PIX/ASA: PPPoE Client Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides a sample configuration for the ASA/PIX security appliance as a Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) client for versions 7.2.(1) and above.
PPPoE combines two widely accepted standards, Ethernet and PPP, in order to provide an authenticated method that assigns IP addresses to client systems. PPPoE clients are typically personal computers connected to an ISP over a remote broadband connection, such as DSL or cable service. ISPs deploy PPPoE because it is easier for customers to use and it uses their existing remote access infrastructure in order to support high-speed broadband access.
PPPoE provides a standard method to employ the authentication methods of the PPPoE network. When used by ISPs, PPPoE allows authenticated assignment of IP addresses. In this type of implementation, the PPPoE client and server are interconnected by Layer 2 bridging protocols that run over a DSL or other broadband connection.
PPPoE is composed of two main phases:
-
Active Discovery Phase—In this phase, the PPPoE client locates a PPPoE server, called an access concentrator, where a session ID is assigned and the PPPoE layer is established
-
PPP Session Phase—In this phase, Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) options are negotiated and authentication is performed. Once the link setup is complete, PPPoE functions as a Layer 2 encapsulation method, which allows data to be transferred over the PPP link within PPPoE headers.
At system initialization, the PPPoE client exchanges a series of packets in order to establish a session with the access concentrator. Once the session is established, a PPP link is set up, which uses Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) for authentication. Once the PPP session is established, each packet is encapsulated in the PPPoE and PPP headers.
Note: PPPoE is not supported when failover is configured on the adaptive security appliance, or in multiple context or transparent mode. PPPoE is only supported in single, routed mode, without failover.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) version 8.x and later.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Related Products
This configuration can also be used with the Cisco PIX 500 Series Security Appliance, which runs version 7.2(1) and later. In order to configure the PPPoE client on the Cisco Secure PIX Firewall, PIX OS version 6.2 introduces this function and is targeted for the low-end PIX (501/506). For more information, refer to Configuring the PPPoE Client on a Cisco Secure PIX Firewall
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Configure
This section provides the information necessary to configure the features described in this document.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) to obtain more information on the commands used in this section.
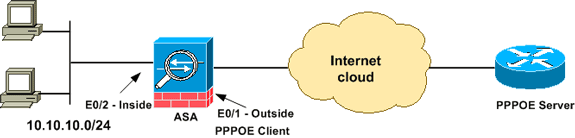
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
CLI Configuration
This document uses these configurations:
| Device Name 1 |
|---|
ciscoasa#show running-config : Saved : ASA Version 8.0(2) ! hostname ciscoasa enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted names ! interface Ethernet0/0 nameif dmz security-level 50 ip address 10.77.241.111 255.255.255.192 ! interface Ethernet0/1 nameif outside security-level 0 !--- Specify a VPDN group for the PPPoE client pppoe client vpdn group CHN !--- "ip address pppoe [setroute]" !--- The setroute option sets the default routes when the PPPoE client has !--- not yet established a connection. When you use the setroute option, you !--- cannot use a statically defined route in the configuration. !--- PPPoE is not supported in conjunction with DHCP because with PPPoE !--- the IP address is assigned by PPP. The setroute option causes a default !--- route to be created if no default route exists. !--- Enter the ip address pppoe command in order to enable the !--- PPPoE client from interface configuration mode. ip address pppoe ! interface Ethernet0/2 nameif inside security-level 100 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/3 shutdown no nameif no security-level no ip address ! interface Management0/0 shutdown no nameif no security-level no ip address ! passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted boot system disk0:/asa802-k8.bin ftp mode passive access-list 100 extended permit ip any any access-list inside_nat0_outbound extended permit ip 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 10. 20.10.0 255.255.255.0 inactive pager lines 24 mtu dmz 1500 !--- The maximum transmission unit (MTU) size is automatically set to 1492 bytes, !--- which is the correct value to allow PPPoE transmission within an Ethernet frame. mtu outside 1492 mtu inside 1500 !--- Output suppressed. global (outside) 1 interface nat (inside) 1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 !--- The NAT statements above are for ASA version 8.2 and earlier. !--- For ASA versions 8.3 and later the NAT statements are modified as follows. object network obj_any subnet 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 nat (inside,outside) dynamic interface !--- Output suppressed. telnet timeout 5 ssh timeout 5 console timeout 0 !--- Define the VPDN group to be used for PPPoE. vpdn group CHN request dialout pppoe !--- Associate the user name assigned by your ISP to the VPDN group. vpdn group CHN localname cisco !--- If your ISP requires authentication, select an authentication protocol. vpdn group CHN ppp authentication pap !--- Create a user name and password for the PPPoE connection. vpdn username cisco password ********* threat-detection basic-threat threat-detection statistics access-list ! class-map inspection_default match default-inspection-traffic ! ! policy-map type inspect dns preset_dns_map parameters message-length maximum 512 policy-map global_policy class inspection_default inspect dns preset_dns_map inspect ftp inspect h323 h225 inspect h323 ras inspect netbios inspect rsh inspect rtsp inspect skinny inspect esmtp inspect sqlnet inspect sunrpc inspect tftp inspect sip inspect xdmcp ! service-policy global_policy global username cisco123 password ffIRPGpDSOJh9YLq encrypted privilege 15 prompt hostname context Cryptochecksum:3cf813b751fe78474dfb1d61bb88a133 : end ciscoasa# |
ASDM Configuration
Complete these steps in order to configure the PPPoE client provided with the adaptive security appliance:
Note: Refer to Allowing HTTPS Access for ASDM in order to allow the ASA to be configured by the ASDM.
-
Access the ASDM on the ASA:
Open your browser, and enter https://<ASDM_ASA_IP_ADDRESS>.
Where ASDM_ASA_IP_ADRESS is the IP address of the ASA interface that is configured for ASDM access.
Note: Make sure to authorize any warnings your browser gives you related to SSL certificate authenticity. The default user name and password are both blank.
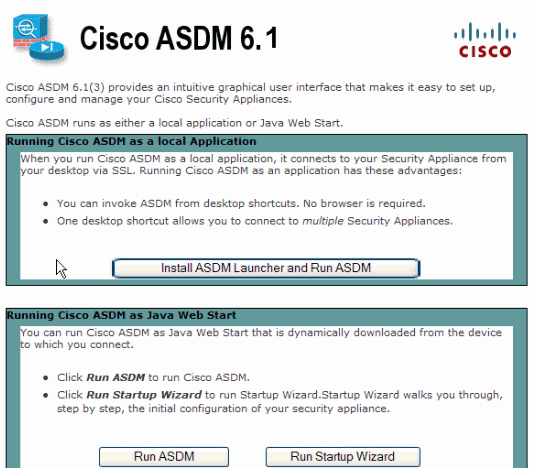
The ASA displays this window to allow the download of the ASDM application. This example loads the application onto the local computer and does not run in a Java applet.
-
Click Download ASDM Launcher and Start ASDM in order to download the installer for the ASDM application.
-
Once the ASDM Launcher downloads, complete the steps directed by the prompts in order to install the software, and run the Cisco ASDM Launcher.
-
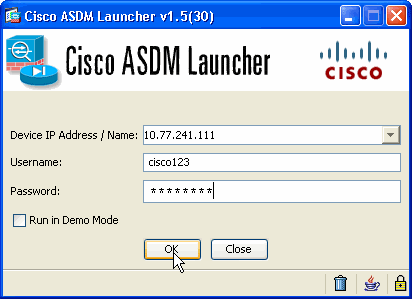
Enter the IP address for the interface you configured with the http - command, and a user name and password if you specified one.
This example uses cisco123 for the user name and cisco123 as the password.
-
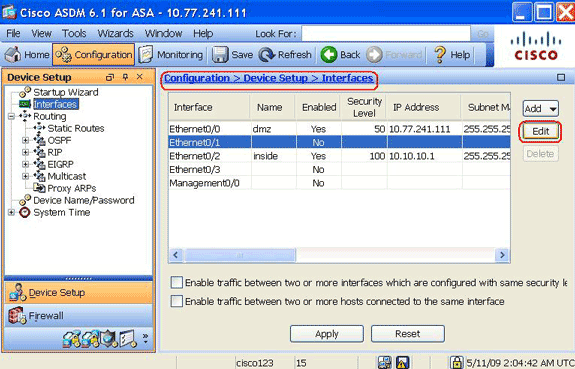
Choose Configuration > Device Setup > Interfaces, highlight the outside interface, and click Edit.
-
In the Interface Name field, enter outside, and check the Enable Interface check box.
-
Click the Use PPPoE radio button in the IP Address area.
-
Enter a group name, PPPoE user name and password, and click the appropriate PPP authentication type (PAP, CHAP, or MSCHAP) radio button.
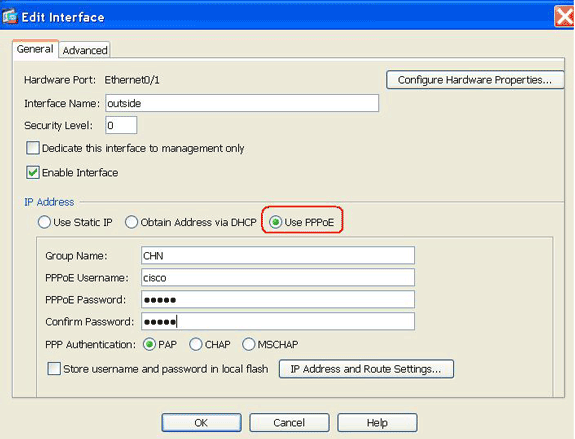
-
Click the Advanced tab, and verify that the MTU size is set to 1492.
Note: The maximum transmission unit (MTU) size is automatically set to 1492 bytes, which is the correct value to allow PPPoE transmission within an Ethernet frame.
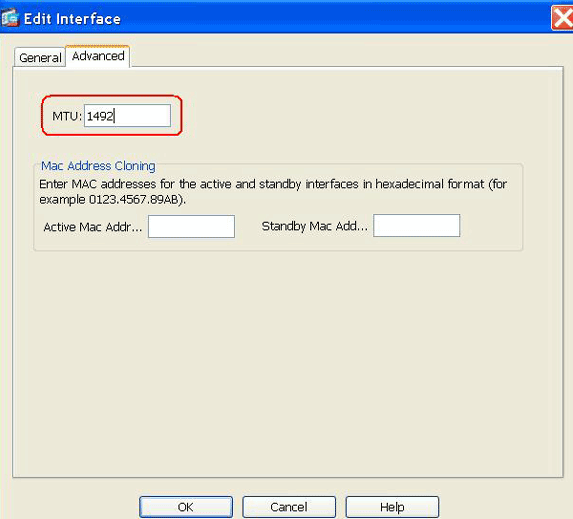
-
Click OK to continue.
-
Verify that the information you entered is correct, and click Apply.
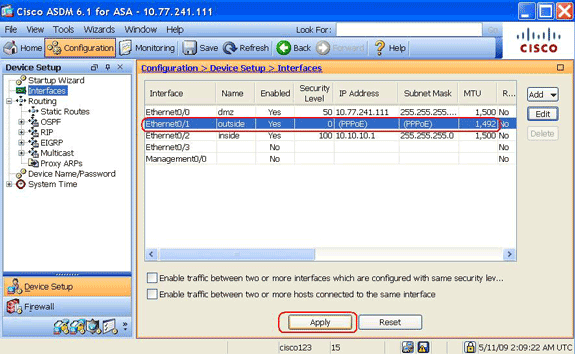
Verify
Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
-
show ip address outside pppoe—Use this command in order to display the current PPPoE client configuration information.
-
show vpdn session [l2tp | pppoe] [id sess_id | packets | state | window]—Use this command in order to view the status of PPPoE sessions.
The following example shows a sample of information provided by this command:
hostname#show vpdn
Tunnel id 0, 1 active sessions
time since change 65862 secs
Remote Internet Address 10.0.0.1
Local Internet Address 199.99.99.3
6 packets sent, 6 received, 84 bytes sent, 0 received
Remote Internet Address is 10.0.0.1
Session state is SESSION_UP
Time since event change 65865 secs, interface outside
PPP interface id is 1
6 packets sent, 6 received, 84 bytes sent, 0 received
hostname#show vpdn session
PPPoE Session Information (Total tunnels=1 sessions=1)
Remote Internet Address is 10.0.0.1
Session state is SESSION_UP
Time since event change 65887 secs, interface outside
PPP interface id is 1
6 packets sent, 6 received, 84 bytes sent, 0 received
hostname#show vpdn tunnel
PPPoE Tunnel Information (Total tunnels=1 sessions=1)
Tunnel id 0, 1 active sessions
time since change 65901 secs
Remote Internet Address 10.0.0.1
Local Internet Address 199.99.99.3
6 packets sent, 6 received, 84 bytes sent, 0 received
hostname#
Clearing the Configuration
In order to remove all vpdn group commands from the configuration, use the clear configure vpdn group command in global configuration mode:
hostname(config)#clear configure vpdn group
In order to remove all vpdn username commands, use the clear configure vpdn username command:
hostname(config)#clear configure vpdn username
Note: These commands have no affect on active PPPoE connections.
Troubleshoot
Troubleshooting Commands
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
Note: Refer to Important Information on Debug Commands before you use debug commands.
-
hostname# [no] debug pppoe {event | error | packet}—Use this command in order to enable or disable debugging for the PPPoE client.
Subnet Mask Appears as /32
Problem
When you use the IP address x.x.x.x 255.255.255.240 pppoe setroute command, the IP address is assigned correctly, but the subnet mask appears as /32 although it is specified in the command as /28. Why does this happen?
Solution
This is the correct behavior. The the subnet mask is irrelevant in the case of the PPPoe interface; the ASA will always change it to /32.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
11-May-2009 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)






 Feedback
Feedback