Configure ISE 2.0 3rd Party Integration with Aruba Wireless
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to troubleshoot 3rd Party Integration feature on Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE).
Note: Be aware that Cisco is not responsible for configuration or support of devices from other vendors.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Aruba IAP configuration
- BYOD flows on ISE
- ISE configuration for password and certificate authentication
Components Used
This document describes how to troubleshoot 3rd Party Integration feature on Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE).
It can be used as a guide for integration with other vendors and flows. ISE version 2.0 supports 3rd Party Integration.
This is a configuration example that presents how to integrate wireless network managed by Aruba IAP 204 with ISE for Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) services.
The information in this document is based on these software versions:
- Aruba IAP 204 software 6.4.2.3
- Cisco ISE, Release 2.0 and later
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Configure
Network Diagram
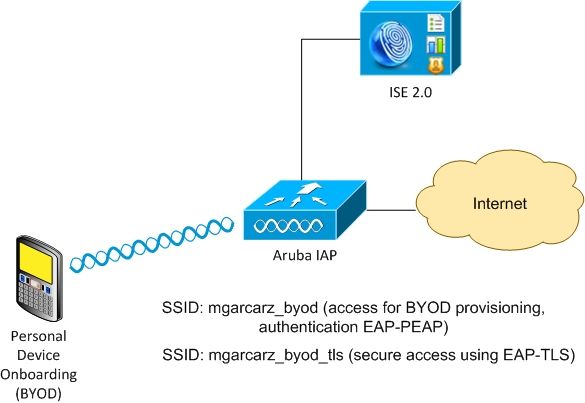
There are two wireless networks managed by Aruba AP.
The first one (mgarcarz_byod) is used for 802.1x Extensible Authentication Protocol-Protected EAP (EAP-PEAP) access.
After a successful authentication, Aruba controller must redirect user to ISE BYOD portal - Native Supplicant Provisioning (NSP) flow.
User is redirected, Network Setup Assistant (NSA) application is executed and certificate is provisioned and installed on Windows client.
ISE internal CA is used for that process (default configuration).
NSA is also responsible for creation of wireless profile for the second Service Set Identifier (SSID) managed by Aruba (mgarcarz_byod_tls) - that one is used for 802.1x Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS) authentication.
As a result, corporate user is able to perform onboarding of personal device and get secure access into corporate network.
This example can be easily modified for different types of access, for example:
- Central Web Authentication (CWA) with BYOD service
- 802.1x authentication with Posture and BYOD redirection
- Typically, for EAP-PEAP authentication Active Directory is used (to keep this article short internal ISE users are used)
- Typically, for Certificate Provisioning external Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) server is used, commonly Microsoft Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES) in order to keep this article short, internal ISE CA is used.
Challenges with 3rd Party Support
There are the challenges when you use ISE Guest flows (like BYOD, CWA, NSP, Client Provisioning Portal (CPP)) with 3rd party devices.
Sessions
Cisco Network Access Devices (NAD) uses Radius cisco-av-pair called audit-session-id in order to inform Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) server about session ID.
That value is used by ISE in order to track the sessions and provide the correct services for each flow. Other vendors do not support cisco-av pair.
ISE has to rely on IETF attributes received in Access-Request and Accounting Request.
After you receive Access-Request, ISE builds synthesized Cisco Session ID (from Calling-Station-ID, NAS-Port, NAS-IP-Address and shared secret). That value has a local significance only (not sent via network).
As a result, it's expected from every flow (BYOD, CWA, NSP, CPP) to attach correct attributes - so ISE is able to recalculate Cisco Session ID and perform a lookup in order to correlate it with the correct session and continue the flow.
URL Redirect
ISE uses Radius cisco-av-pair called url-redirect and url-redirect-acl in order to inform NAD that specific traffic must be redirected.
Other vendors do not support cisco-av pair. So typically, those devices must be configured with static redirection URL which points to specific service (Authorization Profile) on ISE.
Once the user initiates HTTP session, those NADs redirect to the URL and also attach additional arguments (like IP address or MAC address) in order to allow ISE identify specific session and continue the flow.
CoA
ISE uses Radius cisco-av-pair called subscriber:command, subscriber:reauthenticate-type in order to indicate what actions must NAD take for a specific session.
Other vendors do not support cisco-av pair. So typically, those devices use RFC CoA (3576 or 5176) and one of the two defined messages:
- disconnect request (called also packet of disconnect) - that one is used to disconnect the session (very often to force reconnection)
- CoA push - that one is used to change session status transparently without disconnection (for example VPN session and new ACL applied)
ISE supports both Cisco CoA with cisco-av-pair and also both RFC CoA 3576/5176.
Solution on ISE
In order to support 3rd party vendors, ISE 2.0 introduced a concept of Network Device Profiles which describes how specific vendor behaves - how Sessions, URL Redirect and CoA is supported.
Authorization Profiles are of specific type (Network Device Profile) and once the authentication occurs ISE behavior is derived from that profile.
As a result, devices from other vendors can be managed easily by ISE. Also configuration on ISE is flexible and allows to tune or create new Network Device Profiles.
This article presents the usage of default profile for Aruba device.
More information on the feature:
Network Access Device Profiles with Cisco Identity Services Engine
Cisco ISE
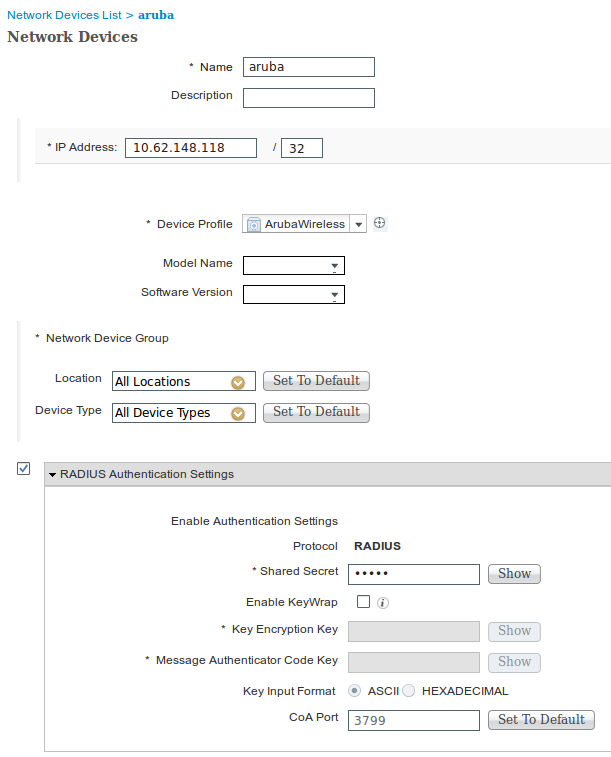
Step 1. Add Aruba Wireless Controller to Network Devices
Navigate to Administration > Network Resources > Network Devices. Choose correct Device Profile for selected vendor, in this case: ArubaWireless. Ensure to configure Shared Secret and CoA port as shown in the images.
In case, there is no available profile for the desired vendor, it can be configured under Administration > Network Resources > Network Device Profiles.
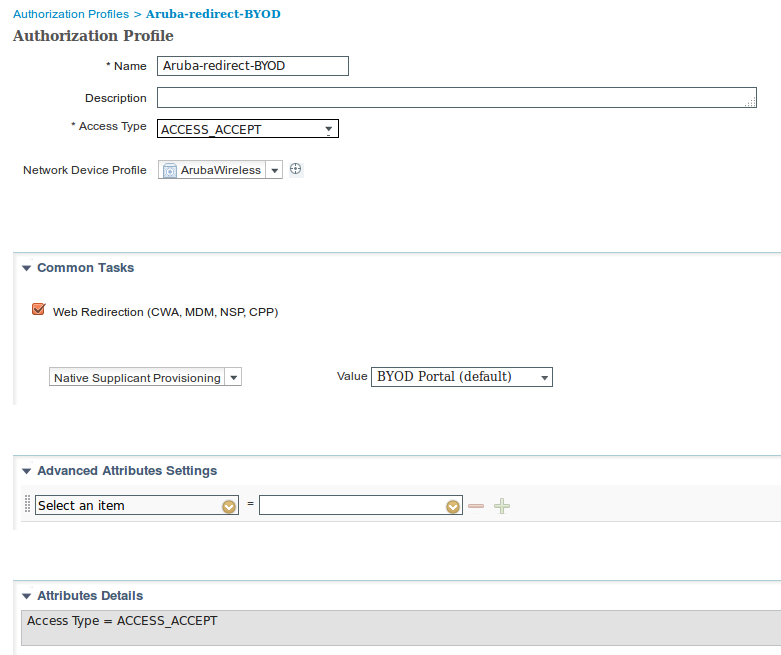
Step 2. Configure Authorization Profile
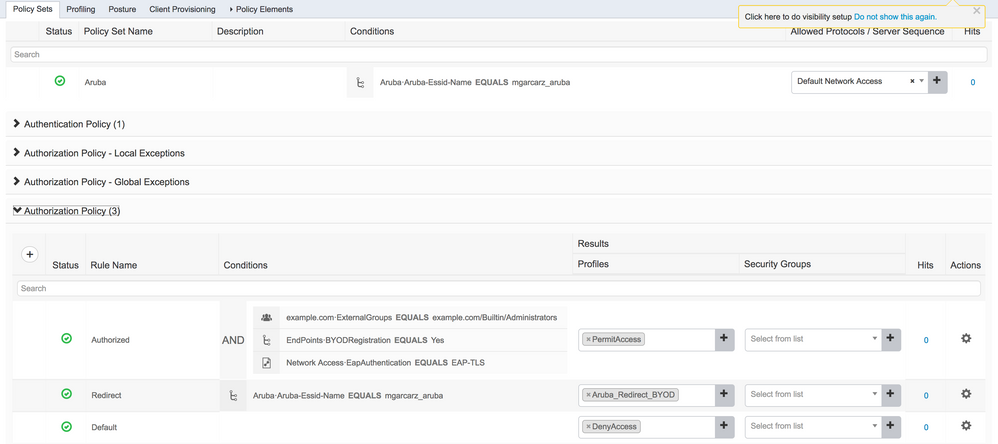
Navigate to Policy > Policy Elements > Results > Authorization > Authorization Profiles choose the same Network Device Profile as in Step 1. ArubaWireless. The profile configured is Aruba-redirect-BYOD with BYOD Portal and as shown in the images.
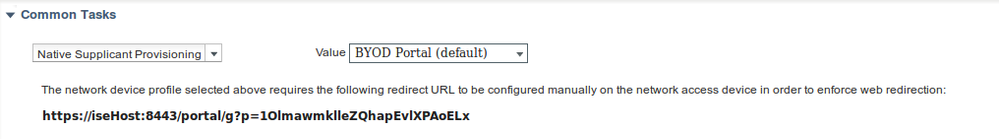
Missing part of the Web Redirection configuration, where static link to Authorization Profile is generated. While Aruba doesn't support dynamic redirection to guest portal, there is one link assigned to each Authorization profile, which is then configured on Aruba and as shown in the image.
Step 3. Configure Authorization Rules
Navigate to Policy > Authorization Rules and the configuration is as shown in the image.

First, user connects to SSID mgracarz_aruba and ISE returns Authorization Profile Aruba-redirect-BYOD which redirects client to default BYOD portal. After the completion of BYOD process, client connects with EAP-TLS and full access to the network is granted.
In the newer versions of ISE the same Policy might look like the following:
Aruba AP
Step 1. Captive Portal Configuration
In order to configure Captive Portal on Aruba 204, navigate to Security > External Captive Portal and add new one. Enter this information for proper configuration and as shown in the image.
- Type: Radius Authentication
- IP or hostname: ISE server
- URL: link that is created on ISE under Authorization Profile configuration; it is specific to particular Authorization Profile and can be found here under the Web Redirection configuration
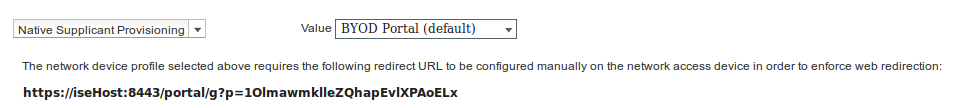
- Port: port number on which selected portal is hosted on ISE (by default: 8443) as shown in the image.
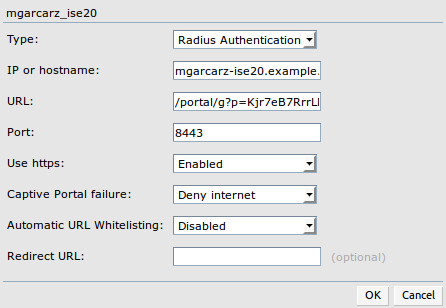
Step 2. Radius Server Configuration
Navigate to Security > Authentication Servers ensure that CoA port is the same as configured on ISE as shown in the image.
By default, on Aruba 204, it is set to 5999, however, that is not compliant with RFC 5176 and it also does not work with ISE.
Note: In Aruba version 6.5 and newer select also "Captive Portal" checkbox.
Step 3. SSID Configuration
- Security tab is as shown in the image.
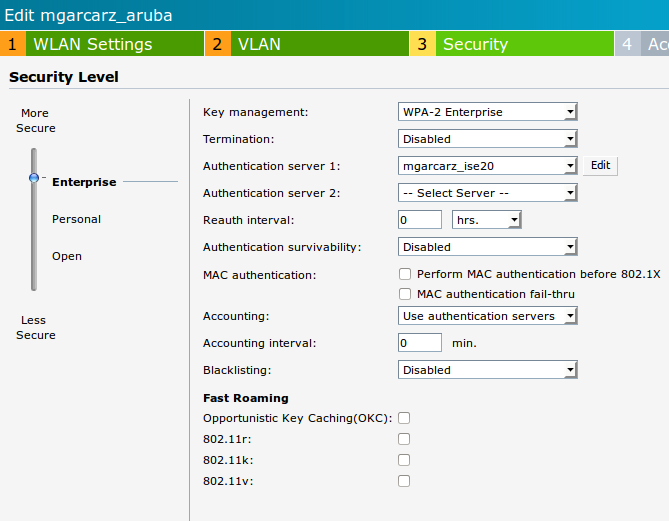
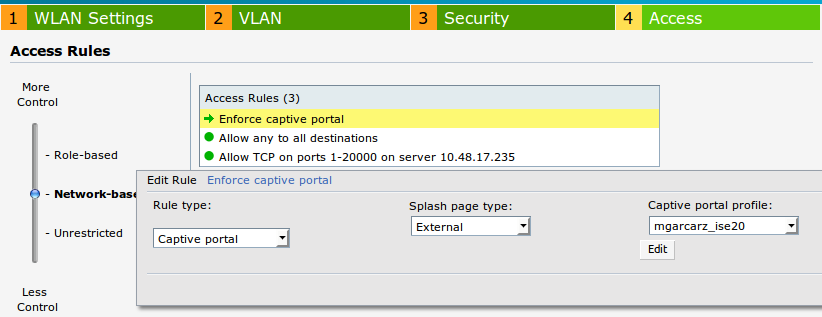
- Access tab: select Network-based Access Rule in order to configure captive portal on SSID.
Use captive portal that was configured in Step 1. Click New, choose Rule type: Captive portal, Splash page type: External as shown in the image.
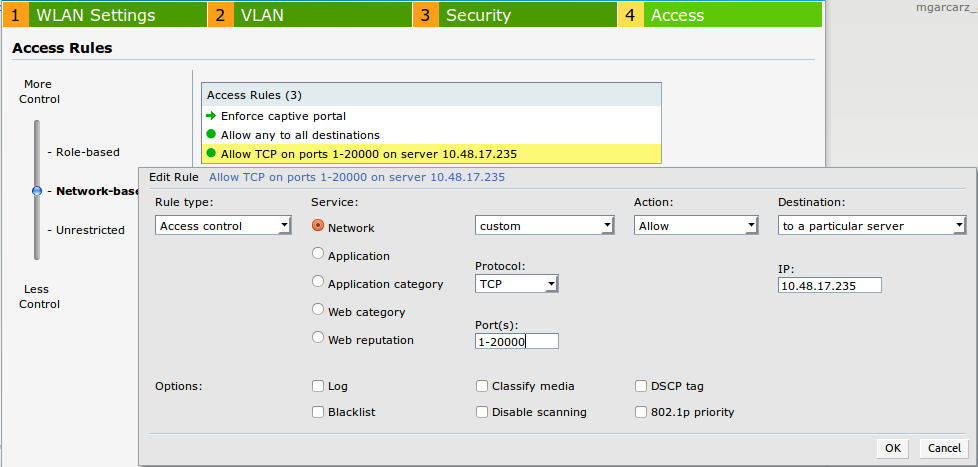
In addition, allow all traffic to ISE server (TCP ports in range 1-20000), while rule configured by default on Aruba: Allow any to all destinations seems to be not working properly as shown in the image.
Verify
Use this section in order to confirm that your configuration works properly.
Step 1. Connection to SSID mgarcarz_aruba with EAP-PEAP
First authentication log on ISE appears. Default authentication policy has been used, Aruba-redirect-BYOD authorization profile has been returned as shown in the image.
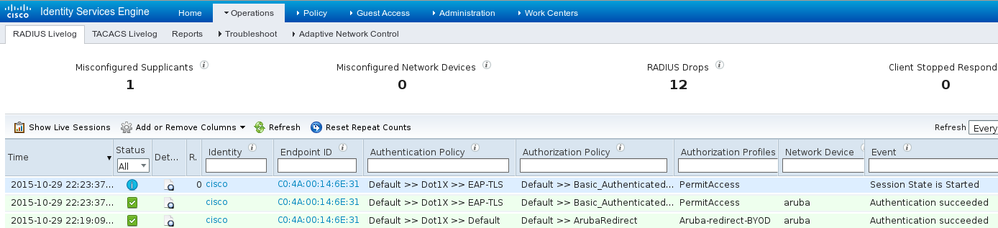
ISE returns Radius Access-Accept message with EAP Success. Note that no additional attributes are returned (no Cisco av-pair url-redirect or url-redirect-acl) as shown in the image.
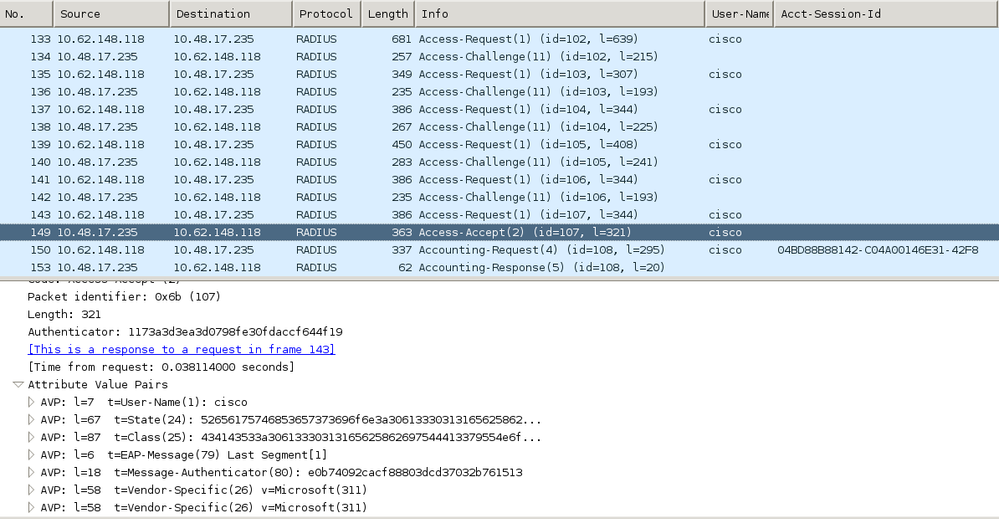
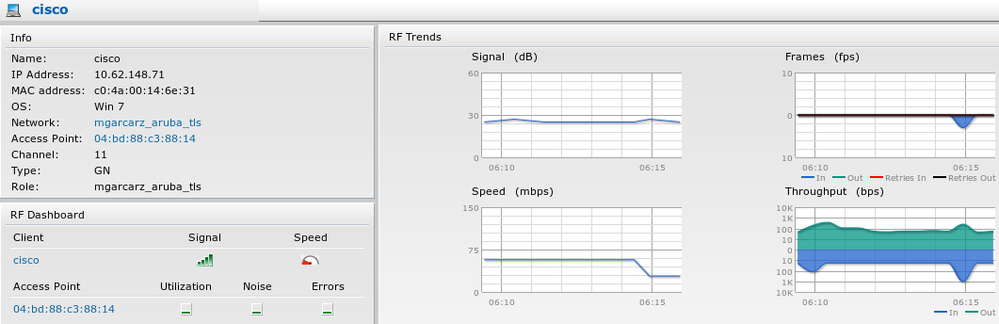
Aruba reports that the session is established (EAP-PEAP identity is cisco) and selected Role is mgarcarz_aruba as shown in the image.
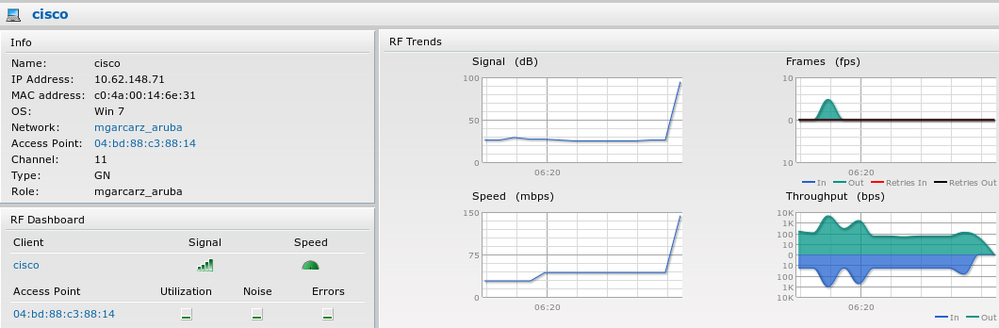
That role is responsible for the redirection to the ISE (captive portal functionality on Aruba).
In Aruba CLI, it is possible to confirm what is the current authorization status for that session:
04:bd:88:c3:88:14# show datapath user
Datapath User Table Entries
---------------------------
Flags: P - Permanent, W - WEP, T- TKIP, A - AESCCM
R - ProxyARP to User, N - VPN, L - local, I - Intercept, D - Deny local routing
FM(Forward Mode): S - Split, B - Bridge, N - N/A
IP MAC ACLs Contract Location Age Sessions Flags Vlan FM
--------------- ----------------- ------- --------- -------- ----- --------- ----- ---- --
10.62.148.118 04:BD:88:C3:88:14 105/0 0/0 0 1 0/65535 P 1 N
10.62.148.71 C0:4A:00:14:6E:31 138/0 0/0 0 0 6/65535 1 B
0.0.0.0 C0:4A:00:14:6E:31 138/0 0/0 0 0 0/65535 P 1 B
172.31.98.1 04:BD:88:C3:88:14 105/0 0/0 0 1 0/65535 P 3333 B
0.0.0.0 04:BD:88:C3:88:14 105/0 0/0 0 0 0/65535 P 1 N
04:bd:88:c3:88:14#
And in order to check ACL ID 138 for the current permissions:
04:bd:88:c3:88:14# show datapath acl 138
Datapath ACL 138 Entries
-----------------------
Flags: P - permit, L - log, E - established, M/e - MAC/etype filter
S - SNAT, D - DNAT, R - redirect, r - reverse redirect m - Mirror
I - Invert SA, i - Invert DA, H - high prio, O - set prio, C - Classify Media
A - Disable Scanning, B - black list, T - set TOS, 4 - IPv4, 6 - IPv6
K - App Throttle, d - Domain DA
----------------------------------------------------------------
1: any any 17 0-65535 8209-8211 P4
2: any 172.31.98.1 255.255.255.255 6 0-65535 80-80 PSD4
3: any 172.31.98.1 255.255.255.255 6 0-65535 443-443 PSD4
4: any mgarcarz-ise20.example.com 6 0-65535 80-80 Pd4
5: any mgarcarz-ise20.example.com 6 0-65535 443-443 Pd4
6: any mgarcarz-ise20.example.com 6 0-65535 8443-8443 Pd4 hits 37
7: any 10.48.17.235 255.255.255.255 6 0-65535 1-20000 P4 hits 18
<....some output removed for clarity ... >
That matches with what was configured in GUI for that Role as shown in the image.
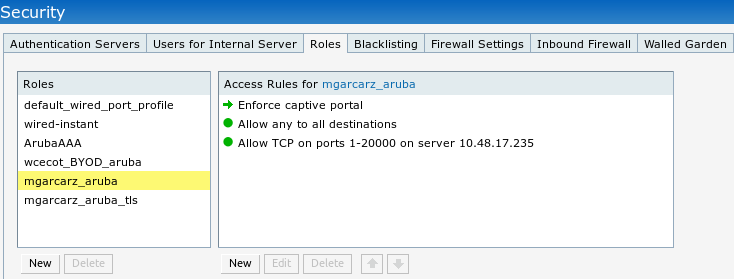
Step 2. Web Browser Traffic Redirection for BYOD
Once user opens the web browser and types any address, redirection occurs as shown in the image.
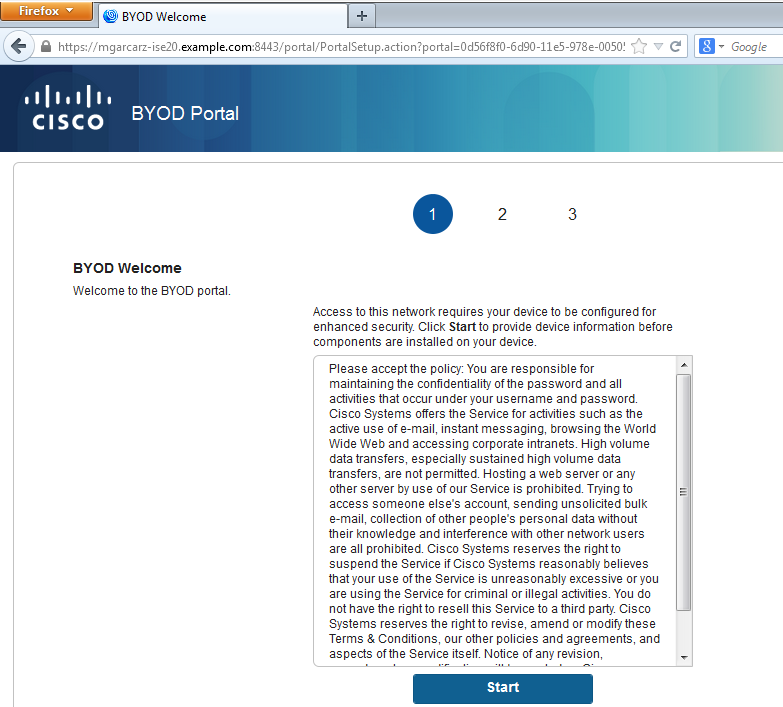
Looking at the packet captures, it is confirmed that Aruba spoofs the destination (5.5.5.5) and returns the HTTP redirection to ISE.
Note that it is the same static URL as configured in ISE and copied to Captive Portal on Aruba - but additionally multiple arguments are added as follows and as shown in the image:
- cmd = login
- mac = c0:4a:00:14:6e:31
- essid = mgarcarz_aruba
- ip = 10.62.148.7
- apname = 4bd88c38814 (mac)
- url = http://5.5.5.5
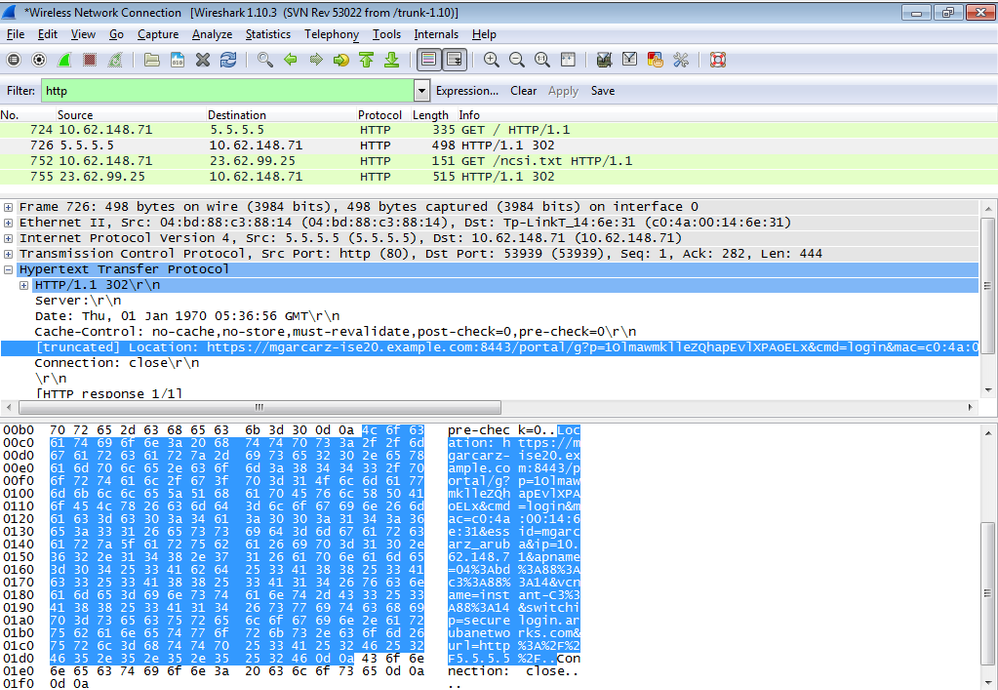
Because of these arguments, ISE is able to recreate Cisco Session ID, find out the corresponding session on ISE and continue with BYOD (or any other configured) flow.
For Cisco devices, audit_session_id would be normally used but that is not supported by other vendors.
In order to confirm that from ISE debugs, it's possible to see the generation of audit-session-id value (which is never sent over the network):
AcsLogs,2015-10-29 23:25:48,538,DEBUG,0x7fc0b39a4700,cntx=0000032947,CallingStationID=
c04a00146e31,FramedIPAddress=10.62.148.71,MessageFormatter::appendValue() attrName:
cisco-av-pair appending value:
audit-session-id=0a3011ebXbiuDA3yUNoLUvtCRyuPFxkqYJ7TT06foOZ7G1HXj1M
And then, correlation of that after registration of the device on BYOD Page 2:
AcsLogs,2015-10-29 23:25:48,538,DEBUG,0x7fc0b39a4700,cntx=0000032947,CallingStationID=
c04a00146e31,FramedIPAddress=10.62.148.71,Log_Message=[2015-10-29 23:25:48.533 +01:00
0000011874 88010 INFO MyDevices: Successfully registered/provisioned the device
(endpoint), ConfigVersionId=145, UserName=cisco, MacAddress=c0:4a:00:14:6e:31,
IpAddress=10.62.148.71, AuthenticationIdentityStore=Internal Users,
PortalName=BYOD Portal (default), PsnHostName=mgarcarz-ise20.example.com,
GuestUserName=cisco, EPMacAddress=C0:4A:00:14:6E:31, EPIdentityGroup=RegisteredDevices
Staticassignment=true, EndPointProfiler=mgarcarz-ise20.example.com, EndPointPolicy=
Unknown, NADAddress=10.62.148.118, DeviceName=ttt, DeviceRegistrationStatus=Registered
AuditSessionId=0a3011ebXbiuDA3yUNoLUvtCRyuPFxkqYJ7TT06foOZ7G1HXj1M,
cisco-av-pair=audit-session-id=0a3011ebXbiuDA3yUNoLUvtCRyuPFxkqYJ7TT06foOZ7G1HXj1M
In subsequent requests, client is redirected to BYOD Page 3. where NSA is downloaded and executed.
Step 3. Network Setup Assistant Execution
NSA has the same task as web browser. First, it needs to detect what is the IP address of ISE. That is achieved via HTTP redirection.
Because this time user does not have a possibility to type IP address (as in the web browser), that traffic is generated automatically.
Default gateway is used (also enroll.cisco.com can be used) as shown in the image.
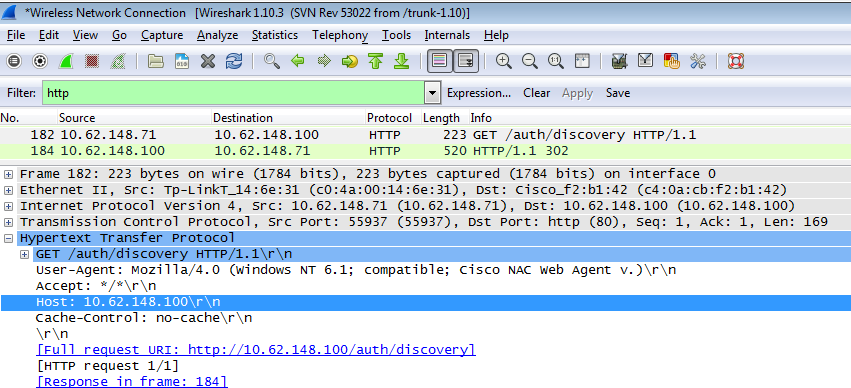
Response is exactly the same as for the web browser.
This way NSA is able to connect to ISE, get xml profile with configuration, generate SCEP request, send it to ISE, get signed certificate (signed by ISE internal CA), configure wireless profile and finally connect to the configured SSID.
Collect logs from the client (on Windows are in %temp%/spwProfile.log). Some outputs are omitted for clarity:
Logging started
SPW Version: 1.0.0.46
System locale is [en]
Loading messages for english...
Initializing profile
SPW is running as High integrity Process - 12288
GetProfilePath: searched path = C:\Users\ADMINI~1.EXA\AppData\Local\Temp\ for file name = spwProfile.xml result: 0
GetProfilePath: searched path = C:\Users\ADMINI~1.EXA\AppData\Local\Temp\Low for file name = spwProfile.xml result: 0
Profile xml not found Downloading profile configuration...
Downloading profile configuration...
Discovering ISE using default gateway
Identifying wired and wireless network interfaces, total active interfaces: 1
Network interface - mac:C0-4A-00-14-6E-31, name: Wireless Network Connection, type: wireless
Identified default gateway: 10.62.148.100
Identified default gateway: 10.62.148.100, mac address: C0-4A-00-14-6E-31
redirect attempt to discover ISE with the response url
DiscoverISE - start
Discovered ISE - : [mgarcarz-ise20.example.com, sessionId: 0a3011ebXbiuDA3yUNoLUvtCRyuPFxkqYJ7TT06foOZ7G1HXj1M]
DiscoverISE - end
Successfully Discovered ISE: mgarcarz-ise20.example.com, session id: 0a3011ebXbiuDA3yUNoLUvtCRyuPFxkqYJ7TT06foOZ7G1HXj1M, macAddress: C0-4A-00-14-6E-31
GetProfile - start
GetProfile - end
Successfully retrieved profile xml
using V2 xml version
parsing wireless connection setting
Certificate template: [keysize:2048, subject:OU=Example unit,O=Company name,L=City,ST=State,C=US, SAN:MAC]
set ChallengePwd
creating certificate with subject = cisco and subjectSuffix = OU=Example unit,O=Company name,L=City,ST=State,C=US
Installed [LAB CA, hash: fd 72 9a 3b b5 33 72 6f f8 45 03 58 a2 f7 eb 27^M
ec 8a 11 78^M
] as rootCA
Installed CA cert for authMode machineOrUser - Success
HttpWrapper::SendScepRequest - Retrying: [1] time, after: [2] secs , Error: [0], msg: [ Pending]
creating response file name C:\Users\ADMINI~1.EXA\AppData\Local\Temp\response.cer
Certificate issued - successfully
ScepWrapper::InstallCert start
ScepWrapper::InstallCert: Reading scep response file [C:\Users\ADMINI~1.EXA\AppData\Local\Temp\response.cer].
ScepWrapper::InstallCert GetCertHash -- return val 1
ScepWrapper::InstallCert end
Configuring wireless profiles...
Configuring ssid [mgarcarz_aruba_tls]
WirelessProfile::SetWirelessProfile - Start
Wireless profile: [mgarcarz_aruba_tls] configured successfully
Connect to SSID
Successfully connected profile: [mgarcarz_aruba_tls]
WirelessProfile::SetWirelessProfile. - End
Those logs are exactly the same as for BYOD process with Cisco devices.
Note: Radius CoA is not required here. It's the application (NSA) which forces reconnection to a newly configured SSID.
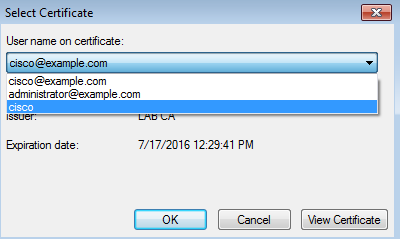
At that stage, user can see that the system tries to associate to a final SSID. If you have more then one user certificate, you must select the correct one (as shown).
After a successful connection, NSA reports is as shown in the image.
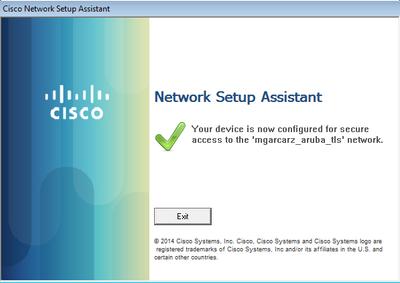
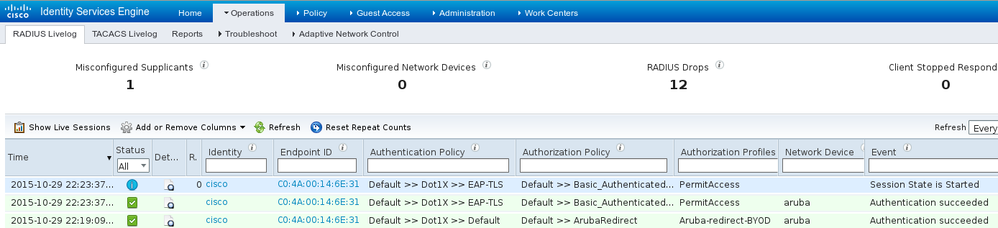
That can be confirmed on ISE - the second log hits EAP-TLS authentication, which matches all the conditions for Basic_Authenticated_Access (EAP-TLS, Employee, and BYOD Registered true).
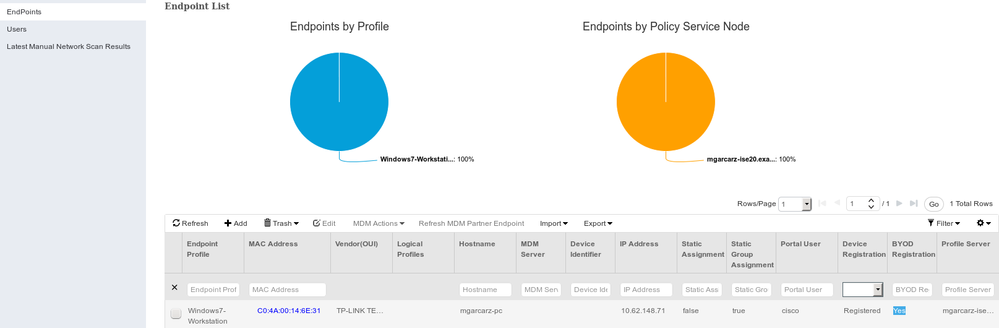
Also, endpoint identity view can confirm that endpoint has BYOD Registered flag set to true as shown in the image.
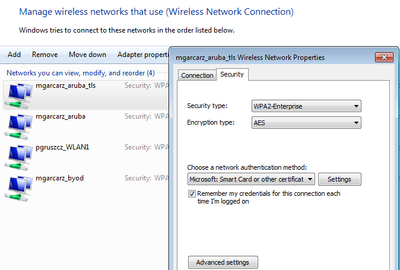
On Windows PC, new wireless profile has been created automatically as preferred (and configured for EAP-TLS) and as shown.
At that stage, Aruba confirms that the user is connected to the final SSID.
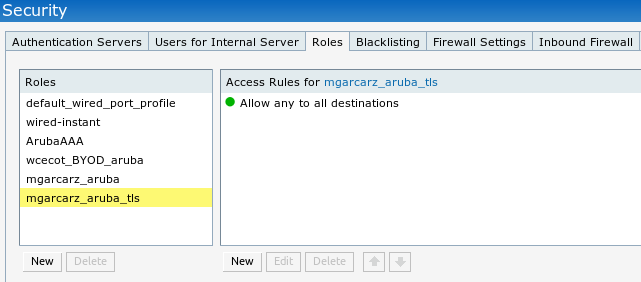
The role which is created automatically and named the same as Network provides full network access.
Other Flows and CoA Support
CWA with CoA
While in BYOD flow there are no CoA messages, CWA flow with Self Registered Guest Portal is demonstrated here:
The Authorization Rules configured are as shown in the image.

User connects to the SSID with MAB authentication and once when it tries to connect to some web page, redirection to Self Registered Guest Portal happens, where Guest can create new account or use current one.
After the guest is successfully connected, CoA message is sent from ISE to Network Device in order to change authorization state.
It can be verified under Operations > Authenitcations and as shown in the image.

CoA message in ISE debugs:
2015-11-02 18:47:49,553 DEBUG [Thread-137][] cisco.cpm.prrt.impl.PrRTLoggerImpl -:::::-
DynamicAuthorizationFlow,DEBUG,0x7fc0e9cb2700,cntx=0000000561,sesn=c59aa41a-e029-4ba0-a31b
-44549024315e,CallingStationID=c04a00157634,[DynamicAuthorizationFlow::createCoACmd]
Processing incoming attribute vendor , name NAS-IP-Address, value=10.62.148.118.,
DynamicAuthorizationFlow.cpp:708
2015-11-02 18:47:49,567 DEBUG [Thread-137][] cisco.cpm.prrt.impl.PrRTLoggerImpl -:::::-
DynamicAuthorizationFlow,DEBUG,0x7fc0e9cb2700,cntx=0000000561,sesn=c59aa41a-e029-4ba0-a31b
-44549024315e,CallingStationID=c04a00157634,[DynamicAuthorizationFlow::createCoACmd]
Processing incoming attribute vendor , name Acct-Session-Id, value=04BD88B88144-
C04A00157634-7AD.,DynamicAuthorizationFlow.cpp:708
2015-11-02 18:47:49,573 DEBUG [Thread-137][] cisco.cpm.prrt.impl.PrRTLoggerImpl -:::::-
DynamicAuthorizationFlow,DEBUG,0x7fc0e9cb2700,cntx=0000000561,sesn=c59aa41a-e029-4ba0-a31b
-44549024315e,CallingStationID=c04a00157634,[DynamicAuthorizationFlow::createCoACmd]
Processing incoming attribute vendor , name cisco-av-pair, v
alue=audit-session-id=0a3011ebisZXypODwqjB6j64GeFiF7RwvyocneEia17ckjtU1HI.,DynamicAuthorizationFlow.cpp:708
2015-11-02 18:47:49,584 DEBUG [Thread-137][] cisco.cpm.prrt.impl.PrRTLoggerImpl -:::::-
DynamicAuthorizationFlow,DEBUG,0x7fc0e9cb2700,cntx=0000000561,sesn=c59aa41a-e029-4ba0-a31b
-44549024315e,CallingStationID=c04a00157634,[DynamicAuthorizationRequestHelper::
setConnectionParams] defaults from nad profile : NAS=10.62.148.118, port=3799, timeout=5,
retries=2 ,DynamicAuthorizationRequestHelper.cpp:59
2015-11-02 18:47:49,592 DEBUG [Thread-137][] cisco.cpm.prrt.impl.PrRTLoggerImpl -:::::-
DynamicAuthorizationFlow,DEBUG,0x7fc0e9cb2700,cntx=0000000561,sesn=c59aa41a-e029-4ba0-a31b
-44549024315e,CallingStationID=c04a00157634,[DynamicAuthorizationRequestHelper::set
ConnectionParams] NAS=10.62.148.118, port=3799, timeout=5, retries=1,
DynamicAuthorizationRequestHelper.cpp:86
2015-11-02 18:47:49,615 DEBUG [Thread-137][] cisco.cpm.prrt.impl.PrRTLoggerImpl -:::::-
DynamicAuthorizationFlow,DEBUG,0x7fc0e9cb2700,cntx=0000000561,sesn=c59aa41a-e029-4ba0-a31b
-44549024315e,CallingStationID=c04a00157634,[DynamicAuthorizationFlow::onLocalHttpEvent]:
invoking DynamicAuthorization,DynamicAuthorizationFlow.cpp:246
and Disconnect-ACK that comes from Aruba:
2015-11-02 18:47:49,737 DEBUG [Thread-147][] cisco.cpm.prrt.impl.PrRTLoggerImpl -:::::-
DynamicAuthorizationFlow,DEBUG,0x7fc0e9eb4700,cntx=0000000561,sesn=c59aa41a-e029-4ba0-a31b
-44549024315e,CallingStationID=c04a00157634,[DynamicAuthorizationFlow::
onResponseDynamicAuthorizationEvent] Handling response
ID c59aa41a-e029-4ba0-a31b-44549024315e, error cause 0, Packet type 41(DisconnectACK).,
DynamicAuthorizationFlow.cpp:303
Packet captures with CoA Diconnect-Request (40) and Diconnect-ACK (41) is as shown.
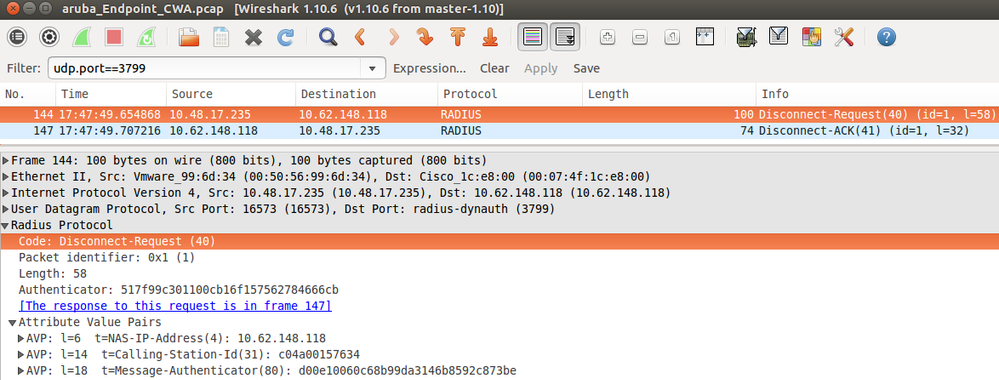
Note: RFC CoA has been used for authentication related to Device Profile Aruba (default settings). For authentication related to Cisco device, it would have been Cisco CoA type reauthenticate.
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use in order to troubleshoot your configuration.
Aruba Captive Portal with IP Address Instead of FQDN
If Captive Portal on Aruba is configured with IP address instead of FQDN of ISE, PSN NSA fails:
Warning - [HTTPConnection] Abort the HTTP connection due to invalid certificate
CN
The reason for that is strict certificate validation when you connect to ISE. When you use IP address in order to connect to ISE (as a result of redirection URL with IP address instead of FQDN) and are presented with ISE certificate with Subject Name = FQDN validation fails.
Note: Web browser continues with BYOD portal (with warning which needs to be approved by user).
Aruba Captive Portal Incorrect Access Policy
By default, Aruba Access-Policy configured with Captive Portal allows for tcp ports 80, 443 and 8080.
NSA is not able to connect to tcp port 8905 in order to get xml profile from ISE. This error is reported:
Failed to get spw profile url using - url
[https://mgarcarz-ise20.example.com:8905/auth/provisioning/evaluate?
typeHint=SPWConfig&referrer=Windows&mac_address=C0-4A-00-14-6E-31&spw_version=
1.0.0.46&session=0a3011ebXbiuDA3yUNoLUvtCRyuPFxkqYJ7TT06foOZ7G1HXj1M&os=Windows All]
- http Error: [2] HTTP response code: 0]
GetProfile - end
Failed to get profile. Error: 2
Aruba CoA Port Number
By default, Aruba provides port number for CoA Air Group CoA port 5999. Unfortunately, Aruba 204 did not respond to such requests (as shown).
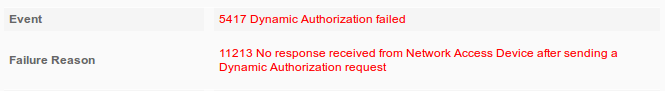
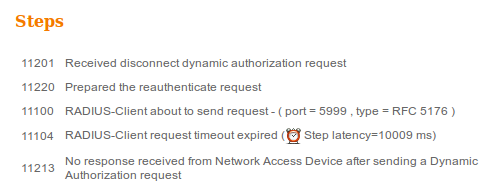
Packet capture is as shown in the image.
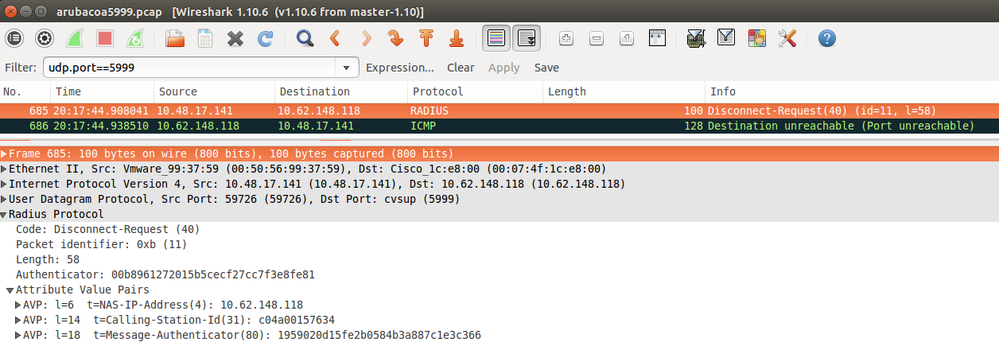
The best option to use here can be CoA port 3977 as described in RFC 5176.
Redirection on Some Aruba Devices
On Aruba 3600 with v6.3 it is noticed that the redirection works slightly different then on other controllers. Packet capture and explanation can be found here.

packet 1: PC is sending GET request to google.com packet 2: Aruba is returning HTTP 200 OK with following content: <meta http-equiv='refresh' content='1; url=http://www.google.com/&arubalp=6b0512fc-f699-45c6-b5cb-e62b3260e5'>\n packet 3: PC is going to link with Aruba attribute returned in packet 2: http://www.google.com/&arubalp=6b0512fc-f699-45c6-b5cb-e62b3260e5 packet 4: Aruba is redirecting to the ISE (302 code): https://10.75.89.197:8443/portal/g?p=4voD8q6W5Lxr8hpab77gL8VdaQ&cmd=login&mac=80:86:f2:59:d9:db&ip=10.75.94.213&essid=SC%2DWiFi&apname=LRC-006&apgroup=default&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww%2Egoogle%2Ecom%2F
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
2.0 |
12-Jul-2023 |
Recertification |
1.0 |
21-Nov-2015 |
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Michal GarcarzCisco TAC Engineer
- Wojciech CecotCisco TAC Engineer
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback