mac OS X 10.3 ("Panther").
Q. When I attempt to unistall the VPN client, I receive this error message: Error msg: failed to find the uninstall file... What does this error message mean and how can I successfully complete the uninstallation?
A. Check the networking Control Panel to ensure that the Deterministic NDIS Extender (DNE) was not installed. Also choose Microsoft > Current Version > Uninstall in order to check for the uninstall file. Remove the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\{5624C000-B109-11D4-9DB4-00E0290FCAC5} file, and retry the uninstallation.
Q. I cannot install the VPN client on Windows 2000 Professional. I receive this error: An installation support file could not be installed. Catastrophic Failure. What should I do?
A. Remove the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Currentversion\Uninstall key. Then reboot your computer, and reinstall the VPN client.
Note: In order to find the correct key for the Cisco VPN Client software under the path HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Currentversion\Uninstall\<key to be determined>, go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Cisco Systems\, and click VPN Client. In the right-hand window, view the Uninstall Path (under the Name column). The corresponding Data column displays the VPN client key value. Take note of this key, go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Currentversion\Uninstall\, select the determined key, and delete it.
Refer to Initialization Error Troubleshooting
and refer to Cisco bug ID CSCdv15391 ( registered customers only) in Bug Toolkit for more information.
Q. When I attempt to install Linux VPN Client on RedHat 8.0, I receive an error that states the module cannot be loaded because the module was compiled with GCC 2 and the kernel was compiled with GCC 3.2. What should I do?
A. This issue occurs because the new release of RedHat has a newer version of the GCC compiler (3.2+), which causes the current Cisco VPN Client to fail. This issue has been fixed and is available in Cisco VPN 3.6.2a. View Cisco bug ID CSCdy49082 ( registered customers only) in Bug Toolkit for more details or download the software from the VPN Software Center ( registered customers only) .
Q. I get a "peer no longer responding" error message when my Linux Client 3.5 tries to establish an IPsec connection to a PIX or to a VPN 3000 Concentrator. What should I do?
A. The symptom of this problem is that the Linux Client seems to try to connect, but it never gets a response from the gateway device.
The Linux OS has a built-in firewall (ipchains) that blocks UDP port 500, UDP port 1000, and Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) packets. Since the firewall is on by default, you either have to disable the firewall or open up the ports for IPsec communication for both inbound and outbound connections to fix the problem.
Q. I receive a kernel extension error when I try to run Cisco VPN 5000 5.2.2 Client on Mac OS X 10.3. What should I do?
A. As stated in the product release notes, the Cisco VPN 5000 Client is supported up to version 10.1.x and, therefore, is not supported on version 10.3. It is possible to make the VPN client work when you reset the permissions on two of the installed files after you run the install script. Here is an example:
Note: This configuration is not supported by Cisco.
sudo chown -R root:wheel /System/Library/Extensions/VPN5000.kext sudo chmod -R go-w /System/Library/Extensions/VPN5000.kext
Q. I am unable to install the new version of the Cisco VPN Client. When I install, I receive one of these error messages: "Error DNEinst execution error while installing DNE, return code -2146500093" or "InstallDNE Error: DNEinst execution error while installing DNE, returncode -2147024891." This issue occurs when I installed the Deterministic Network Enhancer.
A. Install the latest DNE upgrade from Deterministic Networks
.
Q. I get these logs for the Cisco VPN Client when I make a connection:
208 15:09:08.619 01/17/08 Sev=Debug/7 CVPND/0x63400015
Value for ini parameter VAEnableAlt is 1.
209 15:09:08.619 01/17/08 Sev=Warning/2 CVPND/0xE3400003
Function RegOpenKey failed with an error code of 0x00000002(WindowsVirtualAdapter:558)
210 15:09:08.619 01/17/08 Sev=Warning/3 CVPND/0xE340000C
The Client was unable to enable the Virtual Adapter because it could not open the device.
208 15:09:08.619 01/17/08 Sev=Debug/7 CVPND/0x63400015 Value for ini parameter VAEnableAlt is 1. 209 15:09:08.619 01/17/08 Sev=Warning/2 CVPND/0xE3400003 Function RegOpenKey failed with an error code of 0x00000002(WindowsVirtualAdapter:558) 210 15:09:08.619 01/17/08 Sev=Warning/3 CVPND/0xE340000C The Client was unable to enable the Virtual Adapter because it could not open the device.
A. It is a fairly generic error message, which usually requires manual uninstallation of the client. Follow the instructions in this link. Removing a VPN Client Version Installed with MSI Installer.
Once you have done the uninstall, make sure you reboot. Then reinstall the client. Make sure you are logged on as a user that has admin rights on the local machine.
Q. When I attempt to connect the Cisco VPN Client on a Mac OS, I receive this error message: Error 51- Unable to communication with the VPN subsystem. How can I resolve this issue?
A. The issue can be resolved if you restart the service after you close the VPN client in this way:
To stop:
sudo kextunload -b com.cisco.nke.ipsecTo start:
sudo kextload /System/Library/Extensions/CiscoVPN/CiscoVPNAlso verify the following running on the same machine where the VPN client is installed and disable the same.
Any virtual software (such as, VMWare Fusions, Parallels, crossovers).
Any antivirus/firewall software.
Compatibility of the VPN client with the 64-bit operating system; refer to the Cisco VPN Client Release Notes.
Q. I get the "Reason 442: failed to enable virtual adapter" error. How can I resolve this error?
A. The Reason 442: failed to enable virtual adapter error appears after Vista reports that a duplicate IP address is detected. Subsequent connections fail with the same message, but Vista does not report that a duplicate IP address is detected. Refer to Duplicate IP Address Triggers Error 442 on Windows Vista for more information about how to resolve this issue.
Q. When I install the Cisco VPN Client, the Deterministic Network Enhancer Add Plugin Failed error is received. How is this error resolved?
A. Installing the DNE adapter might resolve the issue. It is better to use the Installshield version for installation instead of MSI.
Q. I received this error: Reason 442: failed to enable virtual adapter. How can I resolve this issue?
A. This error appears after Windows 7 and Windows Vista reports a duplicate IP address detected. Subsequent connections fail with same message, but the OS does not report that the duplicate IP address is detected. Refer to Duplicate IP Address Triggers Error 442 on Windows 7 and Vista for more information about how to resolve this issue.
Q. When I try to launch the VPN Client 4.9 for MAC OS 10.6, I receive this error: Error 51: Unable to communicate with the vpn subsystem. How to resolve this issue?
A. This issue occurs because 64-bit support is not available with Cisco VPN client for MAC OS release 4.9. As a workaround, you can boot in 32-bit kernel mode. For more information, refer to Cisco Bug ID CSCth11092 ( registered customers only) and Cisco VPN client for MAC OSX release notes.
Third-Party Compatability
Q. Is the Nortel Client compatible with the Cisco VPN 3000 Concentrators?
A. No. The Nortel Client cannot connect to the Cisco VPN 3000 Concentrator.
Q. Can I have VPN clients from other vendors, such as the Nortel Contivity VPN Client, installed simultaneously with the Cisco VPN Client?
A. No. There are known issues when multiple VPN clients are installed on the same PC.
Q. Are Cisco VPN Clients supported with third-party VPN concentrators?
A. Cisco VPN Clients are not supported with third-party VPN concentrators.
Authentication
Q. How do Cisco VPN Clients versions 1.1 and 3.x internally store digital certificates (X.509v3)?
A. The Cisco VPN Client 1.1 has its own certificate store. The Cisco VPN Client 3.x can either store certificates in the Microsoft store using Common-Application Programming Interface (CAPI), or it can store them in Cisco's own store (RSA Data Security).
Q. Can I have the same group name and user name on the VPN concentrator?
A. No, group name and user name cannot be the same. This is a known issue, found in software versions 2.5.2 and 3.0, and integrated into 3.1.2. View Cisco bug ID CSCdw29034 ( registered customers only) in Bug Toolkit for more information.
Q. Are full-challenge cards such as the Defender supported on the Cisco VPN Client to PIX?
A. No, cards of this type are not supported.
VPN Client Software Version
Q. What happened to the "Set MTU Utility" option that was in the Cisco VPN Client versions 2.5.2 and earlier?
A. The Cisco VPN Client now adjusts the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) size. The Set MTU Utility option is no longer a required installation step. The Set MTU option is used primarily for troubleshooting connectivity problems. The path to select the SetMTU option for a Windows machine is Start > Programs > Cisco Systems VPN Client > SetMTU. For more information on the SetMTU option and setting this option in other operating systems, refer to Changing MTU size through SetMTU option.
Q. What are the languages supported on the Cisco VPN Client GUI versions later than 4.0?
A. The languages supported on the Cisco VPN Client GUI versions later than 4.0 are Canadian, French, and Japanese.
Q. What personal firewalls are supported with the Cisco VPN Client?
A. To provide a higher level of security, the VPN Client can either enforce the operation of a supported firewall or receive a pushed down stateful firewall policy for Internet bound traffic.
Currently, the VPN Client 5.0 supports the following personal firewalls:
BlackIce Defender
Cisco Security Agent
Sygate Personal Firewall
Sygate Personal Firewall Pro
Sygate Security Agent
ZoneAlarm
ZoneAlarmPro
Starting in version 3.1, a new feature is added to the VPN 3000 Concentrator that detects what personal firewall software remote users have installed and prevents the users from connecting in the absence of the appropriate software. Choose Configuration > User Management > Groups > Client FW, and click the tab for the group to configure this feature
For more information about the enforcement of firewall policy on a Cisco VPN Client machine, refer to Firewall Configuration Scenarios.
Q. Are there connectivity issues when using the Cisco VPN Client 3.x with AOL 7.0?
A. The Cisco VPN Client does not work with AOL 7.0 without the use of split tunneling. View Cisco bug ID CSCdx04842 ( registered customers only) in Bug Toolkit for more details.
VPN Client Software Configuration
Q. Why does the Cisco VPN Client disconnect after 30 minutes? Can I extend this time period?
A. If there is no communication activity on a user connection during this 30-minute period, the system terminates the connection. The default idle timeout setting is 30 minutes, with a minimum allowed value of 1 minute and a maximum allowed value of 2,147,483,647 minutes (more than 4,000 years).
Choose Configuration > User Management > Groups, and choose the appropriate group name to modify the idle timeout setting. Choose Modify Group, click the HW Client tab, and type the desired value in the User Idle Timeout field. Type 0 in order to disable timeout and allow an unlimited idle period.
Q. Can the Cisco VPN Client be deployed with all the parameters preconfigured?
A. If the vpnclient.ini file is bundled with the VPN Client software when it is first installed, it automatically configures the VPN Client during installation. You can also distribute the profile files (one .pcf file for each connection entry) as preconfigured connection profiles for automatic configuration. To distribute preconfigured copies of the VPN Client software to users for installation, complete these steps:
Copy the VPN Client software files from the distribution CD-ROM into each directory where you created an vpnclient.ini (global) file and separate connection profiles for a set of users.
Note: For the Mac OS X platform, preconfigured files are placed in the Profiles and Resources folders before the VPN Client is installed. The vpnclient.ini file is placed in the installer directory. You must place custom vpnclient.ini files in the VPN Client Installer directory at the same level as the Profiles and Resources folders. See Chapter 2 of the VPN Client User Guide for Mac OS X for more information
Prepare and distribute the bundled software. CD-ROM or network distribution. Be sure the vpnclient.ini file and profile files are in the same directory with all the CD-ROM image files. You can have users install from this directory through a network connection; or you can copy all files to a new CD-ROM for distribution; or you can create a self-extracting ZIP file that contains all the files from this directory, and have users download it, and then install the software.
Supply users with any other necessary configuration information and instructions. See Chapter 2 of the VPN Client User Guide for your platform.
Q. It seems like the Cisco VPN Client has a conflict with my NIC card. How should I troubleshoot this?
A. Make sure that you run the latest drivers on the NIC card. This is always recommended. If possible, test to see if the problem is specific to the operating system, PC hardware, and other NIC cards.
Q. How do I automate the Cisco VPN Client connection from Dial-Up Networking?
A. Choose Options > Properties > Connections, and have the Cisco VPN Client pull down a Dial-Up Networking phone book entry in order to fully automate the dial-up into the VPN connection.
Q. How do I configure the Cisco VPN 3000 Concentrator to notify remote users for VPN client update?
A. You can notify VPN Client users when it is time to update the VPN Client software on their remote systems. Refer to Notifying Remote Users of a Client Update for a step-by-step approach. Ensure that you type the release information as "(Rel)", as noted in step 7 of the process.
Q. What can cause a delay before the Cisco VPN Client appears, specifically when the "Start Before Logon" option is enabled?
A. The Cisco VPN Client is in fall back mode. This contributes to the delay. In fallback mode, the VPN Client performs differently when start before logon is in use. When operating in fallback mode, the VPN Client does not check to see if the necessary Windows services have started. As a result, the VPN connection could fail if initiated too quickly.Uninstall the Cisco VPN Client, and remove the offending applications to allow startup without being in "fall back" mode. Then reinstall the Cisco VPN Client. For more information on fallback mode, please refer to Start before Logon.
View Cisco bug IDs CSCdt88922 ( registered customers only) and CSCdt55739 ( registered customers only) in Bug Toolkit for more information.
Q. I need to understand the difference between ipsecdialer.exe and vpngui.exe. Why is vpngui.exe installed in STARTUP in my Windows XP, but I still have to manually start ipsecdialer in order to reach my companies resources? And (apart from the size) these programs seem to trigger the same thing: a VPN logon to my company network.
A. The ipsecdialer.exe was the original launching mechanism for the Cisco VPN Client version 3.x. When the GUI was changed in the 4.x versions, a new executable called vpngui.exe was created. The ipsecdialer.exe file was carried forward in name only for backward compatibility and just launches the vpngui.exe. This is the reason you could see the difference in the file size.
So when you downgrade from version 4.x to version 3.x of the Cisco VPN Client, you need the ipsecdialer.exe file to launch this.
Q. Can I safely remove the startup VPN icon? Why is it needed?
A. The Cisco VPN Client in the startup folder supports the "Start Before Logon" feature. If you do not use the feature, then you do not need it in the startup folder.
Q. Why is "user_logon" added and not at the ipsecdialer.exe shortcut? What is the purpose of "user logon"?
A. The "Start Before Logon" feature requires the "user_logon," but a normal launch of the Cisco VPN Client by the user does not need this.
NAT/PAT Problems
Q. I am experiencing problems with only one VPN client (for releases 3.3 and earlier) being able to connect through a Port Address Translation (PAT) device. What can I do to alleviate this problem?
A. There was a bug in several Network Address Translation (NAT)/PAT implementations that causes ports less than 1024 not to be translated. On the Cisco VPN Client 3.1, even with NAT transparency enabled, the Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) session uses UDP 512. The first VPN client goes through the PAT device and keeps source port 512 on the outside. When the second VPN client connects, port 512 is already in use. The attempt fails.
There are three possible workarounds.
Fix the PAT device.
Upgrade the VPN clients to 3.4, and use TCP encapsulation.
Install a VPN 3002 that replaces all VPN clients.
Q. Can two laptops be connected with the Cisco VPN Client from the same location?
A. Two clients can connect to the same head end from the same location as long as the clients are not both behind a device performing PAT such as a SOHO router/firewall. Many PAT devices can map ONE VPN connection to a client behind it, but not two. In order to allow two VPN clients to connect from the same location behind a PAT device, enable some sort of encapsulation such as NAT-T, IPSec over UDP, or IPsec over TCP at the head end. Generally, NAT-T or another encapsulation should be enabled if ANY NAT device is between the client and the head end.
Miscellaneous
Q. When I connect to the network in the office using my laptop and then take the laptop home, I have trouble connecting to the VPN 3000 Concentrator from home. What is the problem?
A. The laptop might be retaining the routing information from the LAN connection. Refer to VPN Clients with Microsoft Routing Problems for information about how to resolve this issue.
Q. How can I tell if a VPN client is connected to the VPN concentrator?
A. Check the registry key named HKLM\Software\Cisco Systems\VPN Client\TunnelEstablished. If a tunnel is active, the value is 1. If no tunnel is present, the value is 0.
Q. I have problems with the NetMeeting connection from a PC behind a VPN Concentrator to a VPN client, but the connection works when I run from the PC to a VPN client behind a VPN Concentrator. How can I resolve this?
A. Follow the appropriate step(s) listed here in order to control the connection settings:
On the main drive of the PC, choose Program Files > Cisco Systems > VPN Client > Profiles. Right-click the profile that you use, and choose Open With in order to open the profile in a text editor (such as Notepad). (When you choose the program to use, be sure to uncheck the box that says Always use this program to open these files.) Locate the profile parameter for ForcekeepAlives, and change the value from 0 to 1, then save the profile.
or
For the VPN client, choose Options > Properties > General, and enter a value for the "Peer response timeout", as shown in this sample window. You can specify a timeout sensitivity of 30 seconds to 480 seconds.
or
For the VPN concentrator, choose Configuration > User Management > Groups > modify group . On the IPsec tab, choose the option for IKE Keepalives, as shown in this sample window.
The Dead Peer Detection (DPD) interval varies based on the sensitivity setting. Once a response is not received, it moves into a more aggressive mode, and sends packets every five seconds until the peer response threshold is met. At that time, the connection is torn down. You can disable the keepalives, but if your connection does actually drop, you need to wait for the timeout. Cisco recommends that you set the sensitivity value very low initially.
Q. Does the Cisco VPN Client support double authentication?
A. No. Double authentication is not supported on the Cisco VPN Client.
Q. How can I configure the Cisco VPN Client to connect in main mode, instead of aggressive mode?
A. You must use digital signatures (certificates) in order to allow Cisco VPN Client to connect in main mode. There are 2 methods to accomplish this:
Obtain CA certificates from the third-party certificate provider (for example, Verisign or Entrust) on the router and all the Cisco VPN Clients. Enroll the identity certificates from the same CA server and use digital signatures as a way to authenticate between the Cisco VPN Client and the router. For more information about this configuration, refer to Configuring IPSec Between Cisco IOS Routers and Cisco VPN Client Using Entrust Certificates.
The second option is to configure the router as the CA server along with the head end to the remote access VPN. Installing the certificates (and everything else) will remain as described in the previous link except that the router will behave as a CA server. For more information, refer to Dynamic LAN-to-LAN VPN between Cisco IOS Routers Using IOS CA on the Hub Configuration Example.
Q. How do I make the required parameters in the VPN client access file read only?
A. Add an exclamation mark (!) to the front of each parameter in the .pcf file for each user in order to make the parameter read only.
The values for parameters that start with an exclamation point (!) cannot be changed by the user in the VPN client. The fields for these values within the GUI will be grayed out (read only).
Here is a sample configuration:
Original .pcf File
[main] Description=connection to TechPubs server Host=10.10.99.30 AuthType=1 GroupName=docusers GroupPwd= enc_GroupPwd=158E47893BDCD398BF863675204775622C494B39523E5CB65434D3C85 1ECF2DCC8BD488857EFA FDE1397A95E01910CABECCE4E040B7A77BF EnableISPConnect=0 ISPConnectType=0 ISPConnect= ISPCommand= Username=aliceChanged .pcf File
[main] !Description=connection to TechPubs server !Host=10.10.99.30 AuthType=1 !GroupName=docusers GroupPwd= enc_GroupPwd=158E47893BDCD398BF863675204775622C494B39523E5CB65434D3C 851ECF2DCC8BD488857EFA FDE1397A95E01910CABECCE4E040B7A77BF EnableISPConnect=0 ISPConnectType=0 ISPConnect= ISPCommand= !Username=aliceIn this example, the user is unable to change the Description, Host, GroupName, and Username values.
Q. Is it possible to limit/restrict access for VPN clients based on MAC addresses?
A. No. It is not possible to limit/restrict access for VPN clients based on MAC addresses.
Related Information
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback