ASA 8.X: AnyConnect Start Before Logon Feature Configuration
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
With Start Before Logon (SBL) enabled, the user sees the AnyConnect GUI logon dialog before the Windows® logon dialog box appears. This establishes the VPN connection first. Available only for Windows platforms, Start Before Logon lets the administrator control the use of login scripts, password caching, mapping network drives to local drives, and more. You can use the SBL feature to activate the VPN as part of the logon sequence. SBL is disabled by default.
For more information on configuring AnyConnect VPN Client features, refer to the section Configuring AnyConnect Client Features.
Note: Within the AnyConnect client, the only configuration you do for SBL is to enable the feature. Network administrators handle the processing that goes on before logon based upon the requirements of their situation. Logon scripts can be assigned to a domain or to individual users. Generally, the administrators of the domain have batch files or the like defined with users or groups in Active Directory. As soon as the user logs on, the login script is executed.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliances that run software version 8.x
-
Cisco AnyConnect VPN version 2.0
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
The point of SBL is that it connects a remote computer to the company infrastructure prior to logon to the PC. For example, a user can be outside the physical corporate network, unable to access corporate resources until his or her PC has joined the corporate network. With SBL enabled, the AnyConnect client connects before the user sees the Microsoft login window. The user must also log in, as usual, to Windows when the Microsoft login window appears.
These are several reasons to use SBL:
-
The PC of the user is joined to an Active Directory infrastructure.
-
The user cannot have cached credentials on the PC, that is, if the group policy disallows cached credentials.
-
The user must run login scripts that execute from a network resource or that require access to a network resource.
-
A user has network-mapped drives that require authentication with the Active Directory infrastructure.
-
Networking components, such as MS NAP/CS NAC, can require connection to the infrastructure.
SBL creates a network that is equivalent to inclusion on the local corporate LAN. With SBL enabled, since the user has access to the local infrastructure, the logon scripts that normally run for a user in the office are also available to the remote user.
For information about how to create logon scripts, refer to this Microsoft TechNet article ![]() .
.
For information about how to use local logon scripts in Windows XP, refer to this Microsoft article ![]() .
.
In another example, a system can be configured to disallow cached credentials for logon to the PC. In this scenario, users must be able to communicate with a domain controller on the corporate network for their credentials to be validated prior to access to the PC. SBL requires a network connection to be present at the time it is invoked. In some cases, this is not possible because a wireless connection can depend on user credentials to connect to the wireless infrastructure. Since SBL mode precedes the credential phase of a login, a connection is not available in this scenario. In this case, the wireless connection needs to be configured to cache the credentials across login, or another wireless authentication needs to be configured for SBL to work.
Install Start Before Logon Components (Windows Only)
The Start Before Logon components must be installed after the core client has been installed. Additionally, the AnyConnect 2.2 Start Before Logon components require that version 2.2, or later, of the core AnyConnect client software be installed. If you pre-deploy the AnyConnect client and the Start Before Logon components with the MSI files (for example, you are at a big company that has its own software deployment (Altiris, Active Directory, or SMS), you must get the order right. The order of the installation is handled automatically when the administrator loads AnyConnect if it is web deployed and/or web updated. For complete installation information, refer to Release Notes for Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.2.
Differences Between Windows-Vista\Windows 7 and Pre-Vista Start Before Logon
The procedures to enable SBL differ slightly on Windows Vista and Windows 7 systems. Pre-Vista systems use a component called virtual private network graphical identification and authentication (VPNGINA) to implement SBL. Vista and Windows 7 systems use a component called PLAP to implement SBL.
In the AnyConnect client, the Windows Vista Start Before Logon feature is known as the Pre-Login Access Provider (PLAP), which is a connectable credential provider. This feature lets network administrators perform specific tasks, such as the collection of credentials or connection to network resources, prior to login. PLAP provides Start Before Logon functions on Windows Vista, Windows 7 and the Windows 2008 server. PLAP supports 32-bit and 64-bit versions of the operating system with vpnplap.dll and vpnplap64.dll, respectively. The PLAP function supports Windows Vista x86 and x64 versions.
Note: In this section, VPNGINA refers to the Start Before Logon feature for pre-Vista platforms, and PLAP refers to the Start Before Logon feature for Windows Vista and Windows 7 systems.
In pre-Vista systems, Start Before Logon uses a component known as the VPN Graphical Identification and Authentication Dynamic Link Library (vpngina.dll) to provide Start Before Logon capabilities. The Windows PLAP component, which is part of Windows Vista, replaces the Windows GINA component.
A GINA is activated when a user presses the Ctrl+Alt+Del key combination. With PLAP, the Ctrl+Alt+Del key combination opens a window where the user can choose either to log in to the system or activate any Network Connections (PLAP components) with the Network Connect button in the lower-right corner of the window.
The sections that immediately follow describe the settings and procedures for both VPNGINA and PLAP SBL. For a complete description of enablement and use of the SBL feature (PLAP) on a Windows Vista platform, refer to Configuring Start Before Logon (PLAP) on Windows Vista Systems.
XML Settings to Enable SBL
The element value for UseStartBeforeLogon allows this feature to be turned on (true) or off (false). If you set this value to true in the profile, additional processing occurs as part of the logon sequence. See the Start Before Logon description for additional details. Set the <UseStartBefore Logon> value in the CiscoAnyConnect.xml file to true to enable SBL:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <Configuration> <ClientInitialization> <UseStartBeforeLogon>true</UseStartBeforeLogon> </ClientInitialization>
In order to disable SBL, set the same value to false.
In order to enable the UserControllable feature, use this statement when you enable SBL:
<UseStartBeforeLogon userControllable="false">true</UseStartBeforeLogon>
Any user setting associated with this attribute is stored elsewhere.
Enable SBL
In order to minimize download time, the AnyConnect client requests downloads (from the security appliance) only of core modules that it needs for each feature that it supports. In order to enable new features, such as SBL, you must specify the module name with the svc modules command from group policy WebVPN or username WebVPN configuration mode:
[no] svc modules {none | value string}
The string value for SBL is vpngina.
In this example, the network administrator enters group-policy attributes mode for the group policy telecommuters; enters WebVPN configuration mode for the group policy; and specifies the string VPNGINA to enable SBL:
hostname(config)# group-policy telecommuters attributes hostname(config-group-policy)# webvpn hostame(config-group-webvpn)# svc modules value vpngina
In addition, the administrator must ensure that the AnyConnect <profile.xml> file, where <profile.xml> is the name that the network administrator has assigned to the XML file, has the <UseStartBeforeLogon> statement set to true, for example:
UseStartBeforeLogon UserControllable="false">true
The system must be rebooted before Start Before Logon takes effect. You must also specify on the security appliance that you want to allow SBL, or any other modules for additional features. Refer to the description in the Enabling Modules for Additional AnyConnect Features, page 2-5 (ASDM) section or Enabling Modules for Additional AnyConnect Features, page 3-4 (CLI) for more information.
Start Before Logon Configuration with CLI
This scenario shows you how to set up the XML file with CLI:
-
Create a profile to be pushed down to the client PCs that looks similar to this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <AnyConnectProfile xmlns="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/encoding/" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi :schemaLocation= "http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/encoding/ AnyConnectProfile.xsd"> <ClientInitialization> <UseStartBeforeLogon>true</UseStartBeforeLogon> </ClientInitialization> <ServerList> <HostEntry> <HostName>text.cisco.com</HostName> </HostEntry> <HostEntry> <HostName>test1.cisco.com</HostName> <HostAddress>1.1.1.1</HostAddress> </HostEntry> . . . <HostEntry> <HostName>test2.cisco.com</HostName> <HostAddress>1.1.1.2</HostAddress> </HostEntry> </ServerList> </AnyConnectProfile>
-
Copy the file to the Flash on the security appliance:
Copy tftp://x.x.x.x/AnyConnectProfile.xml AnyConnectProfile.xml
-
On the security appliance, add the profile as an available profile to the WebVPN global section, as long as everything else is set up correctly for AnyConnect connections:
hostname(config-group-policy)# webvpn hostame(config-group-webvpn)# svc profiles ReallyNewProfile disk0:/AnyConnectProfile.xml
-
Edit the group policy that you use, and add the svc modules and svc profile commands:
hostname(config)# group-policy GroupPolicy internal hostname(config)# group-policy GroupPolicy attributes hostname(config-group-policy)# webvpn hostame(config-group-webvpn)# svc modules value vpngina hostame(config-group-webvpn)# svc profiles value ReallyNewProfile
Start Before Logon Configuration with ASDM
Complete these steps to configure the SBL with ASDM:
-
Create a profile to be pushed down to the client PCs that looks similar to this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <AnyConnectProfile xmlns="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/encoding/" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi :schemaLocation= "http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/encoding/ AnyConnectProfile.xsd"> <ClientInitialization> <UseStartBeforeLogon>true</UseStartBeforeLogon> </ClientInitialization> <ServerList> <HostEntry> <HostName>text.cisco.com</HostName> </HostEntry> <HostEntry> <HostName>test1.cisco.com</HostName> <HostAddress>1.1.1.1</HostAddress> </HostEntry> . . . <HostEntry> <HostName>test2.cisco.com</HostName> <HostAddress>1.1.1.2</HostAddress> </HostEntry> </ServerList> </AnyConnectProfile>
-
Save the profile as AnyConnectProfile.xml in the local computer.
-
Launch the ASDM, and go to the Home page.
-
Go to Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Group Policies > Add , and click the Internal Group Policy.
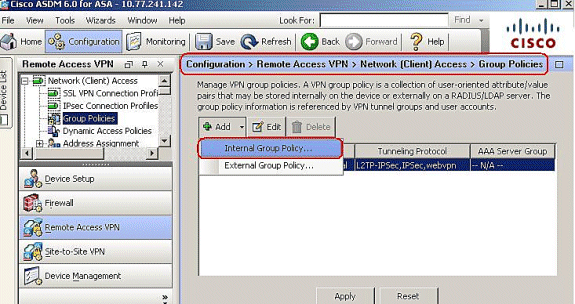
-
Enter the name of the group policy, for example, SBL.
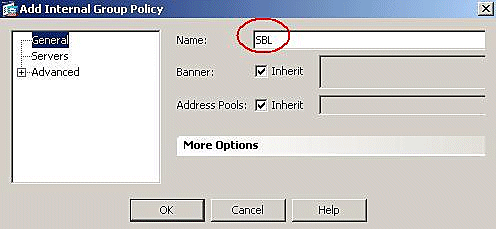
-
Go to Advanced > SSL VPN Client. Remove the Inherit check mark in the Optional Client Module to Download, and choose vpngina from the drop-down box.
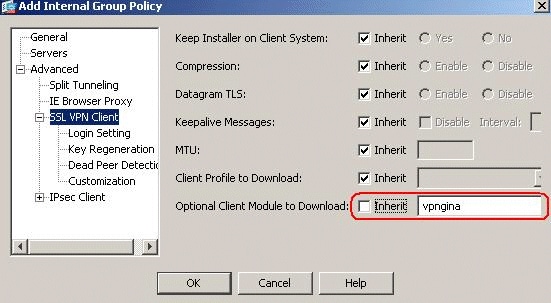
-
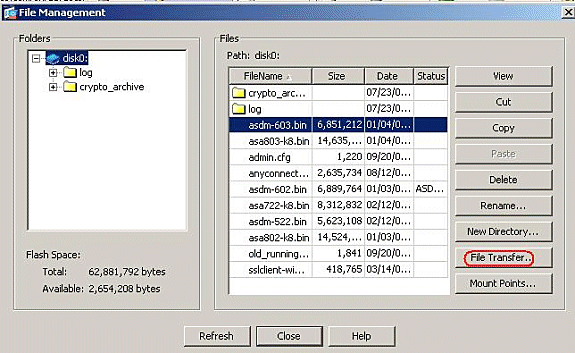
In order to transfer the profile AnyConnectProfile.xml from the local computer to Flash, go to Tools, and click File Management.
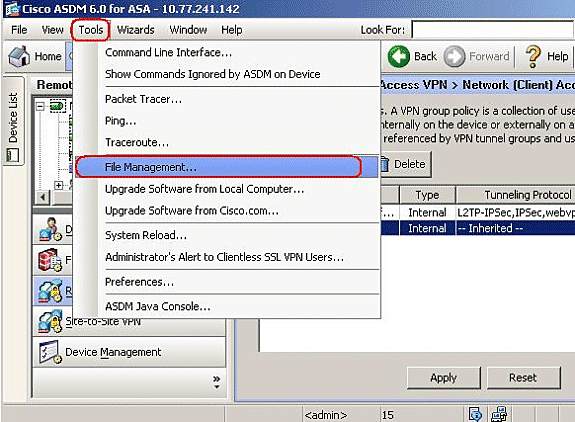
-
Click the File Transfer button.
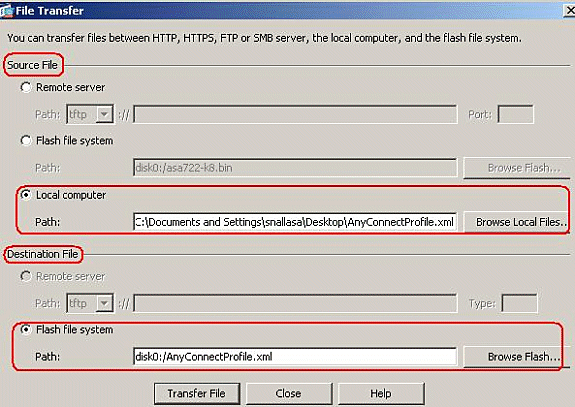
-
In order to transfer the profile from the local computer to ASA Flash memory, choose the Source File, path of the XML file (local computer), and the Destination File path as per your requirement.
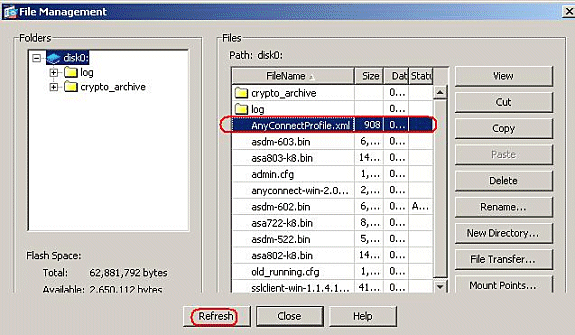
-
After the transfer, click the Refresh button to verify whether the profile file is in the Flash memory.
-
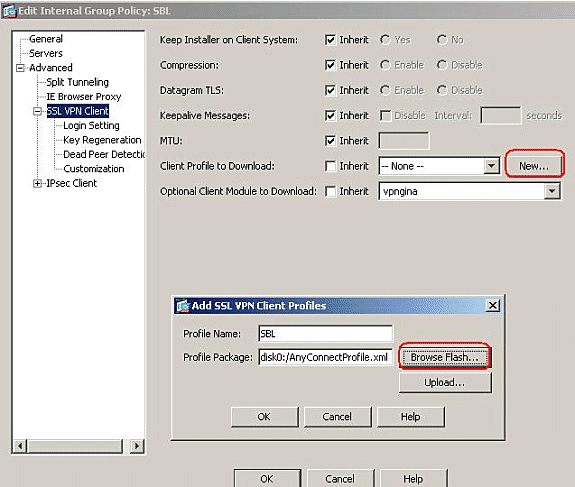
Assign the profile to the internal group policy (SBL).
Follow this path, Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Group Policies > Edit SBL ( Internal Group Policy ) > Advanced > SSL VPN Client > Client Profile to Download, and click the New button.
In the Add SSL VPN Client Profiles, click the Browse button to choose the location of the profile(AnyConnectProfile.xml) stored in the ASA Flash memory. Assign the Name for the profile, for example, SBL. Click OK to complete.
-
Remove the Inherit check box and choose SBL in the Client Profile to Download field. Click OK.
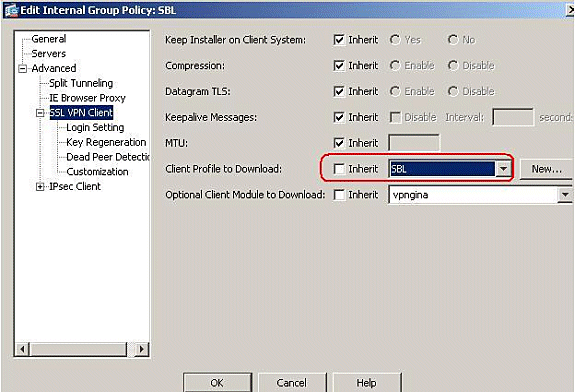
-
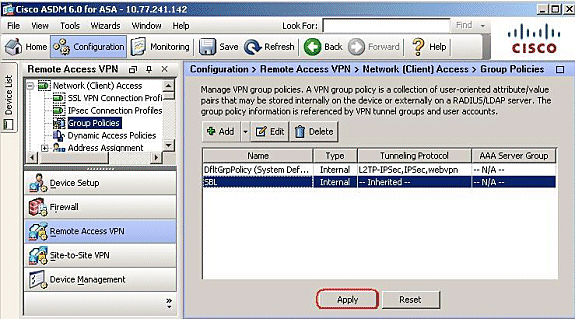
Click Apply to complete.
Use the Manifest File
The AnyConnect package that is uploaded on the security appliance contains a file called VPNManifest.xml. This example shows a sample content of this file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-7"?> <vpn rev="1.0"> <file version="2.1.0150" id="VPNCore" is_core="yes" type="exe" action="install"> <uri>binaries/anyconnect-win-2.1.0150-web-deploy-k9.exe</uri> </file> <file version="2.1.0150" id="gina" is_core="yes" type="exe" action="install" module="vpngina"> <uri>binaries/anyconnect-gina-win-2.1.0150-web-deploy-k9.exe</uri> </file> </vpn>
The security appliance has stored on it configured profiles, as explained in Step 1, and it also stores one or multiple AnyConnect packages that contain the AnyConnect client itself, downloader utility, manifest file, and any other optional modules or support files.
When a remote user connects to the security appliance with WebLaunch or a current standalone client, the downloader is downloaded first and run. It uses the manifest file to ascertain whether there is a current client on the remote user PC that needs to be upgraded, or a fresh installation is required. The manifest file also contains information about whether there are any optional modules that must be downloaded and installed, in this case, the VPNGINA. The client profile also is pushed down from the security appliance. The installation of VPNGINA is activated by the command svc modules value vpngina configured under the group-policy (webvpn) command mode as explained in Step 4. The AnyConnect client and VPNGINA are installed, and the user sees the AnyConnect Client at the next reboot, prior to Windows Domain logon.
When the user connects, the client and profile are passed down to the user PC; the client and VPNGINA are installed; and the user sees the AnyConnect client at the next reboot, prior to logon.
A sample profile is provided on the client PC when AnyConnect is installed: C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Cisco\Cisco\AnyConnect VPN Client\Profile\AnyConnectProfile.
Troubleshoot SBL
Use this procedure if you encounter a problem with SBL:
-
Ensure that the profile is pushed.
-
Delete prior profiles; search for them on the hard drive to find the location: *.xml.
-
When you go to the Add/Remove programs, do you have both an AnyConnect installation and AnyConnect VPNGINA installation?
-
Uninstall the AnyConnect client.
-
Clear the AnyConnect log of the user in the Event Viewer and retest.
-
Web browse back to the security appliance to reinstall the client.
-
Make sure that the profile also appears.
-
Reboot once. On the next reboot, you are prompted with the Start Before Logon prompt.
-
Send the AnyConnect event log to Cisco in .evt format .
-
If you see this error, delete the user profile and use the default profile:
Description: Unable to parse the profile C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Cisco \Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client\Profile\VABaseProfile.xml. Host data not available.
Problem 1
This error message is seen while trying to upload the AnyConnect profile: Error in validating the XML file against the latest schema. How is this error resolved?
Solution 1
This error message mostly occurs due to the syntax or configuration issues in the AnyConnect profile. In order to resolve this issue, make sure that the AnyConnect profile configured is similar to the Sample AnyConnect Profile present in the Sample AnyConnect Profile and XML Schema section of the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Administrator Guide.
Related Information
- Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Administrator Guide, Version 2.0
- Creating Logon Scripts - Windows TechNet

- Configuring Start Before Logon (PLAP) on Windows Vista Systems
- ASA 8.x VPN Access with the AnyConnect SSL VPN Client Configuration Example
- Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client
- Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliances
- Technical Support & Documentation - Cisco Systems
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
02-Sep-2008 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)










 Feedback
Feedback