Configure ASA IPsec VTI Connection Amazon Web Services
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Introduction
This document describes how to configure an Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface (VTI) connection. In ASA 9.7.1, IPsec VTI has been introduced. It is limited to sVTI IPv4 over IPv4 using IKEv1 in this release. This is an example configuration for the ASA to connect to Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Note: Currently VTI is only supported in single-context, routed mode.
Configure AWS
Step 1.
Log in to the AWS console and navigate to the VPC panel.
 Navigate to the VPC Dashboard
Navigate to the VPC Dashboard
Step 2.
Confirm that a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is already created. By default, a VPC with 172.31.0.0/16 is created. This is where Virtual Machines (VMs) will be attached.
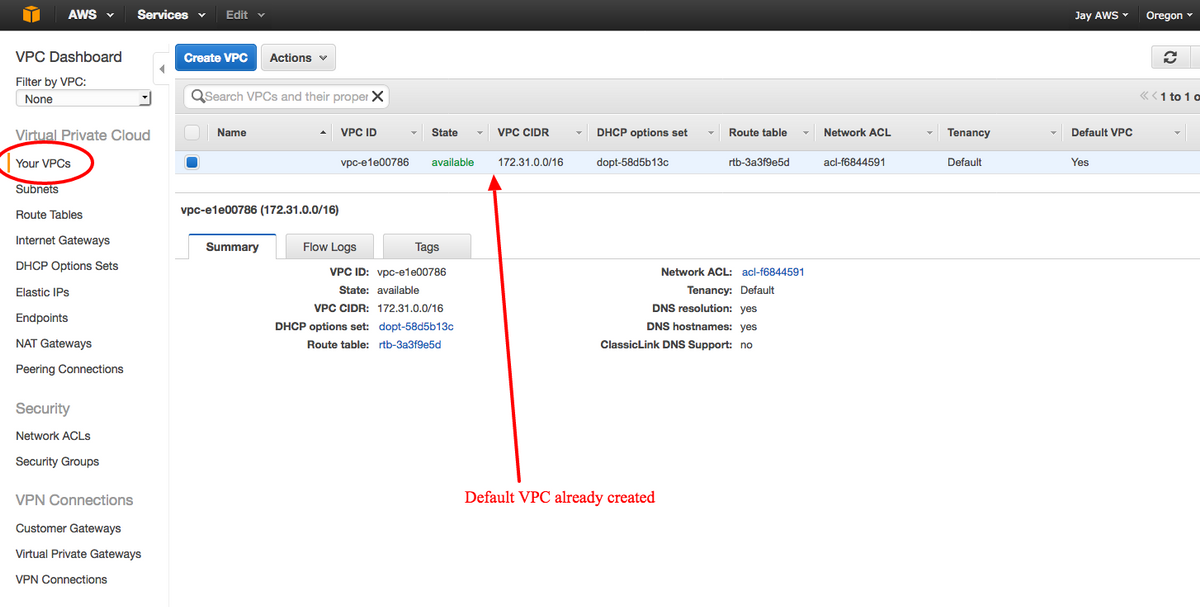
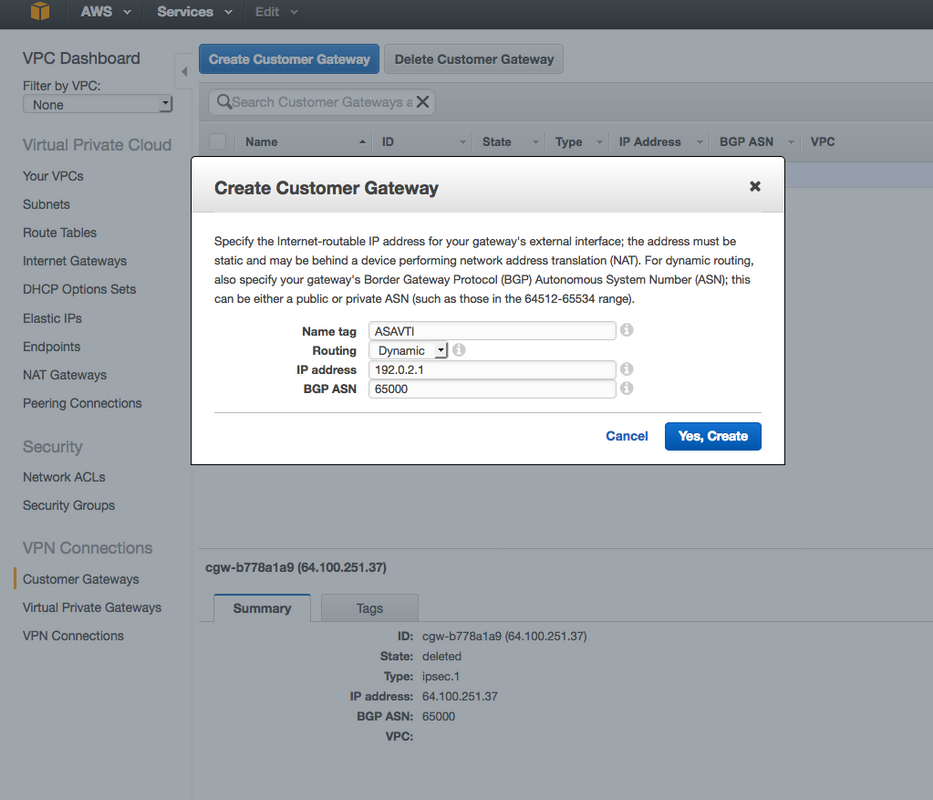
Step 3.
Create a "Customer Gateway". This is a an endpoint that represents the ASA.
| Field | Value |
| Name Tag | This is just a human readable name to recognize the ASA. |
| Routing | Dynamic - This means that Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) will be used in order to exchange routing information. |
| IP Address | This is the Public IP address of the ASA's outside interface. |
| BGP ASN | The Autonomous System (AS) number of the BGP process than runs on the ASA. Use 65000 unless your organization has a public AS number. |
Step 4.
Create a Virtual Private Gateway (VPG). This is a simulated router that is hosted with AWS that terminates the IPsec tunnel.
| Field | Value |
| Name Tag | A human readable name to recognize the VPG. |

Step 5.
Attach the VPG to the VPC.
Choose the Virtual Private Gateway, click Attach to VPC, choose the VPC from the VPC drop-down list, and click Yes, Attach.

Step 6.
Create a VPN connection.

| Field | Value |
| Name Tag | A human readable tag of the VPN connection between AWS and the ASA. |
| Virtual Private Gateway | Choose the VPG just created. |
| Customer Gateway | Click the Existing radio button and choose the gateway of the ASA. |
| Routing Options | Click the Dynamic (requires BGP) radio button. |

Step 7.
Configure the Route Table to propagate the routes learned from the VPG (via BGP) into the VPC.

Step 8.
Download the suggested configuration. Choose the values below in order to generate a configuration that is a VTI style configuration.
| Field | Value |
| Vendor | Cisco Systems, Inc. |
| Platform | ISR Series Routers |
| Software | IOS 12.4+ |

Configure the ASA
Once you download the configuration there is some conversion necessary.
Step 1.
crypto isakmp policy to crypto ikev1 policy. Only one policy is needed since policy 200 and policy 201 are identical.
| Suggested Configuration | To |
|
crypto isakmp policy 200 crypto isakmp policy 201 |
crypto ikev1 enable outside crypto ikev1 policy 10 authentication pre-share encryption aes hash sha group 2 lifetime 28800 |
Step 2.
crypto ipsec transform-set to crypto ipsec ikev1 transform-set. Only one transform-set is needed since the two transform-sets are identical.
| Suggested Configuration | To |
|
crypto ipsec transform-set ipsec-prop-vpn-7c79606e-0 esp-aes 128 esp-sha-hmac crypto ipsec transform-set ipsec-prop-vpn-7c79606e-1 esp-aes 128 esp-sha-hmac |
crypto ipsec ikev1 transform-set AWS esp-aes esp-sha-hmac |
Step 3.
crypto ipsec profile to crypto ipsec profile. Only one profile is needed since the two profiles are identical.
| Suggested Configuration | To |
|
crypto ipsec profile ipsec-vpn-7c79606e-0 crypto ipsec profile ipsec-vpn-7c79606e-1 |
crypto ipsec profile AWS set ikev1 transform-set AWS set pfs group2 set security-association lifetime seconds 3600 |
Step 4.
crypto keyring and crypto isakmp profile need to be converted to a tunnel-group one for each tunnel.
| Suggested Configuration | To |
|
crypto keyring keyring-vpn-7c79606e-0 ! crypto keyring keyring-vpn-7c79606e-1 ! |
tunnel-group 52.34.205.227 type ipsec-l2l isakmp keepalive threshold 10 retry 10 tunnel-group 52.37.194.219 type ipsec-l2l tunnel-group 52.37.194.219 ipsec-attributes ikev1 pre-shared-key JjxCWy4Ae isakmp keepalive threshold 10 retry 10 |
Step 5.
The tunnel configuration is almost identical. The ASA does not support the ip tcp adjust-mss or the ip virtual-reassembly command.
| Suggested Configuration | To |
|
interface Tunnel1 ! interface Tunnel2 |
interface Tunnel1 ! interface Tunnel2 |
Step 6.
In this example, the ASA will only advertise up the inside subnet (192.168.1.0/24) and receive the subnet within AWS (172.31.0.0/16).
|
Suggested Configuration |
To |
|
router bgp 65000 router bgp 65000 |
router bgp 65000 network 192.168.1.0 |
Verify and Optimize
Step 1.
Confirm the ASA establishes the IKEv1 security associations with the two endpoints at AWS. The state of the SA should be MM_ACTIVE.
ASA# show crypto ikev1 sa
IKEv1 SAs:
Active SA: 2
Rekey SA: 0 (A tunnel will report 1 Active and 1 Rekey SA during rekey)
Total IKE SA: 2
1 IKE Peer: 52.37.194.219
Type : L2L Role : initiator
Rekey : no State : MM_ACTIVE
2 IKE Peer: 52.34.205.227
Type : L2L Role : initiator
Rekey : no State : MM_ACTIVE
ASA#
Step 2.
Confirm the IPsec SAs are installed on ASA. There should be an inbound and outbound SPI installed for each peer and there should be some encaps and decaps counters incrementing.
ASA# show crypto ipsec sa
interface: AWS1
Crypto map tag: __vti-crypto-map-5-0-1, seq num: 65280, local addr: 64.100.251.37
access-list __vti-def-acl-0 extended permit ip any any
local ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0/0)
remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0/0)
current_peer: 52.34.205.227
#pkts encaps: 2234, #pkts encrypt: 2234, #pkts digest: 2234
#pkts decaps: 1234, #pkts decrypt: 1234, #pkts verify: 1234
#pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0
#pkts not compressed: 2234, #pkts comp failed: 0, #pkts decomp failed: 0
#pre-frag successes: 0, #pre-frag failures: 0, #fragments created: 0
#PMTUs sent: 0, #PMTUs rcvd: 0, #decapsulated frgs needing reassembly: 0
#TFC rcvd: 0, #TFC sent: 0
#Valid ICMP Errors rcvd: 0, #Invalid ICMP Errors rcvd: 0
#send errors: 0, #recv errors: 0
local crypto endpt.: 64.100.251.37/4500, remote crypto endpt.: 52.34.205.227/4500
path mtu 1500, ipsec overhead 82(52), media mtu 1500
PMTU time remaining (sec): 0, DF policy: copy-df
ICMP error validation: disabled, TFC packets: disabled
current outbound spi: 874FCCF3
current inbound spi : 5E653906
inbound esp sas:
spi: 0x5E653906 (1583692038)
transform: esp-aes esp-sha-hmac no compression
in use settings ={L2L, Tunnel, NAT-T-Encaps, PFS Group 2, IKEv1, VTI, }
slot: 0, conn_id: 73728, crypto-map: __vti-crypto-map-5-0-1
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (kB/sec): (4373986/2384)
IV size: 16 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Anti replay bitmap:
0xFFFFFFFF 0xFFFFFFFF
outbound esp sas:
spi: 0x874FCCF3 (2270153971)
transform: esp-aes esp-sha-hmac no compression
in use settings ={L2L, Tunnel, NAT-T-Encaps, PFS Group 2, IKEv1, VTI, }
slot: 0, conn_id: 73728, crypto-map: __vti-crypto-map-5-0-1
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (kB/sec): (4373986/2384)
IV size: 16 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Anti replay bitmap:
0x00000000 0x00000001
interface: AWS2
Crypto map tag: __vti-crypto-map-6-0-2, seq num: 65280, local addr: 64.100.251.37
access-list __vti-def-acl-0 extended permit ip any any
local ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0/0)
remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0/0)
current_peer: 52.37.194.219
#pkts encaps: 1230, #pkts encrypt: 1230, #pkts digest: 1230
#pkts decaps: 1230, #pkts decrypt: 1230, #pkts verify: 1230
#pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0
#pkts not compressed: 1230, #pkts comp failed: 0, #pkts decomp failed: 0
#pre-frag successes: 0, #pre-frag failures: 0, #fragments created: 0
#PMTUs sent: 0, #PMTUs rcvd: 0, #decapsulated frgs needing reassembly: 0
#TFC rcvd: 0, #TFC sent: 0
#Valid ICMP Errors rcvd: 0, #Invalid ICMP Errors rcvd: 0
#send errors: 0, #recv errors: 0
local crypto endpt.: 64.100.251.37/4500, remote crypto endpt.: 52.37.194.219/4500
path mtu 1500, ipsec overhead 82(52), media mtu 1500
PMTU time remaining (sec): 0, DF policy: copy-df
ICMP error validation: disabled, TFC packets: disabled
current outbound spi: DC5E3CA8
current inbound spi : CB6647F6
inbound esp sas:
spi: 0xCB6647F6 (3412477942)
transform: esp-aes esp-sha-hmac no compression
in use settings ={L2L, Tunnel, NAT-T-Encaps, PFS Group 2, IKEv1, VTI, }
slot: 0, conn_id: 77824, crypto-map: __vti-crypto-map-6-0-2
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (kB/sec): (4373971/1044)
IV size: 16 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Anti replay bitmap:
0xFFFFFFFF 0xFFFFFFFF
outbound esp sas:
spi: 0xDC5E3CA8 (3697163432)
transform: esp-aes esp-sha-hmac no compression
in use settings ={L2L, Tunnel, NAT-T-Encaps, PFS Group 2, IKEv1, VTI, }
slot: 0, conn_id: 77824, crypto-map: __vti-crypto-map-6-0-2
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (kB/sec): (4373971/1044)
IV size: 16 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Anti replay bitmap:
0x00000000 0x00000001
Step 3.
On the ASA, confirm that BGP connections are established with AWS. The State/PfxRcd counter should be 1 as AWS advertises the 172.31.0.0/16 subnet towards the ASA.
ASA# show bgp summary BGP router identifier 192.168.1.55, local AS number 65000 BGP table version is 5, main routing table version 5 2 network entries using 400 bytes of memory 3 path entries using 240 bytes of memory 3/2 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 624 bytes of memory 1 BGP AS-PATH entries using 24 bytes of memory 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory BGP using 1288 total bytes of memory BGP activity 3/1 prefixes, 4/1 paths, scan interval 60 secs Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 169.254.12.85 4 7224 1332 1161 5 0 0 03:41:31 1 169.254.13.189 4 7224 1335 1164 5 0 0 03:42:02 1
Step 4.
On the ASA, verify that the route to 172.31.0.0/16 has been learned via the tunnel interfaces. This output shows that there are two paths to 172.31.0.0 from peer 169.254.12.85 and 169.254.13.189. The path towards 169.254.13.189 out Tunnel 2 (AWS2) is preferred because of the lower metric.
ASA# show bgp
BGP table version is 5, local router ID is 192.168.1.55
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 172.31.0.0 169.254.12.85 200 0 7224 i
*> 169.254.13.189 100 0 7224 i
*> 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
ASA# show route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, V - VPN
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, + - replicated route
Gateway of last resort is 64.100.251.33 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 [1/0] via 64.100.251.33, outside
C 64.100.251.32 255.255.255.224 is directly connected, outside
L 64.100.251.37 255.255.255.255 is directly connected, outside
C 169.254.12.84 255.255.255.252 is directly connected, AWS2
L 169.254.12.86 255.255.255.255 is directly connected, AWS2
C 169.254.13.188 255.255.255.252 is directly connected, AWS1
L 169.254.13.190 255.255.255.255 is directly connected, AWS1
B 172.31.0.0 255.255.0.0 [20/100] via 169.254.13.189, 03:52:55
C 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 is directly connected, inside
L 192.168.1.55 255.255.255.255 is directly connected, inside
Step 5.
In order to ensure that traffic which returns from AWS follows a symmetric path, configure a route-map to match the preferred path and adjust BGP to alter the advertised routes.
route-map toAWS1 permit 10 set metric 100 exit ! route-map toAWS2 permit 10 set metric 200 exit ! router bgp 65000 address-family ipv4 unicast neighbor 169.254.12.85 route-map toAWS2 out neighbor 169.254.13.189 route-map toAWS1 out
Step 6.
On the ASA, confirm that 192.168.1.0/24 is advertised to AWS.
ASA# show bgp neighbors 169.254.12.85 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 5, local router ID is 192.168.1.55
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.31.0.0 169.254.13.189 100 0 7224 i
*> 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
Total number of prefixes 2
ASA# show bgp neighbors 169.254.13.189 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 5, local router ID is 192.168.1.55
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
Total number of prefixes 1
Step 7.
In AWS, confirm that the tunnels for the VPN connection are UP and routes are learned from the peer. Also check that the route has been propagated into the routing table.


Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Jay YoungTechnical Leader Services
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback