ASA VPN Client Connection Through an L2L Tunnel Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to configure the Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) in order to allow a remote VPN client connection from a Lan-to-Lan (L2L) peer address.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Cisco ASA
- Remote Access VPNs
- LAN-to-LAN VPNs
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the Cisco 5520 Series ASA that runs software Version 8.4(7).
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
Although it is not common to encounter a scenario where a VPN client attempts to establish a connection through a L2L tunnel, administrators might want to assign specific privileges or access restrictions to certain remote users and instruct them to use the software client when access to these resources is required.
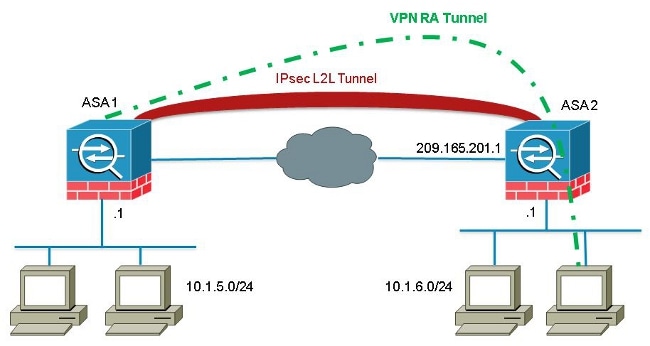
Cisco bug ID CSCuc75090 introduced a behavior change. Previously, with the Private Internet Exchange (PIX), when the Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) proxy did not match a crypto-map Access Control List (ACL), it continued to check entries further down the list. This included matches with a dynamic crypto-map with no peer specified.
This was considered a vulnerability, as remote administrators could gain access to resources that the headend administrator did not intend when the static L2L was configured.
A fix was created that added a check in order to prevent matches with a crypto-map entry without a peer when it already checked a map entry that matched the peer. However, this affected the scenario that is discussed in this document. Specifically, a remote VPN client that attempts to connect from a L2L peer address is not able to connect to the headend.
Configure
Use this section in order to configure the ASA in order to allow a remote VPN client connection from a L2L peer address.
Add a New Dynamic Entry
In order to allow remote VPN connections from L2L peer addresses, you must add a new dynamic entry that contains the same peer IP address.
Here is an example of the previous dynamic crypto-map working configuration:
crypto dynamic-map ra-dyn-map 10 set ikev1 transform-set ESP-AES-128-SHA
crypto map outside_map 1 match address outside_cryptomap_1
crypto map outside_map 1 set peer 209.165.201.1
crypto map outside_map 1 set ikev1 transform-set ESP-AES-128-SHA
crypto map outside_map 65535 ipsec-isakmp dynamic ra-dyn-map
Here is the dynamic crypto-map configuration with the new dynamic entry configured:
crypto dynamic-map ra-dyn-map 10 set ikev1 transform-set ESP-AES-128-SHA
crypto dynamic-map ra-dyn-map 10 set peer 209.165.201.1
crypto dynamic-map ra-dyn-map 20 set ikev1 transform-set ESP-AES-128-SHA
crypto map outside_map 1 match address outside_cryptomap_1
crypto map outside_map 1 set peer 209.165.201.1
crypto map outside_map 1 set ikev1 transform-set ESP-AES-128-SHA
crypto map outside_map 65535 ipsec-isakmp dynamic ra-dyn-map
Verify
There is currently no verification procedure available for this configuration.
Troubleshoot
There is currently no specific troubleshooting information available for this configuration.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
16-Jun-2014 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback