ASA 8.x : Allow Split Tunneling for AnyConnect VPN Client on the ASA Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides step-by-step instructions on how to allow Cisco AnyConnect VPN client access to the Internet while they are tunneled into a Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) 8.0.2. This configuration allows the client secure access to corporate resources via SSL while giving unsecured access to the Internet using split tunneling.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Ensure that you meet these requirements before you attempt this configuration:
-
ASA Security Appliance needs to run version 8.x
-
Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client 2.x
Note: Download the AnyConnect VPN Client package (anyconnect-win*.pkg) from the Cisco Software Download (registered customers only) . Copy the AnyConnect VPN client to the ASA's flash memory, which is to be downloaded to the remote user computers in order to establish the SSL VPN connection with the ASA. Refer to the Installing the AnyConnect Client section of the ASA configuration guide for more information.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco 5500 Series ASA that runs software version 8.0(2)
-
Cisco AnyConnect SSL VPN Client version for Windows 2.0.0343
-
PC which runs Microsoft Visa, Windows XP SP2 or Windows 2000 Professional SP4 with Microsoft Installer version 3.1
-
Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) version 6.0(2)
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
The Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client provides secure SSL connections to the security appliance for remote users. Without a previously installed client, remote users enter the IP address in their browser of an interface configured to accept SSL VPN connections. Unless the security appliance is configured to redirect http:// requests to https://, users must enter the URL in the form https://<address>.
After entering the URL, the browser connects to that interface and displays the login screen. If the user satisfies the login and authentication, and the security appliance identifies the user as requiring the client, it downloads the client that matches the operating system of the remote computer. After downloading, the client installs and configures itself, establishes a secure SSL connection and either remains or uninstalls itself (depending on the security appliance configuration) when the connection terminates.
In the case of a previously installed client, when the user authenticates, the security appliance examines the revision of the client and upgrades the client as necessary.
When the client negotiates an SSL VPN connection with the security appliance, it connects using Transport Layer Security (TLS), and optionally, Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS). DTLS avoids latency and bandwidth problems associated with some SSL connections, and improves the performance of real-time applications that are sensitive to packet delays.
The AnyConnect client can be downloaded from the security appliance, or it can be installed manually on the remote PC by the system administrator. Refer to Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Administrator Guide for more information on how to install the client manually.
The security appliance downloads the client based on the group policy or username attributes of the user establishing the connection. You can configure the security appliance to automatically download the client, or you can configure it to prompt the remote user about whether to download the client. In the latter case, if the user does not respond, you can configure the security appliance to either download the client after a timeout period or present the login page.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) to obtain more information on the commands used in this section.
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
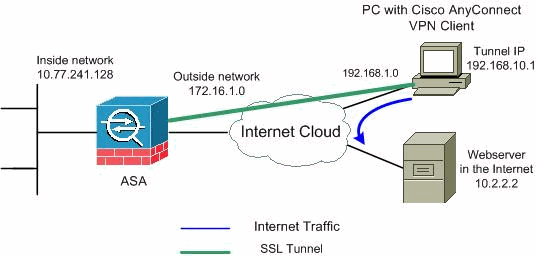
Note: The IP addressing schemes used in this configuration are not legally routable on the Internet. They are RFC 1918 ![]() addresses which have been used in a lab environment.
addresses which have been used in a lab environment.
ASA Configuration Using ASDM 6.0(2)
This document assumes that the basic configuration, such as interface configuration, is already made and works properly.
Note: Refer to Allowing HTTPS Access for ASDM in order to allow the ASA to be configured by the ASDM.
Note: WebVPN and ASDM cannot be enabled on the same ASA interface unless you change the port numbers. Refer to ASDM and WebVPN Enabled on the Same Interface of ASA for more information.
Complete these steps in order to configure the SSL VPN on ASA with split tunneling:
-
Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Address Management > Address Pools > Add in order to create an IP address pool vpnpool.
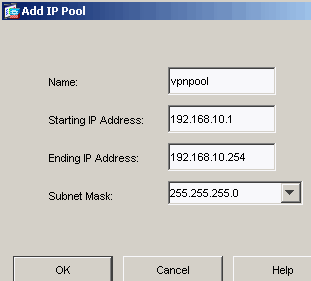
-
Click Apply.
Equivalent CLI Configuration:
Cisco ASA 8.0(2) ciscoasa(config)#ip local pool vpnpool 192.168.10.1-192.168.10.254 mask 255.255.255.0
-
Enable WebVPN.
-
Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > SSL VPN Connection Profiles and under Access Interfaces, click the check boxes Allow Access and Enable DTLS for the outside interface. Also, check the Enable Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client or legacy SSL VPN Client access on the interface selected in the table below check box in order to enable SSL VPN on the outside interface.
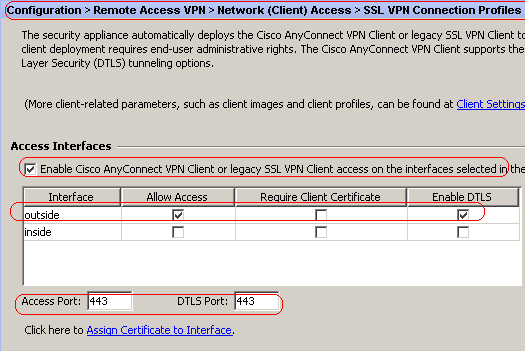
-
Click Apply.
-
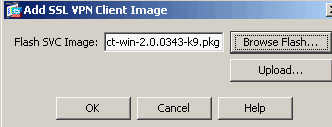
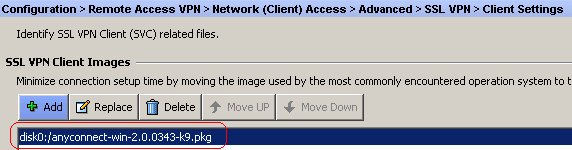
Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Advanced > SSL VPN > Client Settings > Add in order to add the Cisco AnyConnect VPN client image from the flash memory of ASA as shown.
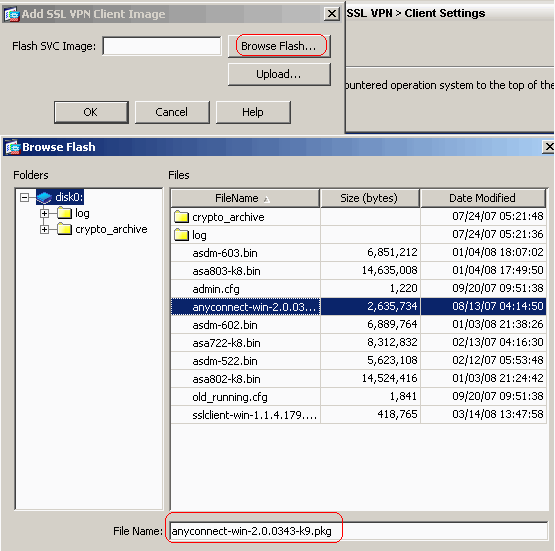
-
Click OK.
-
Click Add.
Equivalent CLI Configuration:
Cisco ASA 8.0(2) ciscoasa(config)#webvpn ciscoasa(config-webvpn)#enable outside ciscoasa(config-webvpn)#svc image disk0:/anyconnect-win-2.0.0343-k9.pkg 1 ciscoasa(config-webvpn)#tunnel-group-list enable ciscoasa(config-webvpn)#svc enable
-
-
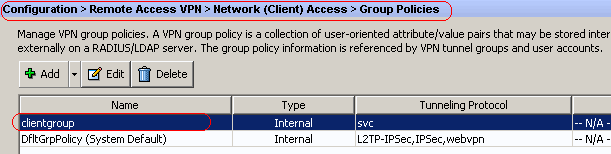
Configure Group Policy.
-
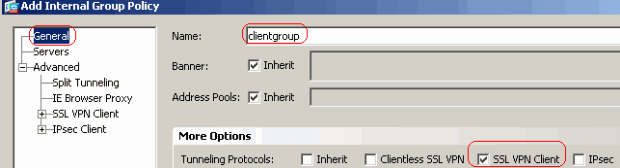
Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Group Policies in order to create an internal group policy clientgroup. Under the General tab, select the SSL VPN Client check box in order to enable the WebVPN as tunneling protocol.
-
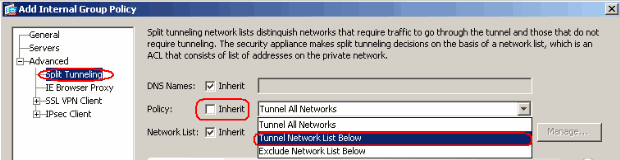
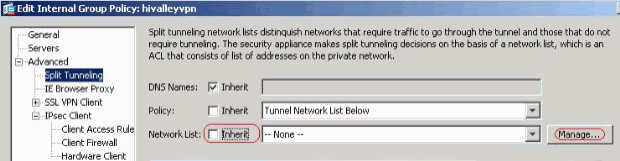
In the Advanced > Split Tunneling tab, uncheck the Inherit check box for Split Tunnel Policy and chose Tunnel Network List Below from the drop down list.
-
Uncheck the Inherit check box for Split Tunnel Network List and then click Manage in order to launch the ACL Manager.
-
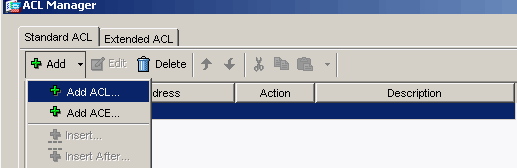
Within the ACL Manager, choose Add > Add ACL... in order to create a new access list.
-
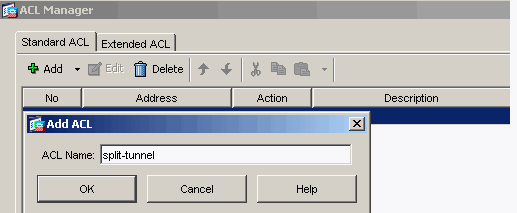
Provide a name for the ACL and click OK.
-
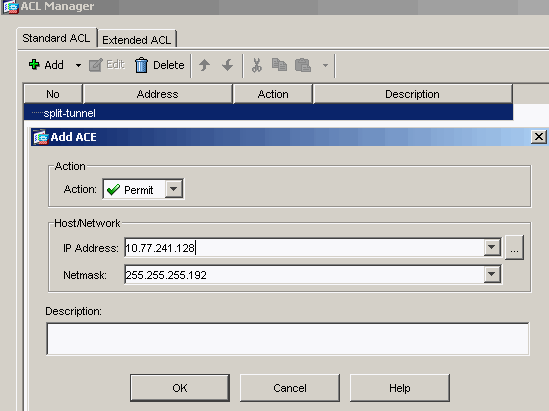
Once the ACL name is created, choose Add > Add ACE in order to add an Access Control Entry (ACE).
Define the ACE that corresponds to the LAN behind the ASA. In this case, the network is 10.77.241.128/26 and select Permit as the Action.
-
Click OK in order to exit the ACL Manager.
-
Make sure that the ACL you just created is selected for the split-tunnel Network List. Click OK in order to return to the Group Policy configuration.
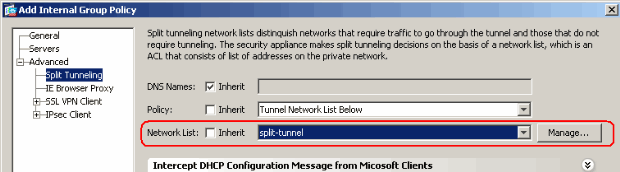
-
On the main page, click Apply and then Send (if required) in order to send the commands to the ASA.
-
Configure the SSL VPN settings under Group policy mode.
-
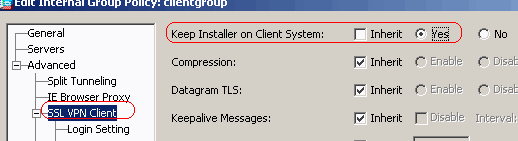
For the Keep Installer on Client System option, uncheck the Inherit check box, and click the Yes radio button.
This action allows the SVC software to remain on the client machine. Therefore, the ASA is not required to download the SVC software to the client each time a connection is made. This option is a good choice for remote users who often access the corporate network.
-
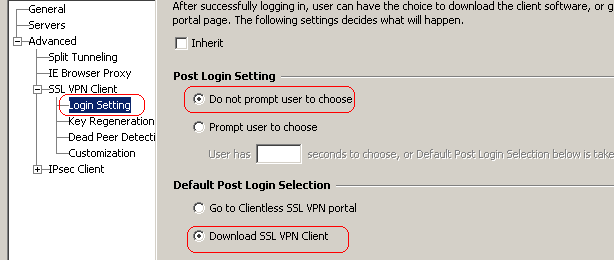
Click Login Setting in order to set the Post Login Setting and Default Post Login Selection as shown.
-
For the Renegotiation Interval option, uncheck the Inherit box, uncheck the Unlimited check box, and enter the number of minutes until rekey.
Security is enhanced by setting limits on the length of time a key is valid.
-
For the Renegotiation Method option, uncheck the Inherit check box, and click the SSL radio button.
Renegotiation can use the present SSL tunnel or a new tunnel created expressly for renegotiation.

-
-
Click OK and then Apply.
Equivalent CLI Configuration:
Cisco ASA 8.0(2) ciscoasa(config)#access-list split-tunnel standard permit 10.77.241.128 255.255.255.1922 ciscoasa(config)#group-policy clientgroup internal ciscoasa(config)#group-policyclientgroup attributes ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#vpn-tunnel-protocol webvpn ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#split-tunnel-policy tunnelspecified ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#split-tunnel-network-list value split-tunnel ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#webvpn ciscoasa(config-group-webvpn)#svc ask none default svc ciscoasa(config-group-webvpn)#svc keep-installer installed ciscoasa(config-group-webvpn)#svc rekey time 30 ciscoasa(config-group-webvpn)#svc rekey method ssl
-
-
Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > AAA Setup > Local Users > Add in order to create a new user account ssluser1. Click OK and then Apply.
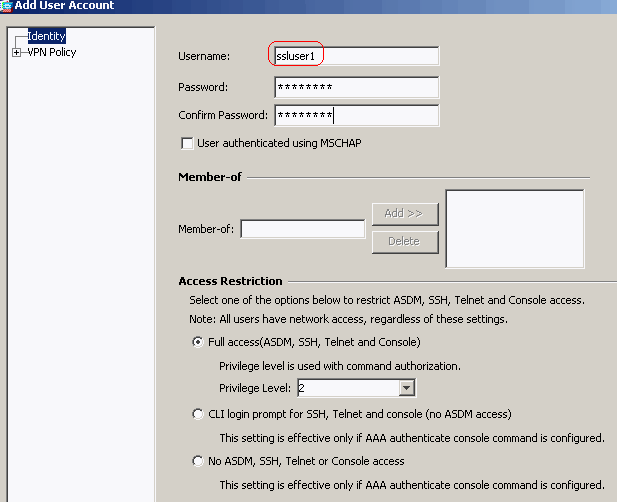
Equivalent CLI Configuration:
Cisco ASA 8.0(2) ciscoasa(config)#username ssluser1 password asdmASA@
-
Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > AAA Setup > AAA Servers Groups > Edit in order to modify the default server group LOCAL by checking the Enable Local User Lockout check box with maximum attempts value as 16.
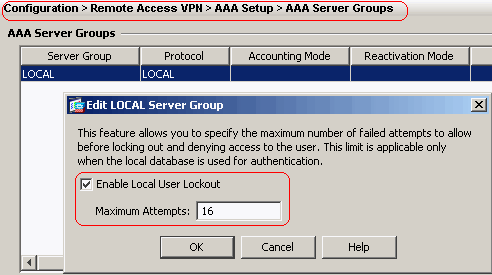
-
Click OK and then Apply.
Equivalent CLI Configuration:
Cisco ASA 8.0(2) ciscoasa(config)#aaa local authentication attempts max-fail 16
-
Configure Tunnel Group.
-
Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > SSL VPN Connection Profiles Connection Profiles > Add in order to create a new tunnel group sslgroup.
-
In the Basic tab, you can perform the list of configurations as shown:
-
Name the Tunnel group as sslgroup.
-
Under Client Address Assignment, choose the address pool vpnpool from the drop down list.
-
Under Default Group Policy, choose the group policy clientgroup from the drop down list.
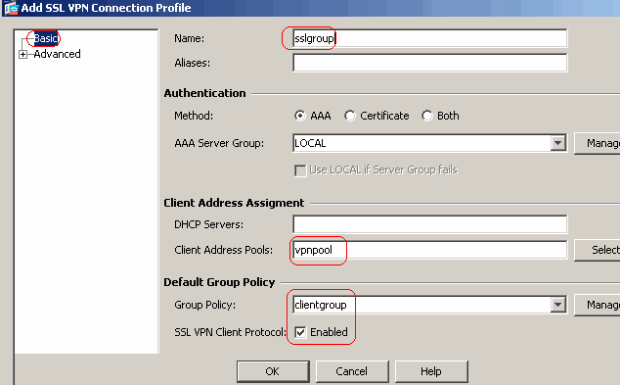
-
-
Under the SSL VPN > Connection Aliases tab, specify the group alias name as sslgroup_users and click OK.
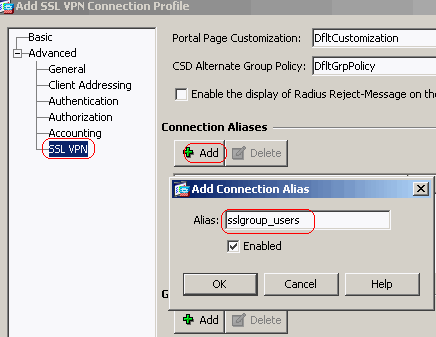
-
Click OK and then Apply.
Equivalent CLI Configuration:
Cisco ASA 8.0(2) ciscoasa(config)#tunnel-group sslgroup type remote-access ciscoasa(config)#tunnel-group sslgroup general-attributes ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#address-pool vpnpool ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#default-group-policy clientgroup ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#exit ciscoasa(config)#tunnel-group sslgroup webvpn-attributes ciscoasa(config-tunnel-webvpn)#group-alias sslgroup_users enable
-
-
Configure NAT.
-
Choose Configuration > Firewall > NAT Rules > Add Dynamic NAT Rule so the traffic that comes from the inside network can be translated with outside IP address 172.16.1.5.
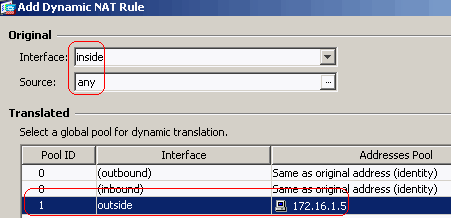
-
Click OK.
-
Click OK.
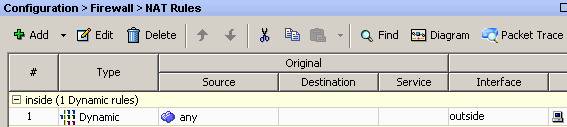
-
Click Apply.
Equivalent CLI Configuration:
Cisco ASA 8.0(2) ciscoasa(config)#global (outside) 1 172.16.1.5 ciscoasa(config)#nat (inside) 1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
-
-
Configure the nat-exemption for the return-traffic from inside network to the VPN client.
ciscoasa(config)#access-list nonat permit ip 10.77.241.0 192.168.10.0 ciscoasa(config)#access-list nonat permit ip 192.168.10.0 10.77.241.0 ciscoasa(config)#nat (inside) 0 access-list nonat
ASA CLI Configuration
| Cisco ASA 8.0(2) |
|---|
ciscoasa(config)#show running-config : Saved : ASA Version 8.0(2) ! hostname ciscoasa domain-name default.domain.invalid enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted names ! interface Ethernet0/0 nameif inside security-level 100 ip address 10.77.241.142 255.255.255.192 ! interface Ethernet0/1 nameif outside security-level 0 ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/2 shutdown no nameif no security-level no ip address ! interface Ethernet0/3 shutdown no nameif no security-level no ip address ! interface Management0/0 shutdown no nameif no security-level no ip address ! passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted boot system disk0:/asa802-k8.bin ftp mode passive clock timezone IST 5 30 dns server-group DefaultDNS domain-name default.domain.invalid access-list split-tunnel standard permit 10.77.241.128 255.255.255.192 !--- ACL for Split Tunnel network list for encryption. access-list nonat permit ip 10.77.241.0 192.168.10.0 access-list nonat permit ip 192.168.10.0 10.77.241.0 !--- ACL to define the traffic to be exempted from NAT. pager lines 24 logging enable logging asdm informational mtu inside 1500 mtu outside 1500 ip local pool vpnpool 192.168.10.1-192.168.10.254 mask 255.255.255.0 !--- The address pool for the Cisco AnyConnect SSL VPN Clients no failover icmp unreachable rate-limit 1 burst-size 1 asdm image disk0:/asdm-602.bin no asdm history enable arp timeout 14400 global (outside) 1 172.16.1.5 !--- The global address for Internet access used by VPN Clients. !--- Note: Uses an RFC 1918 range for lab setup. !--- Apply an address from your public range provided by your ISP. nat (inside) 0 access-list nonat !--- The traffic permitted in "nonat" ACL is exempted from NAT. nat (inside) 1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.1.2 1 timeout xlate 3:00:00 timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02 timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00 mgcp-pat 0:05:00 timeout sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 sip-invite 0:03:00 sip-disconnect 0:02:00 timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute dynamic-access-policy-record DfltAccessPolicy http server enable http 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 inside no snmp-server location no snmp-server contact snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkup linkdown coldstart no crypto isakmp nat-traversal telnet timeout 5 ssh timeout 5 console timeout 0 threat-detection basic-threat threat-detection statistics access-list ! class-map inspection_default match default-inspection-traffic ! ! policy-map type inspect dns preset_dns_map parameters message-length maximum 512 policy-map global_policy class inspection_default inspect dns preset_dns_map inspect ftp inspect h323 h225 inspect h323 ras inspect netbios inspect rsh inspect rtsp inspect skinny inspect esmtp inspect sqlnet inspect sunrpc inspect tftp inspect sip inspect xdmcp ! service-policy global_policy global webvpn enable outside !--- Enable WebVPN on the outside interface svc image disk0:/anyconnect-win-2.0.0343-k9.pkg 1 !--- Assign an order to the AnyConnect SSL VPN Client image svc enable !--- Enable the security appliance to download SVC images to remote computers tunnel-group-list enable !--- Enable the display of the tunnel-group list on the WebVPN Login page group-policy clientgroup internal !--- Create an internal group policy "clientgroup" group-policy clientgroup attributes vpn-tunnel-protocol svc !--- Specify SSL as a permitted VPN tunneling protocol split-tunnel-policy tunnelspecified split-tunnel-network-list value split-tunnel !--- Encrypt the traffic specified in the split tunnel ACL only webvpn svc keep-installer installed !--- When the security appliance and the SVC perform a rekey, they renegotiate !--- the crypto keys and initialization vectors, increasing the security of the connection. svc rekey time 30 !--- Command that specifies the number of minutes from the start of the !--- session until the rekey takes place, from 1 to 10080 (1 week). svc rekey method ssl !--- Command that specifies that SSL renegotiation takes place during SVC rekey. svc ask none default svc username ssluser1 password ZRhW85jZqEaVd5P. encrypted !--- Create a user account "ssluser1" tunnel-group sslgroup type remote-access !--- Create a tunnel group "sslgroup" with type as remote access tunnel-group sslgroup general-attributes address-pool vpnpool !--- Associate the address pool vpnpool created default-group-policy clientgroup !--- Associate the group policy "clientgroup" created tunnel-group sslgroup webvpn-attributes group-alias sslgroup_users enable !--- Configure the group alias as sslgroup-users prompt hostname context Cryptochecksum:af3c4bfc4ffc07414c4dfbd29c5262a9 : end ciscoasa(config)# |
Establish the SSL VPN Connection with SVC
Complete these steps in order to establish a SSL VPN connection with ASA:
-
Enter the URL or IP address of the ASA's WebVPN interface in your web browser in the format as shown.
https://url
OR
https://<IP address of the ASA WebVPN interface>
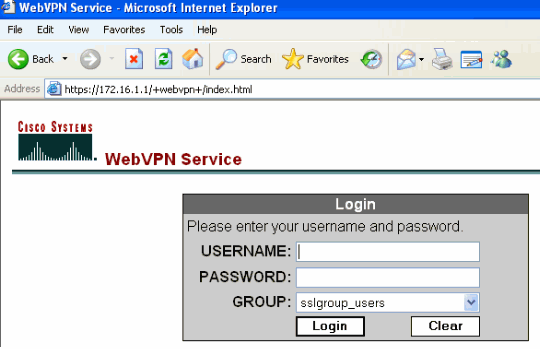
-
Enter your username and password. Also, choose your respective group from the drop down list as shown.
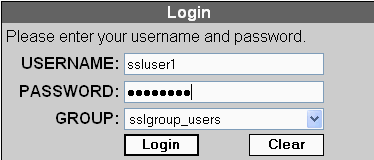
This window appears before the SSL VPN connection is established.
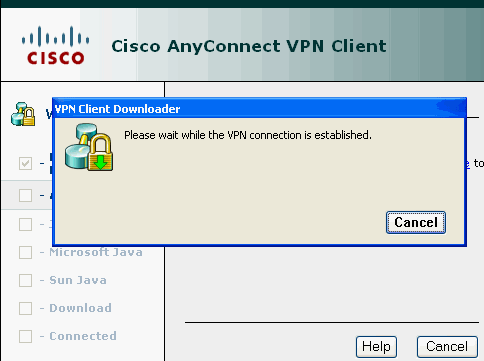
Note: ActiveX software must be installed in your computer before you download the SVC.
You receive this window once the connection is established.
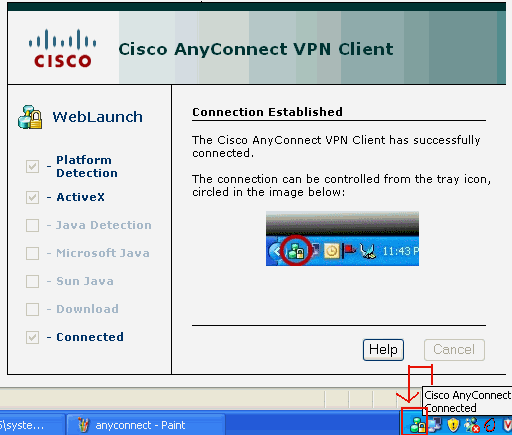
-
Click the lock which appears in the task bar of your computer.
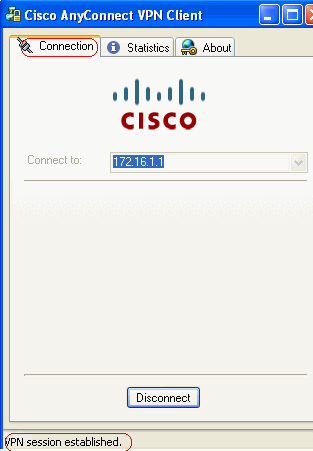
This window appears and provides information about the SSL connection. For example, 192.168.10.1 is the assigned IP by the ASA, etc.
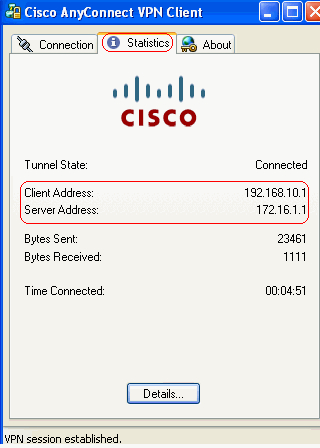
This window shows the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Version information.

Verify
Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
-
show webvpn svc—Displays the SVC images stored in the ASA flash memory.
ciscoasa#show webvpn svc 1. disk0:/anyconnect-win-2.0.0343-k9.pkg 1 CISCO STC win2k+ 2,0,0343 Mon 04/23/2007 4:16:34.63 1 SSL VPN Client(s) installed
-
show vpn-sessiondb svc—Displays the information about the current SSL connections.
ciscoasa#show vpn-sessiondb svc Session Type: SVC Username : ssluser1 Index : 12 Assigned IP : 192.168.10.1 Public IP : 192.168.1.1 Protocol : Clientless SSL-Tunnel DTLS-Tunnel Encryption : RC4 AES128 Hashing : SHA1 Bytes Tx : 194118 Bytes Rx : 197448 Group Policy : clientgroup Tunnel Group : sslgroup Login Time : 17:12:23 IST Mon Mar 24 2008 Duration : 0h:12m:00s NAC Result : Unknown VLAN Mapping : N/A VLAN : none
-
show webvpn group-alias—Displays the configured alias for various groups.
ciscoasa#show webvpn group-alias Tunnel Group: sslgroup Group Alias: sslgroup_users enabled
-
In ASDM, choose Monitoring > VPN > VPN Statistics > Sessions in order to know the current WebVPN sessions in the ASA.
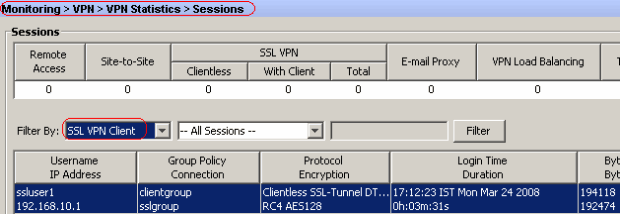
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use to troubleshoot your configuration.
-
vpn-sessiondb logoff name <username> —Command to logoff the SSL VPN session for the particular username.
ciscoasa#vpn-sessiondb logoff name ssluser1 Do you want to logoff the VPN session(s)? [confirm] Y INFO: Number of sessions with name "ssluser1" logged off : 1 ciscoasa#Called vpn_remove_uauth: success! webvpn_svc_np_tear_down: no ACL webvpn_svc_np_tear_down: no IPv6 ACL np_svc_destroy_session(0xB000)
Similarly, you can use the vpn-sessiondb logoff svc command in order to terminate all the SVC sessions.
-
Note: If the PC goes to standby or hibernate mode, then the SSL VPN connection can be terminated.
webvpn_rx_data_cstp webvpn_rx_data_cstp: got message SVC message: t/s=5/16: Client PC is going into suspend mode (Sleep, Hibernate, e tc) Called vpn_remove_uauth: success! webvpn_svc_np_tear_down: no ACL webvpn_svc_np_tear_down: no IPv6 ACL np_svc_destroy_session(0xA000)
ciscoasa#show vpn-sessiondb svc INFO: There are presently no active sessions
-
debug webvpn svc <1-255> —Provides the real time webvpn events in order to establish the session.
Ciscoasa#debug webvpn svc 7 webvpn_rx_data_tunnel_connect CSTP state = HEADER_PROCESSING http_parse_cstp_method() ...input: 'CONNECT /CSCOSSLC/tunnel HTTP/1.1' webvpn_cstp_parse_request_field() ...input: 'Host: 172.16.1.1' Processing CSTP header line: 'Host: 172.16.1.1' webvpn_cstp_parse_request_field() ...input: 'User-Agent: Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client 2, 0, 0343' Processing CSTP header line: 'User-Agent: Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client 2, 0, 0343 ' Setting user-agent to: 'Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client 2, 0, 0343' webvpn_cstp_parse_request_field() ...input: 'Cookie: webvpn=16885952@12288@1206098825@D251883E8625B92C1338D631B08B 7D75F4EDEF26' Processing CSTP header line: 'Cookie: webvpn=16885952@12288@1206098825@D251883E8 625B92C1338D631B08B7D75F4EDEF26' Found WebVPN cookie: 'webvpn=16885952@12288@1206098825@D251883E8625B92C1338D631B 08B7D75F4EDEF26' WebVPN Cookie: 'webvpn=16885952@12288@1206098825@D251883E8625B92C1338D631B08B7D7 5F4EDEF26' webvpn_cstp_parse_request_field() ...input: 'X-CSTP-Version: 1' Processing CSTP header line: 'X-CSTP-Version: 1' Setting version to '1' webvpn_cstp_parse_request_field() ...input: 'X-CSTP-Hostname: tacweb' Processing CSTP header line: 'X-CSTP-Hostname: tacweb' Setting hostname to: 'tacweb' webvpn_cstp_parse_request_field() ...input: 'X-CSTP-Accept-Encoding: deflate;q=1.0' Processing CSTP header line: 'X-CSTP-Accept-Encoding: deflate;q=1.0' webvpn_cstp_parse_request_field() ...input: 'X-CSTP-MTU: 1206' Processing CSTP header line: 'X-CSTP-MTU: 1206' webvpn_cstp_parse_request_field() ...input: 'X-CSTP-Address-Type: IPv4' Processing CSTP header line: 'X-CSTP-Address-Type: IPv4' webvpn_cstp_parse_request_field() ...input: 'X-DTLS-Master-Secret: CE151BA2107437EDE5EC4F5EE6AEBAC12031550B1812D40 642E22C6AFCB9501758FF3B7B5545973C06F6393C92E59693' Processing CSTP header line: 'X-DTLS-Master-Secret: CE151BA2107437EDE5EC4F5EE6AE BAC12031550B1812D40642E22C6AFCB9501758FF3B7B5545973C06F6393C92E59693' webvpn_cstp_parse_request_field() ...input: 'X-DTLS-CipherSuite: AES256-SHA:AES128-SHA:DES-CBC3-SHA:DES-CBC-SHA' Processing CSTP header line: 'X-DTLS-CipherSuite: AES256-SHA:AES128-SHA:DES-CBC3 -SHA:DES-CBC-SHA' Validating address: 0.0.0.0 CSTP state = WAIT_FOR_ADDRESS webvpn_cstp_accept_address: 192.168.10.1/0.0.0.0 CSTP state = HAVE_ADDRESS No subnetmask... must calculate it SVC: NP setup np_svc_create_session(0x3000, 0xD41611E8, TRUE) webvpn_svc_np_setup SVC ACL Name: NULL SVC ACL ID: -1 SVC ACL ID: -1 vpn_put_uauth success! SVC IPv6 ACL Name: NULL SVC IPv6 ACL ID: -1 SVC: adding to sessmgmt SVC: Sending response Unable to initiate NAC, NAC might not be enabled or invalid policy CSTP state = CONNECTED webvpn_rx_data_cstp webvpn_rx_data_cstp: got internal message Unable to initiate NAC, NAC might not be enabled or invalid policy
-
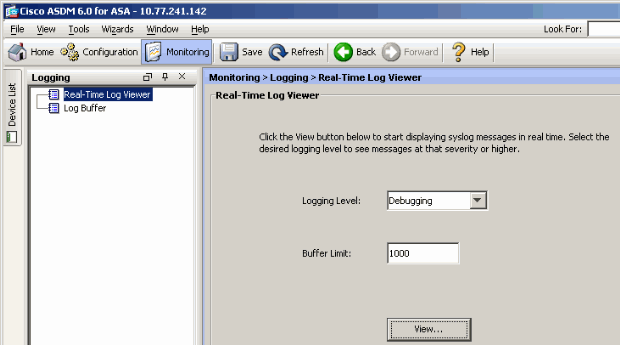
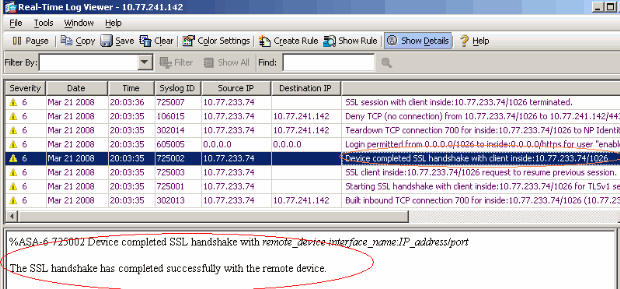
In ASDM, choose Monitoring > Logging > Real-time Log Viewer > View in order to see the real time events.
This example shows that the SSL session has been established with the head end device.
Related Information
- Cisco 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Support Page
- Release Notes for AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.0
- ASA/PIX: Allow Split Tunneling for VPN Clients on the ASA Configuration Example
- Router Allows VPN Clients to Connect IPsec and Internet Using Split Tunneling Configuration Example
- PIX/ASA 7.x and VPN Client for Public Internet VPN on a Stick Configuration Example
- SSL VPN Client (SVC) on ASA with ASDM Configuration Example
- Technical Support & Documentation - Cisco Systems
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
02-Oct-2009 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
































 Feedback
Feedback