How to Configure the VPN 3000 Concentrator PPTP with Local Authentication
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
The Cisco VPN 3000 Concentrator supports the Point-to-Point Tunnel Protocol (PPTP) tunneling method for native Windows clients. There is 40-bit and 128-bit encryption support available on these VPN Concentrators for a secured reliable connection.
Refer to Configuring the VPN 3000 Concentrator PPTP With Cisco Secure ACS for Windows RADIUS Authentication in order to configure the VPN Concentrator for PPTP users with extended authentication using the Cisco Secure Access Control Server (ACS).
Prerequisites
Requirements
Ensure that you meet the prerequisites mentioned in When is PPTP Encryption Supported on a Cisco VPN 3000 Concentrator? before you attempt this configuration.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
VPN 3015 Concentrator with version 4.0.4.A
-
Windows PC with PPTP client
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
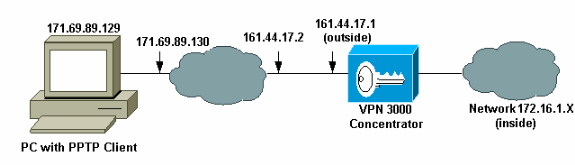
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Configure the VPN 3000 Concentrator with Local Authentication
Complete these steps to configure the VPN 3000 Concentrator with Local Authentication.
-
Configure the respective IP addresses in the VPN Concentrator and ensure that you have connectivity.
-
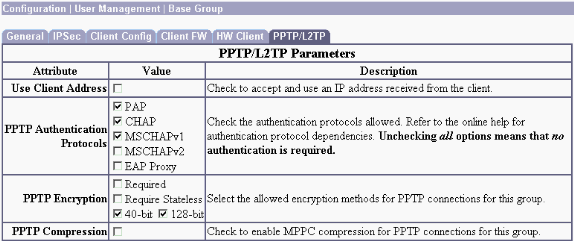
Ensure that PAP authentication is selected in the Configuration > User Management > Base Group PPTP/L2TP tab.
-
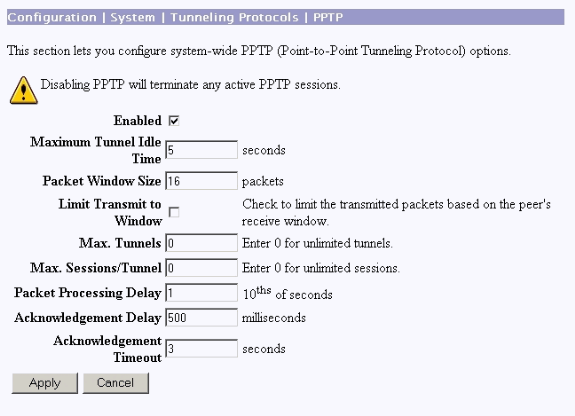
Select Configuration > System > Tunneling Protocols > PPTP and ensure that Enabled is checked.
-
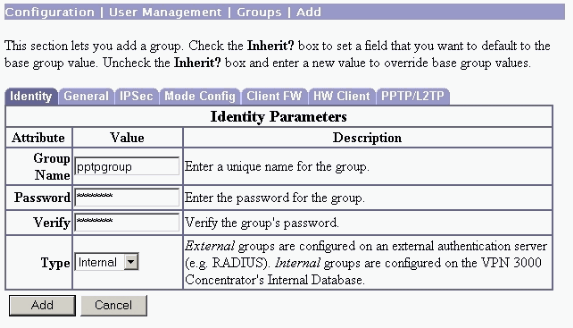
Select Configuration > User Management > Groups > Add, and configure a PPTP group. In this example, the group name is "pptpgroup" and the password (and verify password) is "cisco123".
-
Under the group's General tab, make certain that the PPTP option is enabled in authentication protocols.
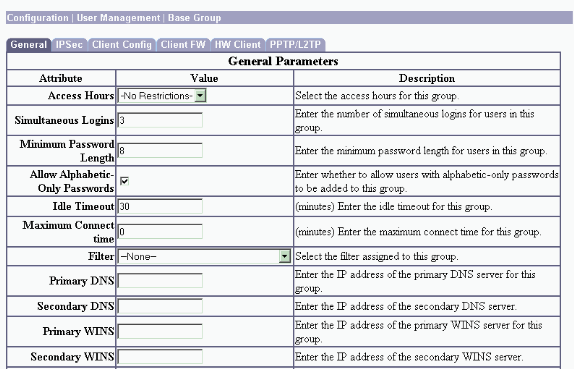
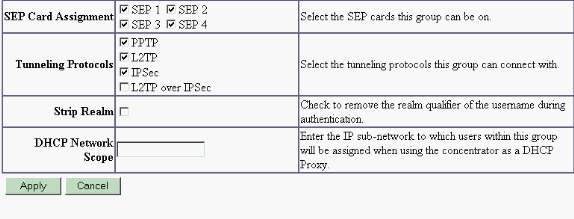
-
Under the PPTP/L2TP tab, enable PAP authentication, and disable encryption (encryption can be enabled at any time in the future).
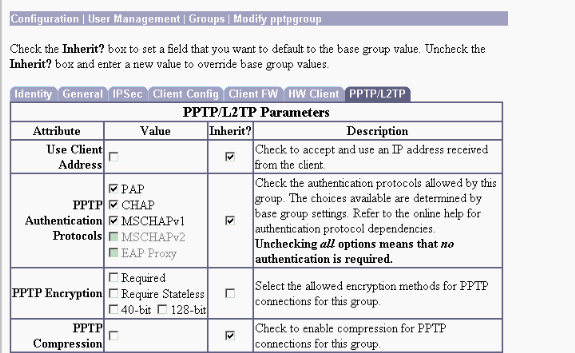
-
Select Configuration > User Management > Users > Add, and configure a local user (called "pptpuser") with the password cisco123 for PPTP authentication. Put the user in the previously defined "pptpgroup":
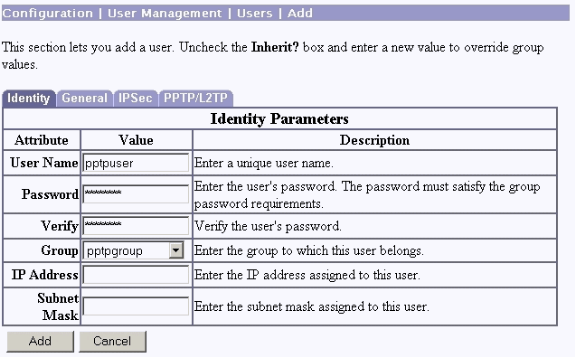
-
Under the General tab for the user, make sure that the PPTP option is enabled in tunneling protocols.
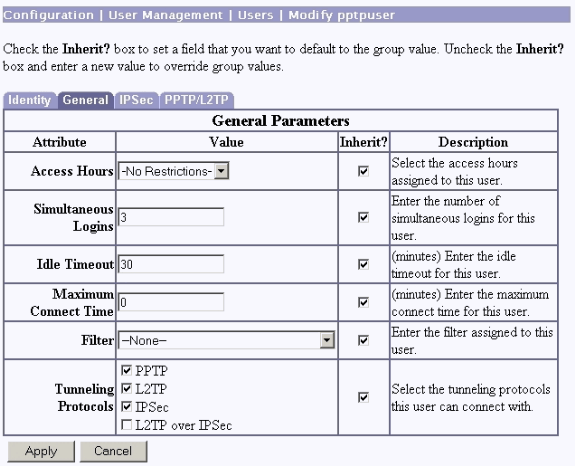
-
Select Configuration > System > Address Management > Pools to define an address pool for address management.
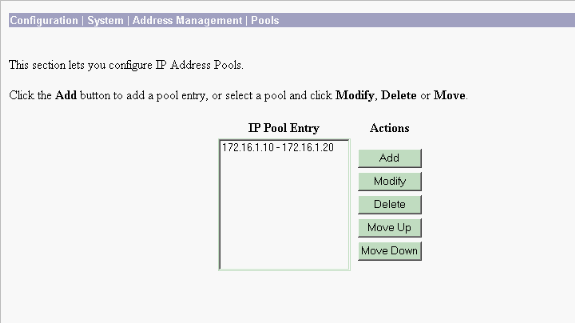
-
Select Configuration > System > Address Management > Assignment and direct the VPN Concentrator to use the address pool.

Microsoft PPTP Client Configuration
Note: None of the information available here on configuring Microsoft software comes with any warranty or support for Microsoft software. Support for Microsoft software is available from Microsoft ![]() .
.
Windows 98 - Install and Configure the PPTP Feature
Install
Complete these steps to install the PPTP feature.
-
Select Start > Settings > Control Panel > Add New Hardware (Next) > Select from List > Network Adapter (Next).
-
Select Microsoft in the left panel and Microsoft VPN Adapter on the right panel.
Configure
Complete these steps to configure the PPTP feature.
-
Select Start > Programs > Accessories > Communications > Dial Up Networking > Make new connection.
-
Connect using the Microsoft VPN Adapter at the Select a device prompt. The VPN Server IP is the 3000 tunnel endpoint.
The Windows 98 default authentication uses password encryption (for example, CHAP or MSCHAP). In order to initially disable this encryption, select Properties > Server types, and uncheck the Encrypted Password and Require Data Encryption boxes.
Windows 2000 - Configuring the PPTP Feature
Complete these steps to configure the PPTP feature.
-
Select Start > Programs > Accessories > Communications > Network and Dialup connections > Make new connection.
-
Click Next, and select Connect to a private network through the Internet > Dial a connection prior (do not select this if you use a LAN).
-
Click Next again, and enter the Hostname or IP of the tunnel endpoint, which is the outside interface of the VPN 3000 Concentrator. In this example the IP address is 161.44.17.1.
Select Properties > Security for the connection > Advanced to add a password type as PAP. The default is MSCHAP and MSCHAPv2, not CHAP or PAP.
Data encryption is configurable in this area. You can disable it initially.
Windows NT
You can access information about setting up Windows NT clients for PPTP at Microsoft's website ![]() .
.
Windows Vista
Complete these steps to configure the PPTP feature.
-
From the Start button, choose Connect To.
-
Choose Set up a connection or network.
-
Choose Connect to a workplace and click Next.
-
Choose Use my Internet Connection (VPN).
Note: If prompted for "Do you want to use a connection that you already have," choose No, create a new connection and click Next.
-
In the Internet Address field, type pptp.vpn.univ.edu, for example.
-
In the Destination Name field, type UNIVVPN, for example.
-
In the User Name field, type your UNIV Logon ID. Your UNIV Logon ID is the part of your email address before @univ.edu.
-
In the Password field, type your UNIV Logon ID password.
-
Click the Create button and then click the Close button.
-
In order to connect to the VPN server after you create the VPN connection, click Start, and then Connect to.
-
Choose the VPN connection in the window and click Connect.
Add MPPE (Encryption)
Make sure that the PPTP connection works without encryption before you add encryption. For example, click the Connect button on the PPTP client to make sure that the connection completes. If you decide to require encryption, MSCHAP authentication must be used. On the VPN 3000, select Configuration > User Management > Groups. Then, under the PPTP/L2TP tab for the group, uncheck PAP, check MSCHAPv1, and check Required for PPTP Encryption.
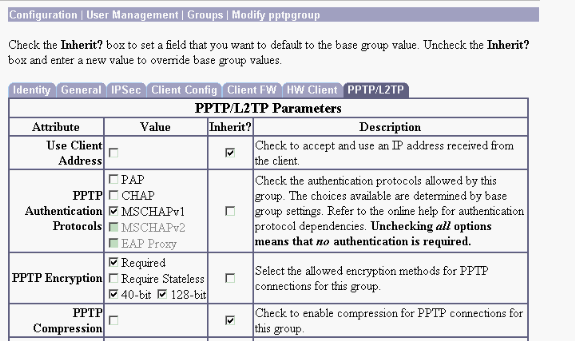
The PPTP client should be reconfigured for optional or required data encrytption and MSCHAPv1 (if it is an option).
Verify
This section provides information you can use to confirm your configuration is working properly.
Verify the VPN Concentrator
You can start the PPTP session by dialing form the PPTP client created earlier in the Microsoft PPTP Client Configuration section.
Use the Administration >Administer Sessions window on the VPN Concentrator to view the parameters and statistics for all active PPTP sessions.
Verify the PC
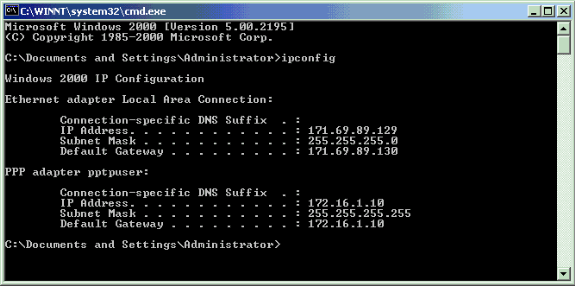
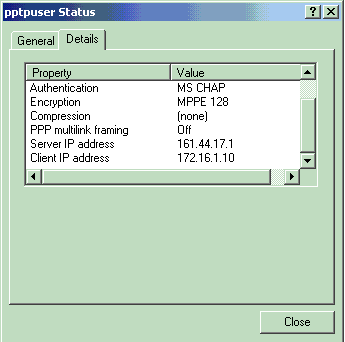
Issue the ipconfig command in the command mode of the PC to see that the PC has two IP addresses. One is its own IP address and the other is assigned by the VPN Concentrator from the pool of IP address. In this example the IP address 172.16.1.10 is the IP address assigned by the VPN Concentrator.
Debug
If the connection does not work, the PPTP event class debug can be added to the VPN Concentrator. Select Configuration > System > Events > Classes > Modify or Add (shown here). PPTPDBG and PPTPDECODE event classes are also available, but might provide too much information.
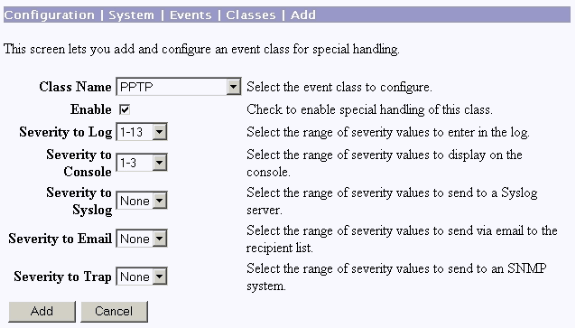
The event log can be retrieved from Monitoring > Filterable Event Log.
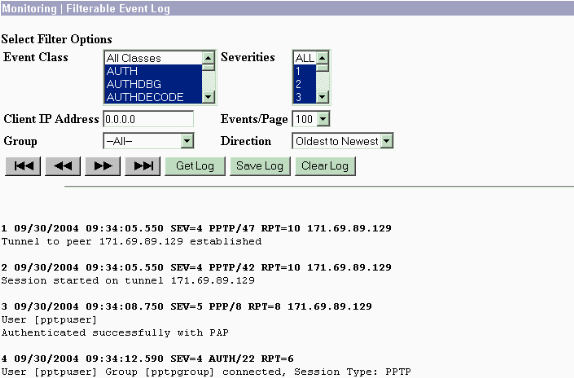
VPN 3000 Debug - Good Authentication
1 09/28/2004 21:36:52.800 SEV=4 PPTP/47 RPT=29 171.69.89.129 Tunnel to peer 171.69.89.129 established 2 09/28/2004 21:36:52.800 SEV=4 PPTP/42 RPT=29 171.69.89.129 Session started on tunnel 171.69.89.129 3 09/28/2004 21:36:55.910 SEV=5 PPP/8 RPT=22 171.69.89.129 User [pptpuser] Authenticated successfully with MSCHAP-V1 4 09/28/2004 21:36:59.840 SEV=4 AUTH/22 RPT=22 User [pptpuser] Group [Base Group] connected, Session Type: PPTP
Click on the PPTP user status Details window to check the parameters on the Windows PC.
Troubleshoot
These are possible errors you can encounter:
-
Bad username or password
VPN 3000 Concentrator debug output:
1 09/28/2004 22:08:23.210 SEV=4 PPTP/47 RPT=44 171.69.89.129 Tunnel to peer 171.69.89.129 established 2 09/28/2004 22:08:23.220 SEV=4 PPTP/42 RPT=44 171.69.89.129 Session started on tunnel 171.69.89.129 3 09/28/2004 22:08:26.330 SEV=3 AUTH/5 RPT=11 171.69.89.129 Authentication rejected: Reason = User was not found handle = 44, server = (none), user = pptpusers, domain = <not specified> 5 09/28/2004 22:08:26.330 SEV=5 PPP/9 RPT=11 171.69.89.129 User [pptpusers] disconnected.. failed authentication ( MSCHAP-V1 ) 6 09/28/2004 22:08:26.340 SEV=4 PPTP/35 RPT=44 171.69.89.129 Session closed on tunnel 171.69.89.129 (peer 32768, local 22712, serial 40761), reason: Error (No additional info) 8 09/28/2004 22:08:26.450 SEV=4 PPTP/34 RPT=44 171.69.89.129 Tunnel to peer 171.69.89.129 closed, reason: None (No additional info)
The message that the user sees ( from Windows 98):
Error 691: The computer you have dialed in to has denied access because the username and/or password is invalid on the domain.
The message that the user sees ( from Windows 2000):
Error 691: Access was denied because the username and/or password was invalid on the domain.
-
"Encryption Required" is selected on the PC, but not on the VPN Concentrator
The message that the user sees (from Windows 98):
Error 742: The computer you're dialing in to does not support the data encryption requirements specified. Please check your encryption settings in the properties of the connection. If the problem persists, contact your network administrator.
The message that the user sees (from Windows 2000):
Error 742: The remote computer does not support the required data encryption type
-
"Encryption Required" (128-bit) is selected on the VPN Concentrator with a PC that only supports 40-bit encryption
VPN 3000 Concentrator debug output:
4 12/05/2000 10:02:15.400 SEV=4 PPP/6 RPT=7 171.69.89.129 User [ pptpuser ] disconnected. PPTP Encryption configured as REQUIRED.. remote client not supporting it.
The message that the user sees (from Windows 98):
Error 742: The remote computer does not support the required data encryption type.
The message that the user sees (from Windows 2000):
Error 645 Dial-Up Networking could not complete the connection to the server. Check your configuration and try the connection again.
-
The VPN 3000 Concentrator is configured for MSCHAPv1 and the PC is configured for PAP, but they cannot agree on an authentication method
VPN 3000 Concentrator debug output:
8 04/22/2002 14:22:59.190 SEV=5 PPP/12 RPT=1 171.69.89.129 User [pptpuser] disconnected. Authentication protocol not allowed.
The message that the user sees (from Windows 2000):
Error 691: Access was denied because the username and/or password was invalid on the domain.
Possible Microsoft Issues to Troubleshoot
-
How to Keep RAS Connections Active After Logging Off
When you log off from a Windows Remote Access Service (RAS) client, any RAS connections are automatically disconnected. Enable the KeepRasConnections key in the registry on the RAS client to remain connected after you log off. Refer to Microsoft Knowledge Base Article - 158909
 for more information.
for more information. -
User Is Not Alerted When Logging On with Cached Credentials
The symptoms of this issue are when you attempt to log on to a domain from a Windows-based workstation or member server and a domain controller cannot be located and no error message is displayed. Instead, you are logged on to the local computer using cached credentials. Refer to Microsoft Knowledge Base Article - 242536
 for more information.
for more information. -
How to Write an LMHOSTS File for Domain Validation and Other Name Resolution Issues
There can be instances when you experience name resolution issues on your TCP/IP network and you need to use LMHOSTS files to resolve NetBIOS names. This article discusses the proper method used to create an LMHOSTS file to aid in name resolution and domain validation. Refer to Microsoft Knowledge Base Article - 180094
 for more information.
for more information.
Related Information
- RFC 2637: Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)

- Cisco Secure ACS for Windows Support Pages
- When is PPTP Encryption Supported on a Cisco VPN 3000 Concentrator?
- Configuring the VPN 3000 Concentrator and PPTP with Cisco Secure ACS for Windows RADIUS Authentication
- Cisco VPN 3000 Concentrator Support Pages
- Cisco VPN 3000 Client Support Pages
- IP Security (IPSec) Product Support Pages
- PPTP Product Support Pages
- Technical Support & Documentation - Cisco Systems
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
11-Dec-2001 |
Initial Release |










 Feedback
Feedback