SSL VPN Client (SVC) on IOS with SDM Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
The SSL VPN Client (SVC) provides a full tunnel for secure communications to the corporate internal network. You can configure access on a user by user basis, or you can create different WebVPN contexts into which you place one or more users.
SSL VPN or WebVPN technology is supported on these IOS router platforms:
-
870, 1811, 1841, 2801, 2811, 2821, 2851
-
3725, 3745, 3825, 3845, 7200, and 7301
You can configure SSL VPN technology in these modes:
-
Clientless SSL VPN (WebVPN)—Provides a remote client that requires an SSL-enabled Web browser to access HTTP or HTTPS Web servers on a corporate local-area network (LAN). In addition, clientless SSL VPN provides access for Windows file browsing through the Common Internet File System (CIFS) protocol. Outlook Web Access (OWA) is an example of HTTP access.
Refer to Clientless SSL VPN (WebVPN) on Cisco IOS with SDM Configuration Example in order to learn more about the Clientless SSL VPN.
-
Thin-Client SSL VPN (Port Forwarding)—Provides a remote client that downloads a small Java-based applet and allows secure access for Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) applications that use static port numbers. Point of presence (POP3), Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP), secure shell (ssh), and Telnet are examples of secure access. Because files on the local machine change, users must have local administrative privileges to use this method. This method of SSL VPN does not work with applications that use dynamic port assignments, such as some file transfer protocol (FTP) applications.
Refer to Thin-Client SSL VPN (WebVPN) IOS Configuration Example with SDM in order to learn more about the Thin-Client SSL VPN.
Note: User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is not supported.
-
SSL VPN Client (SVC Full Tunnel Mode)—Downloads a small client to the remote workstation and allows full secure access to resources on an internal corporate network. You can download the SVC to a remote workstation permanently, or you can remove the client once the secure session is closed.
This document demonstrates the configuration of a Cisco IOS router for use by an SSL VPN Client.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Ensure that you meet these requirements before you attempt this configuration:
-
Microsoft Windows 2000 or XP
-
Web Browser with SUN JRE 1.4 or later or an ActiveX controlled browser
-
Local administrative privileges on the client
-
One of the routers listed in the Introduction with an Advanced Security image (12.4(6)T or later)
-
Cisco Security Device Manager (SDM) version 2.3
If the Cisco SDM is not already loaded on your router, you can obtain a free copy of the software from Software Download (registered customers only) . You must have a CCO account with a service contract. For detailed information on the installation and configuration of SDM, refer to Cisco Router and Security Device Manager.
-
A digital certificate on the router
You can use a persistent self-signed certificate or an external Certificate Authority (CA) to satisfy this requirement. For more information on persistent self-signed certificates, refer to Persistent Self-Signed Certificates.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco IOS router 3825 series with 12.4(9)T
-
Security Device Manager (SDM) version 2.3.1
Note: The information in this document was created from devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
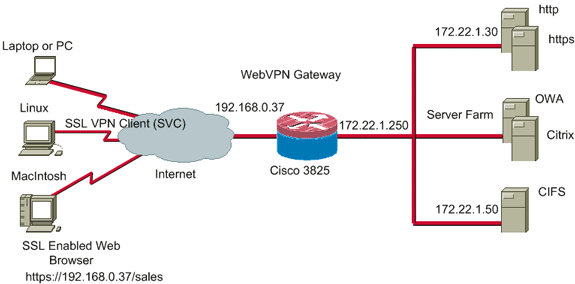
Preconfiguration Tasks
-
Configure the router for SDM. (Optional)
Routers with the appropriate security bundle license already have the SDM application loaded in flash. Refer to Downloading and Installing Cisco Router and Security Device Manager (SDM) to obtain and configure the software.
-
Download a copy of the SVC to your management PC.
You can obtain a copy of the SVC package file from Software Download: Cisco SSL VPN Client (registered customers only) . You must have a valid CCO account with a service contract.
-
Set the correct date, time, and time zone, and then configure a digital certificate on the router.
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
The SVC is initially loaded onto the WebVPN gateway router. Every time the client connects, a copy of the SVC is dynamically downloaded onto the PC. In order to change this behavior, configure the router to enable the software to remain permanently on the client computer.
Configure SVC on IOS
In this section, you are presented with the steps necessary to configure the features described in this document. This example configuration uses the SDM Wizard to enable the operation of the SVC on the IOS router.
Complete these steps in order to configure SVC on the IOS router:
Step 1. Install and Enable the SVC Software on the IOS Router
Complete these steps in order to install and enable the SVC software on the IOS router:
-
Open the SDM application, click Configure, and then click VPN.
-
Expand WebVPN, and choose Packages.
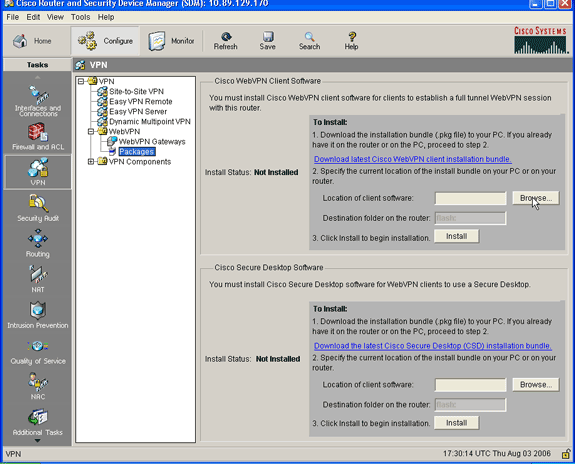
-
Within the Cisco WebVPN Client Software area, click the Browse button.
The Select SVC location dialog box appears.
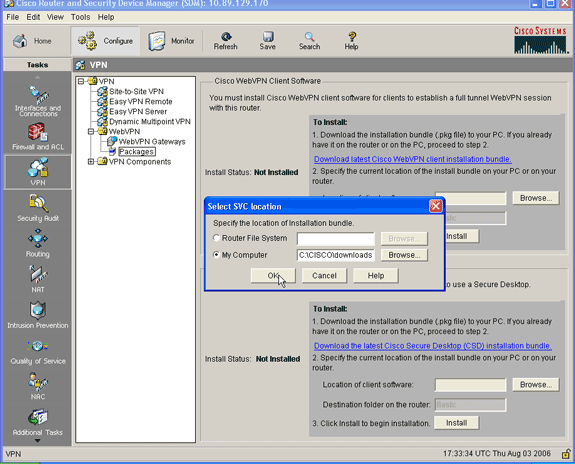
-
Click the My Computer radio button, and then click Browse to locate the SVC package on your management PC.
-
Click OK, and then click the Install button.
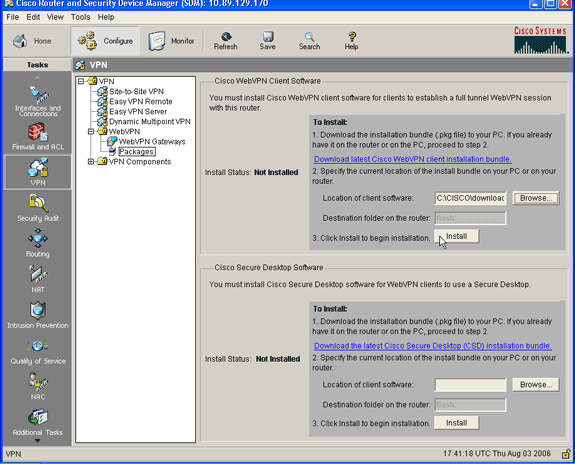
-
Click Yes, and then click OK.
A successful install of the SVC package is shown in this image:
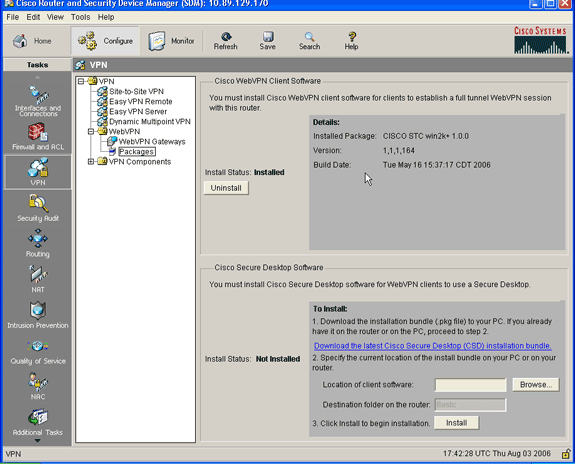
Step 2. Configure a WebVPN Context and WebVPN Gateway with the SDM Wizard
Complete these steps in order to configure a WebVPN context and WebVPN gateway:
-
After the SVC is installed on the router, click Configure, and then click VPN.
-
Click WebVPN, and click the Create WebVPN tab.
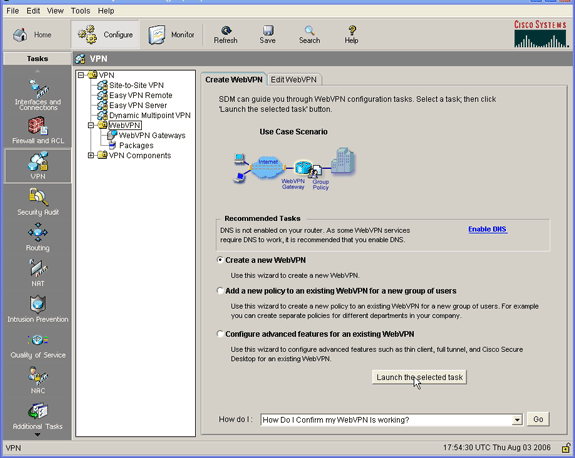
-
Check the Create a New WebVPN radio button, and then click Launch the selected task.
The WebVPN Wizard dialog box appears.
-
Click Next.
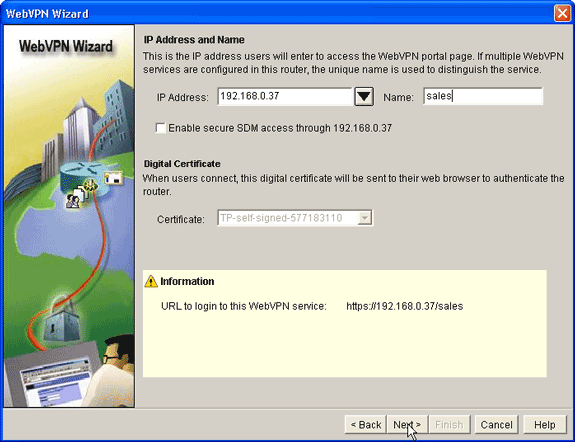
-
Enter the IP Address of the new WebVPN gateway, and enter a unique name for this WebVPN context.
You can create different WebVPN contexts for the same IP address (WebVPN gateway), but each name must be unique. This example uses this IP address: https://192.168.0.37/sales
-
Click Next, and continue to Step 3.
Step 3. Configure the User Database for SVC Users
For authentication, you can use an AAA Server, local users, or both. This configuration example uses locally created users for authentication.
Complete these steps in order to configure the user database for SVC users:
-
After you complete Step 2, click the Locally on this router radio button located in the WebVPN Wizard User Authentication dialog box.
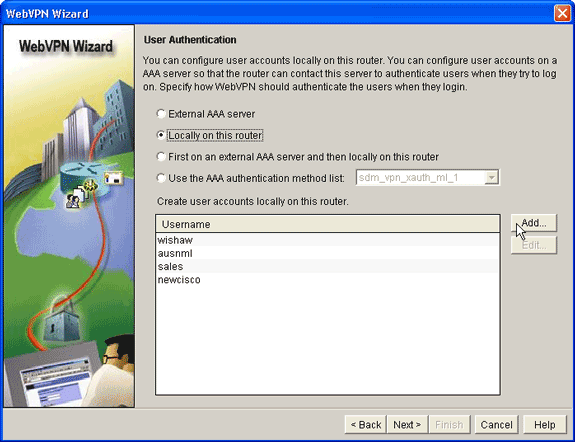
This dialog box allows you to add users to the local database.
-
Click Add, and enter user information.
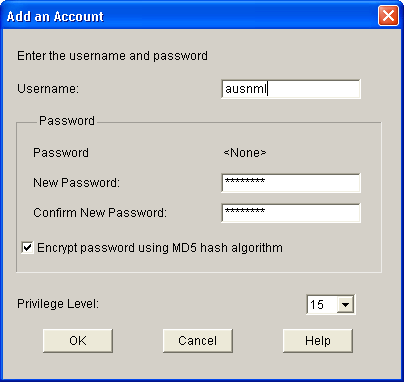
-
Click OK, and add additional users as necessary.
-
After you add the necessary users, click Next, and continue to Step 4.
Step 4. Configure the Resources to Expose to Users
The Configure Intranet Websites WebVPN Wizard dialog box allows you to select the intranet resources that you want to expose to your SVC clients.
Complete these steps in order to configure the resources to expose to users:
-
After you complete Step 3, click the Add button located in the Configure Intranet Websites dialog box.
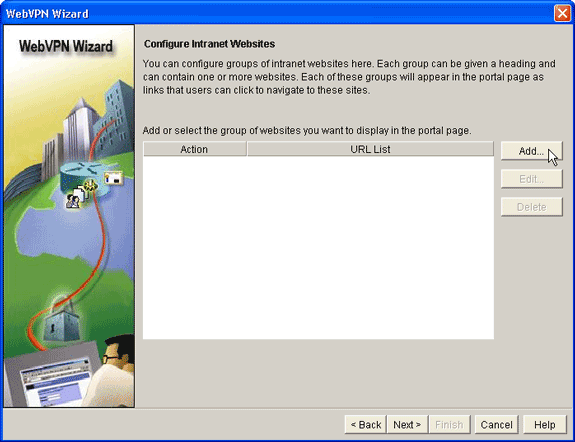
-
Enter a URL list name, and then enter a heading.
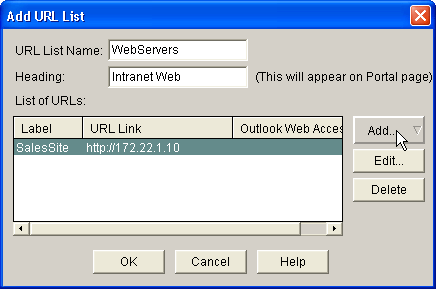
-
Click Add, and choose Website to add the websites you want to expose to this client.
-
Enter URL and link information, and then click OK.
-
To add access to OWA Exchange Servers, click Add and choose E-mail.
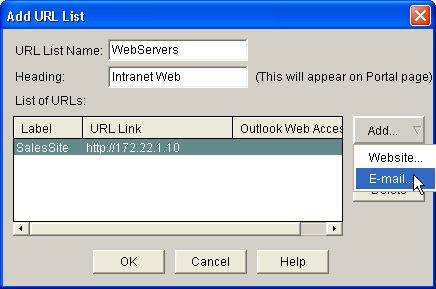
-
Check the Outlook Web Access check box, enter URL label and link information, and then click OK.
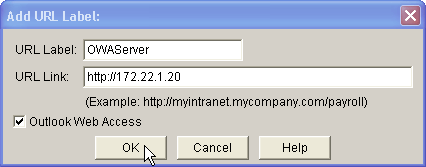
-
After you add the desired resources, click OK, and then click Next.
The WebVPN Wizard full tunnel dialog box appears.
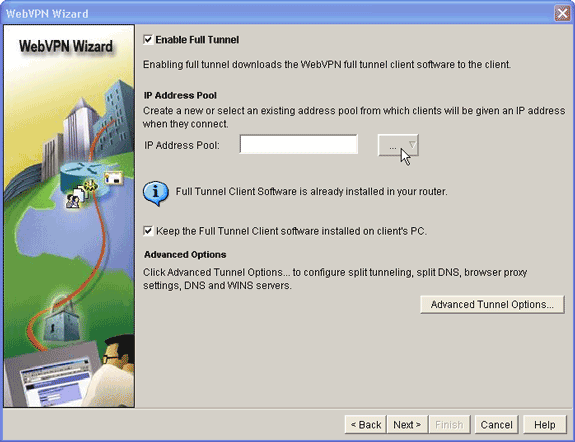
-
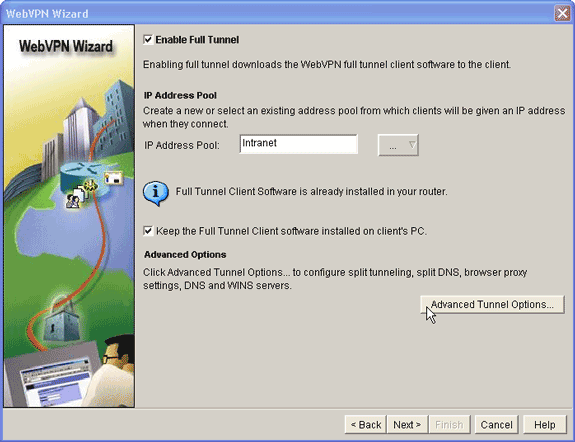
Verify that the Enable Full Tunnel check box is checked.
-
Create a pool of IP addresses that clients of this WebVPN context can use. The pool of addresses must correspond to addresses available and routable on your Intranet.
-
Click the ellipses (...) next to the IP Address Pool field, and choose Create a new IP Pool.
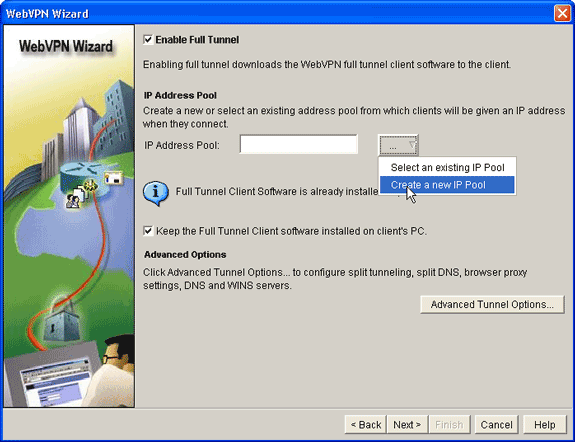
-
In the Add IP Local Pool dialog box, enter a name for the pool, and click Add.
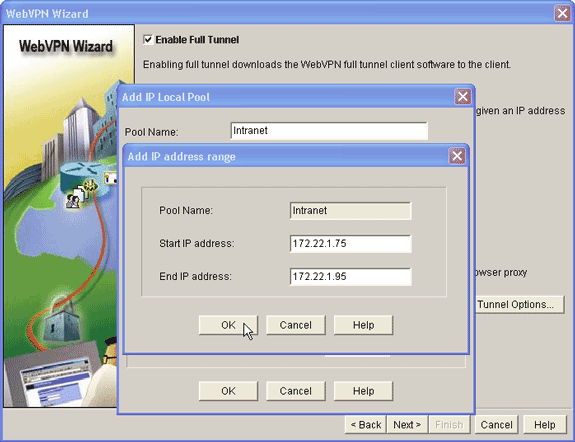
-
In the Add IP address range dialog box, enter the address pool range for the SVC clients, and click OK.
Note: The IP address pool should be in a range of an interface directly connected to the router. If you want to use a different pool range, you can create a loopback address associated with your new pool to satisfy this requirement.
-
Click OK.
-
If you want your remote clients to permanently store a copy of the SVC click the Keep the Full Tunnel Client Software installed on client's PC check box. Clear this option to require the client to download the SVC software each time a client connects.
-
Configure advanced tunnel options, such as split tunneling, split DNS, browser proxy settings, and DNS and WNS servers. Cisco recommends you configure at least DNS and WINS servers.
To configure advanced tunnel options, complete these steps:
-
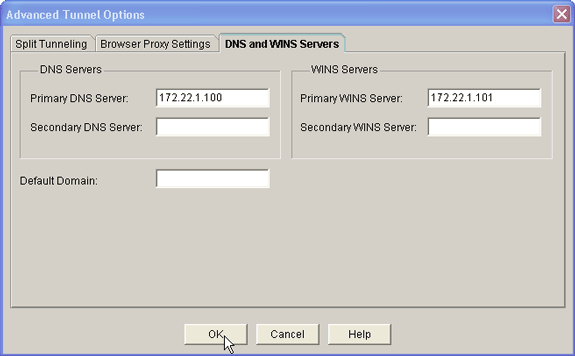
Click the Advanced Tunnel Options button.
-
Click the DNS and WINS Servers tab, and enter the primary IP addresses for the DNS and WINS servers.
-
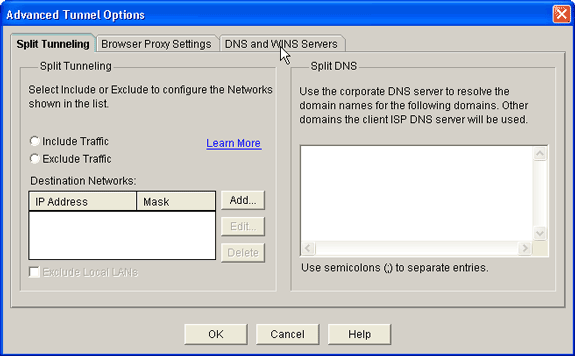
To configure split tunneling and browser proxy settings, click the Split Tunneling or Browser Proxy Settings tab.
-
-
After you configure the necessary options, click Next.
-
Customize the WebVPN Portal Page or select the default values.
The Customize WebVPN Portal Page allows you to customize how the WebVPN Portal Page appears to your customers.
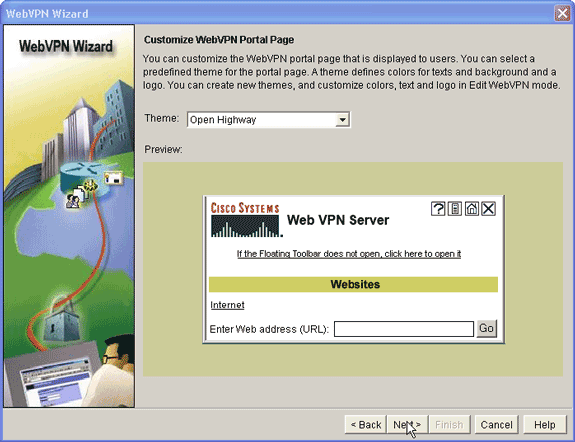
-
After you configure the WebVPN Portal Page, click Next, click Finish, and then click OK.
The WebVPN Wizard submits tour commands to the router.
-
Click OK to save your configuration.
Note: If you receive an error message, the WebVPN license may be incorrect. A sample error message is shown in this image:
To correct a license issue, complete these steps:
-
Click Configure, and then click VPN.
-
Expand WebVPN, and click the Edit WebVPN tab.
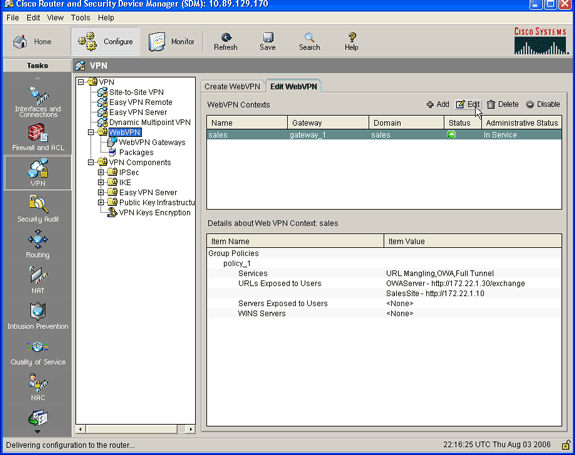
-
Highlight your newly created context, and click the Edit button.
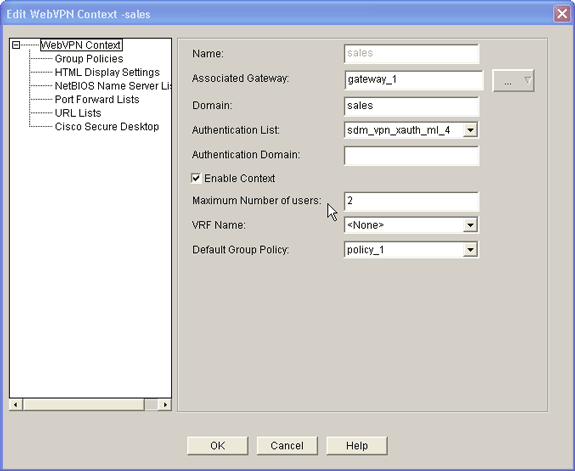
-
In the Maximum Number of users field, enter the correct number of users for your license.
-
Click OK, and then click OK.
Your commands are written to the configuration file.
-
Click Save, and then click Yes to accept the changes.
-
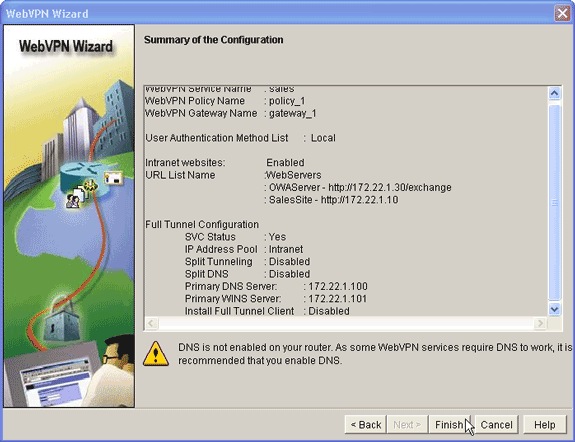
Results
The ASDM creates these command-line configurations:
| ausnml-3825-01 |
|---|
ausnml-3825-01#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 4393 bytes ! ! Last configuration change at 22:24:06 UTC Thu Aug 3 2006 by ausnml ! NVRAM config last updated at 22:28:54 UTC Thu Aug 3 2006 by ausnml ! version 12.4 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname ausnml-3825-01 ! boot-start-marker boot system flash c3825-adventerprisek9-mz.124-9.T.bin boot-end-marker ! no logging buffered ! aaa new-model ! !--- Added by SDM for local aaa authentication. aaa authentication login sdm_vpn_xauth_ml_1 local aaa authentication login sdm_vpn_xauth_ml_2 local aaa authentication login sdm_vpn_xauth_ml_3 local aaa authentication login sdm_vpn_xauth_ml_4 local ! aaa session-id common ! resource policy ! ip cef ! ip domain name cisco.com ! voice-card 0 no dspfarm !--- Digital certificate information. crypto pki trustpoint TP-self-signed-577183110 enrollment selfsigned subject-name cn=IOS-Self-Signed-Certificate-577183110 revocation-check none rsakeypair TP-self-signed-577183110 ! crypto pki certificate chain TP-self-signed-577183110 certificate self-signed 01 3082024E 308201B7 A0030201 02020101 300D0609 2A864886 F70D0101 04050030 30312E30 2C060355 04031325 494F532D 53656C66 2D536967 6E65642D 43657274 69666963 6174652D 35373731 38333131 30301E17 0D303630 37323731 37343434 365A170D 32303031 30313030 30303030 5A303031 2E302C06 03550403 1325494F 532D5365 6C662D53 69676E65 642D4365 72746966 69636174 652D3537 37313833 31313030 819F300D 06092A86 4886F70D 01010105 0003818D 00308189 02818100 F43F6DD9 32A264FE 4C5B0829 698265DC 6EC65B17 21661972 D363BC4C 977C3810 !--- Output suppressed. quit username wishaw privilege 15 secret 5 $1$r4CW$SeP6ZwQEAAU68W9kbR16U. username ausnml privilege 15 password 7 044E1F505622434B username sales privilege 15 secret 5 $1$/Lc1$K.Zt41zF1jSdKZrPgNK1A. username newcisco privilege 15 secret 5 $1$Axlm$7k5PWspXKxUpoSReHo7IQ1 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.0.37 255.255.255.0 ip virtual-reassembly duplex auto speed auto media-type rj45 no keepalive ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 172.22.1.151 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto media-type rj45 !--- Clients receive an address from this pool. ip local pool Intranet 172.22.1.75 172.22.1.95 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.22.1.1 ! ip http server ip http authentication local ip http secure-server ip http timeout-policy idle 600 life 86400 requests 100 ! control-plane ! line con 0 stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 !--- Identify the gateway and port. webvpn gateway gateway_1 ip address 192.168.0.37 port 443 http-redirect port 80 ssl trustpoint TP-self-signed-577183110 inservice !--- SVC package file. webvpn install svc flash:/webvpn/svc.pkg ! !--- WebVPN context. webvpn context sales title-color #CCCC66 secondary-color white text-color black ssl authenticate verify all ! !--- Resources available to this context. url-list "WebServers" heading "Intranet Web" url-text "SalesSite" url-value "http://172.22.1.10" url-text "OWAServer" url-value "http://172.22.1.20/exchange" ! nbns-list NBNS-Servers nbns-server 172.22.1.15 master !--- Group policy for the context. policy group policy_1 url-list "WebServers" functions svc-enabled svc address-pool "Intranet" svc default-domain "cisco.com" svc keep-client-installed svc dns-server primary 172.22.1.100 svc wins-server primary 172.22.1.101 default-group-policy policy_1 aaa authentication list sdm_vpn_xauth_ml_4 gateway gateway_1 domain sales max-users 2 inservice ! ! end |
Verify
Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly.
Procedure
To test your configuration, enter http://192.168.0.37/sales into an SSL-enabled client Web browser.
Commands
Several show commands are associated with WebVPN. You can execute these commands at the command-line interface (CLI) to show statistics and other information. For detailed information about show commands, refer to Verifying WebVPN Configuration.
Note: The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
Troubleshoot
Use this section to troubleshoot your configuration.
SSL Connectivity Issue
Problem: SSL VPN clients are unable to connect the router.
Solution: Insufficient IP addresses in the IP address pool might cause this issue. Increase the number of IP addresses in the pool of IP addresses on the router in order to resolve this issue.
Troubleshooting Commands
Several clear commands are associated with WebVPN. For detailed information about these commands, refer to Using WebVPN Clear Commands.
Several debug commands are associated with WebVPN. For detailed information about these commands, refer to Using WebVPN Debug Commands.
Note: The use of debug commands can adversely impact your Cisco device. Before you use debug commands, refer to Important Information on Debug Commands.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
21-Jul-2006 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)























 Feedback
Feedback