ASA 8.3(x) Dynamic PAT with Two Internal Networks and Internet Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides a sample configuration for dynamic PAT on a Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) that runs software version 8.3(1). Dynamic PAT translates multiple real addresses to a single mapped IP address by translating the real source address and source port to the mapped address and unique mapped port. Each connection requires a separate translation session because the source port differs for each connection.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Ensure that you meet these requirements before you attempt this configuration:
-
Make sure the internal network has two networks located on the inside of the ASA:
-
192.168.0.0/24—Network directly connected to the ASA.
-
192.168.1.0/24—Network on the inside of the ASA, but behind another device (for example, a router).
-
-
Make sure the internal users get PAT as follows:
-
Hosts on the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet will get PAT to a spare IP address given by the ISP (10.1.5.5).
-
Any other host behind the inside of the ASA will get PAT to the outside interface IP address of the ASA (10.1.5.1).
-
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) with version 8.3(1)
-
ASDM version 6.3(1)
Note: Refer to Allowing HTTPS Access for ASDM in order to allow the ASA to be configured by the ASDM.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for information on document conventions.
Configuration
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
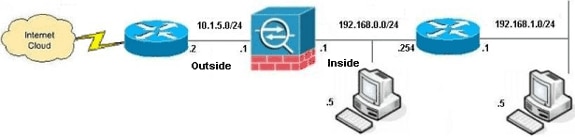
Note: The IP addressing schemes used in this configuration are not legally routable on the Internet. They are RFC 1918 ![]() addresses, which have been used in a lab environment.
addresses, which have been used in a lab environment.
ASA CLI Configuration
This document uses the configurations shown below.
| ASA Dynamic PAT Configuration |
|---|
ASA#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. !--- Creates an object called OBJ_GENERIC_ALL. !--- Any host IP not already matching another configured !--- object will get PAT to the outside interface IP !--- on the ASA (or 10.1.5.1), for internet bound traffic. ASA(config)#object network OBJ_GENERIC_ALL ASA(config-obj)#subnet 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ASA(config-obj)#exit ASA(config)#nat (inside,outside) source dynamic OBJ_GENERIC_ALL interface !--- The above statements are the equivalent of the !--- nat/global combination (as shown below) in v7.0(x), !--- v7.1(x), v7.2(x), v8.0(x), v8.1(x) and v8.2(x) ASA code: nat (inside) 1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 global (outside) 1 interface !--- Creates an object called OBJ_SPECIFIC_192-168-1-0. !--- Any host IP facing the the ‘inside’ interface of the ASA !--- with an address in the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet will get PAT !--- to the 10.1.5.5 address, for internet bound traffic. ASA(config)#object network OBJ_SPECIFIC_192-168-1-0 ASA(config-obj)#subnet 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 ASA(config-obj)#exit ASA(config)#nat (inside,outside) source dynamic OBJ_SPECIFIC_192-168-1-0 10.1.5.5 !--- The above statements are the equivalent of the nat/global !--- combination (as shown below) in v7.0(x), v7.1(x), v7.2(x), v8.0(x), !--- v8.1(x) and v8.2(x) ASA code: nat (inside) 2 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 global (outside) 2 10.1.5.5 |
| ASA 8.3(1) Running Config |
|---|
ASA#show run : Saved : ASA Version 8.3(1) ! hostname ASA enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted names ! !--- Configure the outside interface. ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 nameif outside security-level 0 ip address 10.1.5.1 255.255.255.0 !--- Configure the inside interface. ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 nameif inside security-level 100 ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 shutdown no nameif no security-level no ip address ! interface GigabitEthernet0/3 shutdown no nameif no security-level no ip address ! interface Management0/0 shutdown no nameif no security-level no ip address management-only ! boot system disk0:/asa831-k8.bin ftp mode passive object network OBJ_SPECIFIC_192-168-1-0 subnet 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 object network OBJ_GENERIC_ALL subnet 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 pager lines 24 no failover icmp unreachable rate-limit 1 burst-size 1 asdm image disk0:/asdm-631.bin no asdm history enable arp timeout 14400 nat (inside,outside) source dynamic OBJ_GENERIC_ALL interface nat (inside,outside) source dynamic OBJ_SPECIFIC_192-168-1-0 10.1.5.5 route inside 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.254 1 route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.5.2 timeout xlate 3:00:00 timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02 timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00 mgcp-pat 0:05:00 timeout sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 sip-invite 0:03:00 sip-disconnect 0:02:00 timeout sip-provisional-media 0:02:00 uauth 0:05:00 absolute timeout tcp-proxy-reassembly 0:01:00 dynamic-access-policy-record DfltAccessPolicy http server enable http 192.168.0.0 255.255.254.0 inside no snmp-server location no snmp-server contact snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkup linkdown coldstart crypto ipsec security-association lifetime seconds 28800 crypto ipsec security-association lifetime kilobytes 4608000 telnet timeout 5 ssh timeout 5 console timeout 0 threat-detection basic-threat threat-detection statistics access-list no threat-detection statistics tcp-intercept ! class-map inspection_default match default-inspection-traffic ! ! policy-map type inspect dns preset_dns_map parameters message-length maximum client auto message-length maximum 512 policy-map global_policy class inspection_default inspect dns preset_dns_map inspect ftp inspect h323 h225 inspect h323 ras inspect rsh inspect rtsp inspect esmtp inspect sqlnet inspect skinny inspect sunrpc inspect xdmcp inspect sip inspect netbios inspect tftp inspect ip-options ! service-policy global_policy global prompt hostname context Cryptochecksum:6fffbd3dc9cb863fd71c71244a0ecc5f : end |
ASDM Configuration
In order to complete this configuration through the ASDM interface, you must:
-
Add three network objects; this examples adds these network objects:
-
OBJ_GENERIC_ALL
-
OBJ_SPECIFIC_192-168-1-0
-
10.1.5.5
-
-
Create two NAT/PAT rules; this examples creates NAT rules for these network objects:
-
OBJ_GENERIC_ALL
-
OBJ_SPECIFIC_192-168-1-0
-
Add Network Objects
Complete these steps in order to add network objects:
-
Log in to ASDM, and choose Configuration > Firewall > Objects > Network Objects/Groups.
-
Choose Add > Network Object in order to add a network object.
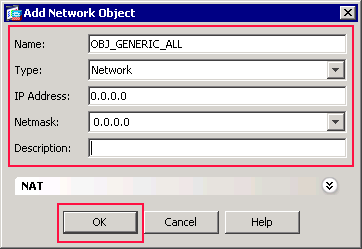
The Add Network Object dialog box appears.
-
Enter this information in the Add Network Object dialog box:
-
Name of the network object. (This example uses OBJ_GENERIC_ALL.)
-
Type of network object. (This example uses Network.)
-
IP address for the network object. (This example uses 0.0.0.0.)
-
Netmask for the network object. (This example uses 0.0.0.0.)
-
-
Click OK.
The network object is created and appears in the Network Objects/Groups list, as shown in this image:
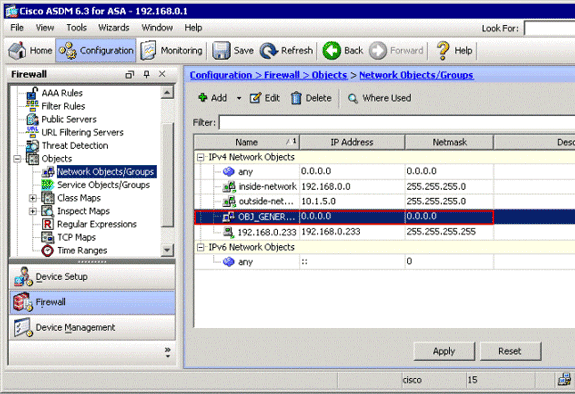
-
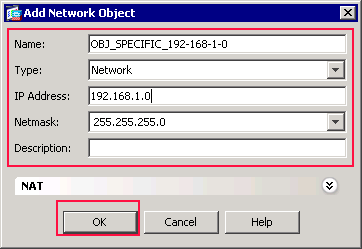
Repeat the previous steps in order to add a second network object, and click OK.
This example uses these values:
-
Name: OBJ_SPECIFIC_192-168-1-0
-
Type: Network
-
IP Address: 192.168.1.0
-
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
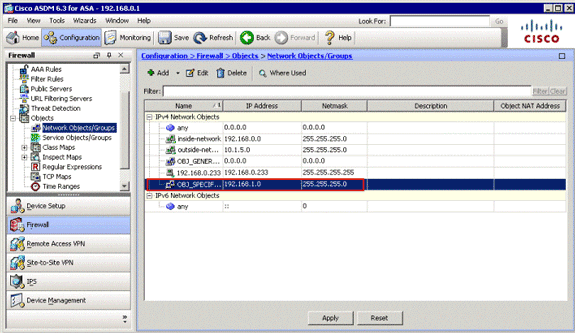
The second object is created and appears in the Network Objects/Groups list, as shown in this image:
-
-
Repeat the previous steps in order to add a third network object, and click OK.
This example uses these values:
-
Name: 10.1.5.5
-
Type: Host
-
IP Address: 10.1.5.5
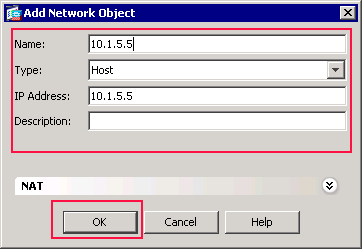
The third network objects is created and appears in the Network Objects/Groups list.
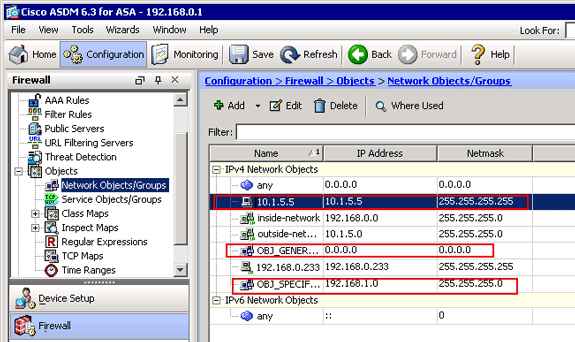
The Network Objects/Groups list should now include the three required objects necessary for the NAT rules to reference.
-
Create NAT/PAT Rules
Complete these steps in order to create NAT/PAT rules:
-
Create the first NAT/PAT rule:
-
In ASDM, choose Configuration > Firewall > NAT Rules, and click Add.
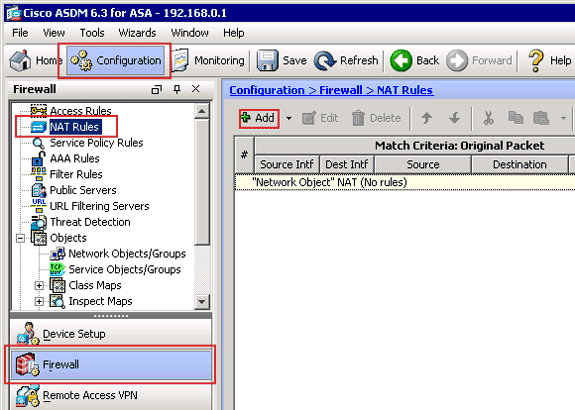
The Add NAT Rule dialog box appears.
-
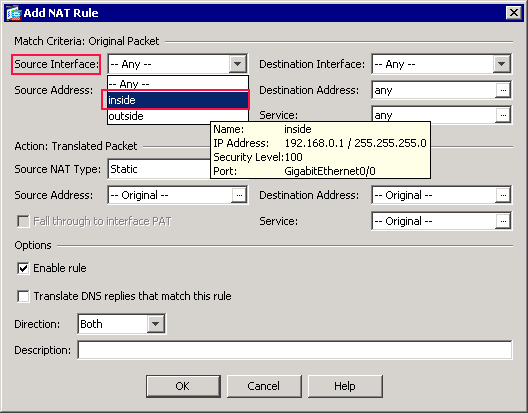
In the Match Criteria: Original Packet area of the Add NAT Rule dialog box, choose inside from the Source Interface drop-down list.
-
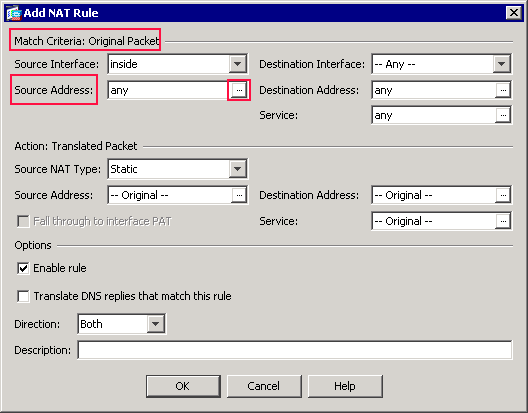
Click the browse (…) button located to the right of the Source Address text field.
The Browse Original Source Address dialog box appears.
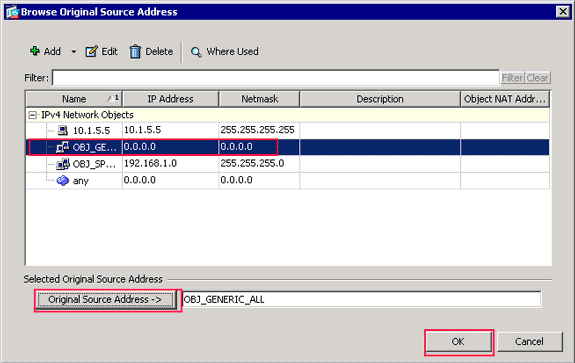
-
In the Browse Original Source Address dialog box, choose the first network object you created. (For this example, choose OBJ_GENERIC_ALL.)
-
Click Original Source Address, and click OK.
The OBJ_GENERIC_ALL network object now appears in the Source Address field in the Match Criteria: Original Packet area of the Add NAT Rule dialog box.
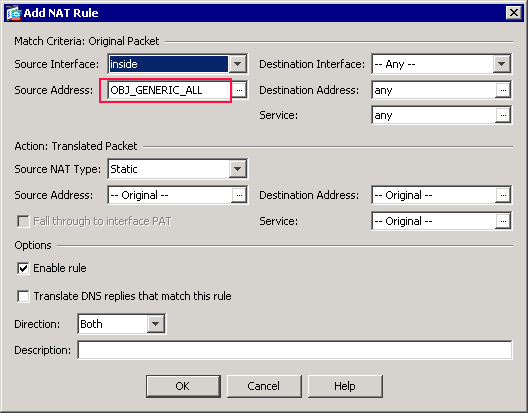
-
In the Action: Translated Packet area of the Add NAT Rule dialog box, choose Dynamic PAT (Hide) from the Source NAT Type dialog box.
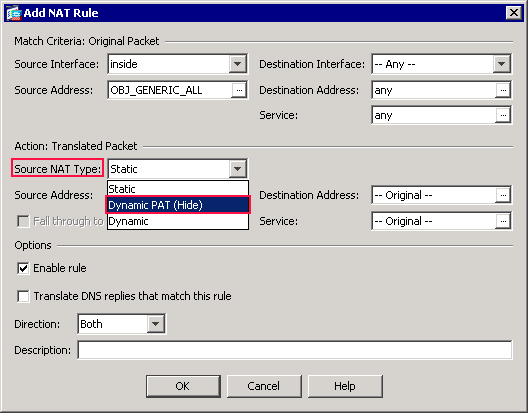
-
Click the browse (…) button located to the right of the Source Address field.
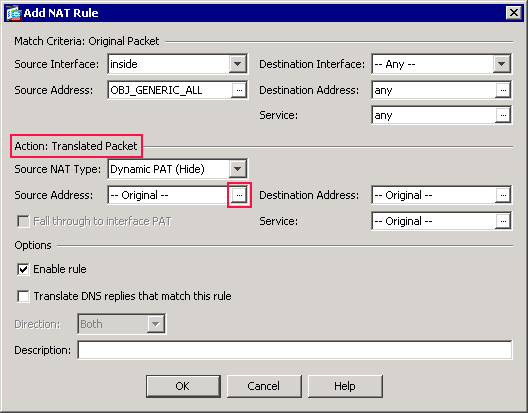
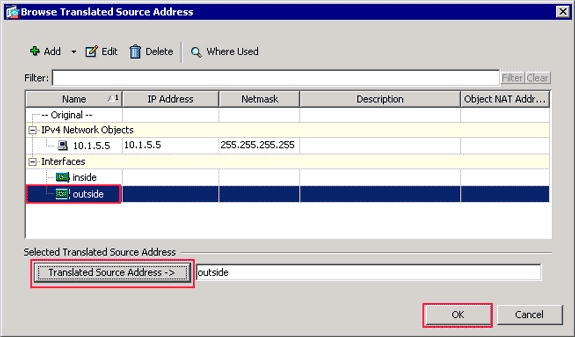
The Browse Translated Source Address dialog box appears.
-
In the Browse Translated Source Address dialog box, choose the outside interface object. (This interface has already been created because it is part of the original configuration.)
-
Click Translated Source Address, and click OK.
The outside interface now appears in the Source Address field in the Action: Translated Packet area on the Add NAT Rule dialog box.
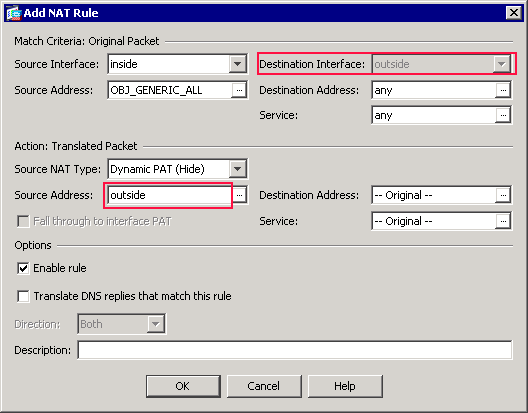
Note: The Destination Interface field also changes to the outside interface.
-
Verify that the first completed PAT Rule appears as follows:
In the Match Criteria: Original Packet area, verify these values:
-
Source Interface = inside
-
Source Address = OBJ_GENERIC_ALL
-
Destination Address = any
-
Service = any
In the Action: Translated Packet area, verify these values:
-
Source NAT Type = Dynamic PAT (Hide)
-
Source Address = outside
-
Destination Address = Original
-
Service = Original
-
-
Click OK.
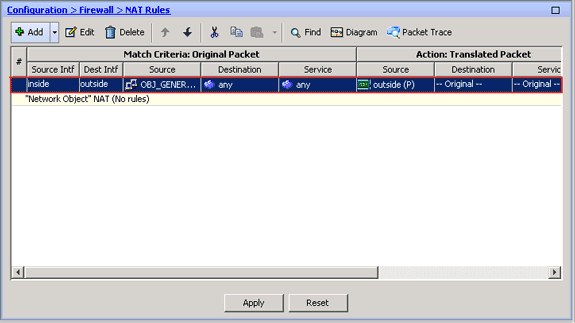
The first NAT rule appears in ASDM, as shown in this image:
-
-
Create the second NAT/PAT rule:
-
In ASDM, choose Configuration > Firewall > NAT Rules, and click Add.
-
In the Match Criteria: Original Packet area of the Add NAT Rule dialog box, choose inside from the Source Interface drop-down list.
-
Click the browse (...) button located to the right of the Source Address field.
The Browse Original Source Address dialog box appears.
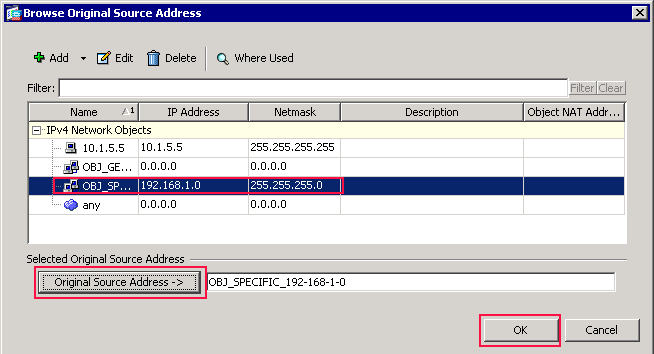
-
In the Browse Original Source Address dialog box, choose the second object you created. (For this example, choose OBJ_SPECIFIC_192-168-1-0.)
-
Click Original Source Address, and click OK.
The OBJ_SPECIFIC_192-168-1-0 network object appears in the Source Address field in the Match Criteria: Original Packet area of the Add NAT Rule dialog box..
-
In the Action: Translated Packet area of the Add NAT Rule dialog box, choose Dynamic PAT (Hide) from the Source NAT Type dialog box.
-
Click the … button located to the right of the Source Address field.
The Browse Translated Source Address dialog box appears.
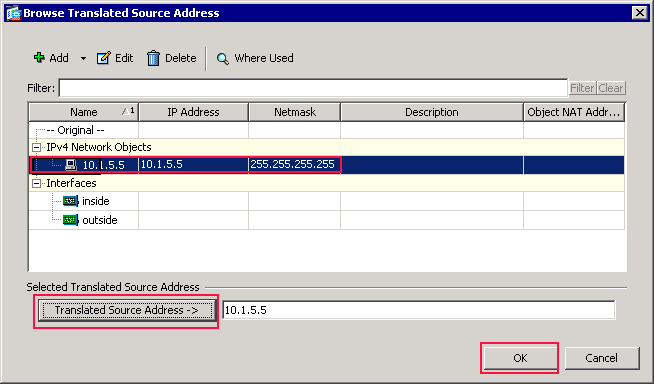
-
In the Browse Translated Source Address dialog box, choose the 10.1.5.5 object. (This interface has already been created because it is part of the original configuration).
-
Click Translated Source Address, and then click OK.
The 10.1.5.5 network object appears in the Source Address field in the Action: Translated Packet area of the Add NAT Rule dialog box..
-
In the Match Criteria: Original Packet area, choose outside from the Destination Interface drop-down list.
Note: If you do not choose outside for this option, the destination interface will reference Any.
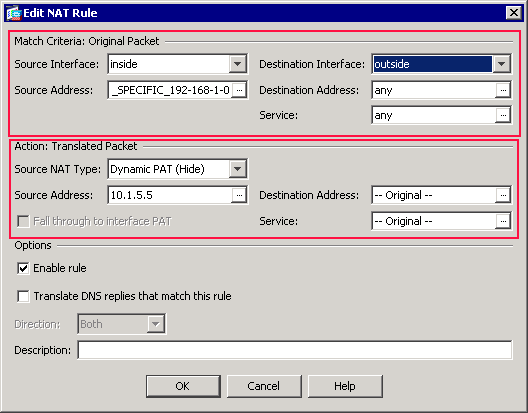
-
Verify that the second completed NAT/PAT rule appears as follows:
In the Match Criteria: Original Packet area, verify these values:
-
Source Interface = inside
-
Source Address = OBJ_SPECIFIC_192-168-1-0
-
Destination Address = outside
-
Service = any
In the Action: Translated Packet area, verify these values:
-
Source NAT Type = Dynamic PAT (Hide)
-
Source Address = 10.1.5.5
-
Destination Address = Original
-
Service = Original
-
-
Click OK.
The completed NAT configuration appears in ASDM, as shown in this image:
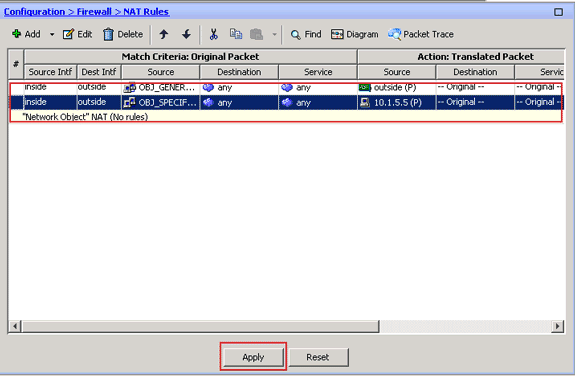
-
-
Click the Apply button in order to apply the changes to the running configuration.
This completes the configuration of dynamic PAT on a Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA).
Verify
Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
Verifying Generic PAT Rule
-
show local-host —Shows the network states of local hosts.
ASA#show local-host Interface outside: 1 active, 2 maximum active, 0 denied local host: <125.252.196.170>, TCP flow count/limit = 2/unlimited TCP embryonic count to host = 0 TCP intercept watermark = unlimited UDP flow count/limit = 0/unlimited !--- The TCP connection outside address corresponds !--- to the actual destination of 125.255.196.170:80 Conn: TCP outside 125.252.196.170:80 inside 192.168.0.5:1051, idle 0:00:03, bytes 13758, flags UIO TCP outside 125.252.196.170:80 inside 192.168.0.5:1050, idle 0:00:04, bytes 11896, flags UIO Interface inside: 1 active, 1 maximum active, 0 denied local host: <192.168.0.5>, TCP flow count/limit = 2/unlimited TCP embryonic count to host = 0 TCP intercept watermark = unlimited UDP flow count/limit = 0/unlimited !--- The TCP PAT outside address corresponds to the !--- outside IP address of the ASA – 10.1.5.1. Xlate: TCP PAT from inside:192.168.0.5/1051 to outside:10.1.5.1/32988 flags ri idle 0:00:17 timeout 0:00:30 TCP PAT from inside:192.168.0.5/1050 to outside:10.1.5.1/17058 flags ri idle 0:00:17 timeout 0:00:30 Conn: TCP outside 125.252.196.170:80 inside 192.168.0.5:1051, idle 0:00:03, bytes 13758, flags UIO TCP outside 125.252.196.170:80 inside 192.168.0.5:1050, idle 0:00:04, bytes 11896, flags UIO -
show conn —Shows the connection state for the designated connection type.
ASA#show conn 2 in use, 3 most used TCP outside 125.252.196.170:80 inside 192.168.0.5:1051, idle 0:00:06, bytes 13758, flags UIO TCP outside 125.252.196.170:80 inside 192.168.0.5:1050, idle 0:00:01, bytes 13526, flags UIO -
show xlate —Shows the information about the translation slots.
ASA#show xlate 4 in use, 7 most used Flags: D - DNS, I - dynamic, r - portmap, s - static, I - identity, T - twice TCP PAT from inside:192.168.0.5/1051 to outside:10.1.5.1/32988 flags ri idle 0:00:23 timeout 0:00:30 TCP PAT from inside:192.168.0.5/1050 to outside:10.1.5.1/17058 flags ri idle 0:00:23 timeout 0:00:30
Verifying Specific PAT Rule
-
show local-host —Shows the network states of local hosts.
ASA#show local-host Interface outside: 1 active, 2 maximum active, 0 denied local host: <125.252.196.170>, TCP flow count/limit = 2/unlimited TCP embryonic count to host = 0 TCP intercept watermark = unlimited UDP flow count/limit = 0/unlimited !--- The TCP connection outside address corresponds to !--- the actual destination of 125.255.196.170:80. Conn: TCP outside 125.252.196.170:80 inside 192.168.1.5:1067, idle 0:00:07, bytes 13758, flags UIO TCP outside 125.252.196.170:80 inside 192.168.1.5:1066, idle 0:00:03, bytes 11896, flags UIO Interface inside: 1 active, 1 maximum active, 0 denied local host: <192.168.0.5>, TCP flow count/limit = 2/unlimited TCP embryonic count to host = 0 TCP intercept watermark = unlimited UDP flow count/limit = 0/unlimited !--- The TCP PAT outside address corresponds to an !--- outside IP address of 10.1.5.5. Xlate: TCP PAT from inside:192.168.1.5/1067 to outside:10.1.5.5/35961 flags ri idle 0:00:17 timeout 0:00:30 TCP PAT from inside:192.168.1.5/1066 to outside:10.1.5.5/23673 flags ri idle 0:00:17 timeout 0:00:30 Conn: TCP outside 125.252.196.170:80 inside 192.168.1.5:1067, idle 0:00:07, bytes 13758, flags UIO TCP outside 125.252.196.170:80 inside 192.168.1.5:1066, idle 0:00:03, bytes 11896, flags UIO -
show conn —Shows the connection state for the designated connection type.
ASA#show conn 2 in use, 3 most used TCP outside 125.252.196.170:80 inside 192.168.1.5:1067, idle 0:00:07, bytes 13653, flags UIO TCP outside 125.252.196.170:80 inside 192.168.1.5:1066, idle 0:00:03, bytes 13349, flags UIO -
show xlate —Shows the information about the translation slots.
ASA#show xlate 3 in use, 9 most used Flags: D - DNS, I - dynamic, r - portmap, s - static, I - identity, T - twice TCP PAT from inside:192.168.1.5/1067 to outside:10.1.5.5/35961 flags ri idle 0:00:23 timeout 0:00:30 TCP PAT from inside:192.168.1.5/1066 to outside:10.1.5.5/29673 flags ri idle 0:00:23 timeout 0:00:30
Troubleshoot
There is currently no specific troubleshooting information available for this configuration.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
09-Mar-2010 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)






















 Feedback
Feedback