Introduction
This document describes how to configure Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) with a focus on ASA AnyConnect through Microsoft Azure MFA.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Basic knowledge of RA VPN configuration on Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA).
- Basic knowledge of SAML and Microsoft Azure.
- AnyConnect Licenses enabled (APEX or VPN-Only).
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- A Microsoft Azure AD subscription.
- Cisco ASA 9.7+ and Anyconnect 4.6+
- Working AnyConnect VPN profile
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
SAML is an XML-based framework for exchanging authentication and authorization data between security domains. It creates a circle of trust between the user, a Service Provider (SP), and an Identity Provider (IdP) which allows the user to sign in a single time for multiple services. Microsoft Azure MFA seamlessly integrates with Cisco ASA VPN appliance to provide additional security for the Cisco AnyConnect VPN logins.
SAML Components
Metadata: It is an XML based document that ensures a secure transaction between an IdP and an SP. It allows the IdP and SP to negotiate agreements.
Roles supported by the devices (IdP, SP)
A device can support more than one role and could contain values for both an SP and an IdP. Under the EntityDescriptor field is an IDPSSODescriptor, if the information contained is for a Single Sign-On IdP, or a SPSSODescriptor if the information contained is for a Single Sign-On SP. This is important since the correct values must be taken from the appropriate sections in order to set up SAML successfully.
Entity ID: This field is a unique identifier for an SP or an IdP. A single device can have several services and can use different Entity IDs to differentiate them. For example, ASA has different Entity IDs for different tunnel-groups that need to be authenticated. An IdP that authenticates each tunnel-group has a separate Entity ID entries for each tunnel-group in order to accurately identify those services.
ASA can support multiple IdPs and has a separate entity ID for each IdP to differentiate them. If either side receives a message from a device that does not contain an entity ID that has been previously configured, the device likely drops this message, and SAML authentication fails. The Entity ID can be found within the EntityDescriptor field beside entityID.
Service URLs: These define the URL to a SAML service provided by the SP or IdP. For IdPs, this is most commonly the Single Logout Service and Single Sign-On Service. For SPs, this is commonly the Assertion Consumer Service and the Single Logout Service.
The Single Sign-On Service URL found in the IdP metadata is used by the SP to redirect the user to the IdP for authentication. If this value is incorrectly configured, the IdP does not receive or is unable to successfully process the Authentication request sent by the SP.
The Assertion Consumer Service URL found in the SP metadata is used by the IdP to redirect the user back to the SP and provide information about the user's authentication attempt. If this is configured incorrectly, the SP does not receive the assertion (the response) or is unable to successfully process it.
The Single Logout Service URL can be found on both the SP and the IdP. It is used to facilitate logging out of all SSO services from the SP and is optional on the ASA. When the SLO service URL from the IdP metadata is configured on the SP, when the user logs out of the service on the SP, the SP sends the request to the IdP. Once the IdP has successfully logged the user out of the services, it redirects the user back to the SP and uses the SLO service URL found within the SP’s metadata.
SAML Bindings for Service URLs: Bindings are the method the SP uses to uses to transfer information to the IdP and vice versa for services. This includes HTTP Redirect, HTTP POST, and Artifact. Each method has a different way to transfer data. The binding method supported by the service is included within the definition of that services. For example: SingleSignOnService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect" Location= SSO Service >. The ASA does not support the Artifact binding. ASA always uses the HTTP Redirect method for SAML authentication requests, so it is important to choose the SSO Service URL that uses the HTTP Redirect binding so that the IdP expects this.
Certificates for Signature and Encryption Operations
To provide confidentiality and integrity for the messages sent between the SP and the IdP, SAML includes the ability to encrypt and sign the data. The certificate used to encrypt and/or sign the data can be included within the metadata so that the end that receives can verify the SAML message and ensure that it comes from the expected source. The certificates used for signing and encryption can be found within the metadata under KeyDescriptor use=signing and KeyDescriptor use=encryption, respectfully, then X509Certificate. The ASA does not support encrypting SAML messages.
Network Diagram
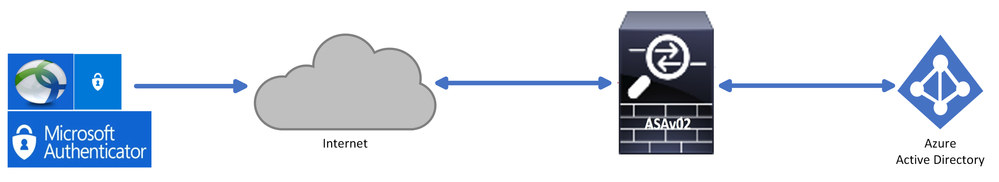
Configure
Add Cisco AnyConnect from the Microsoft App Gallery
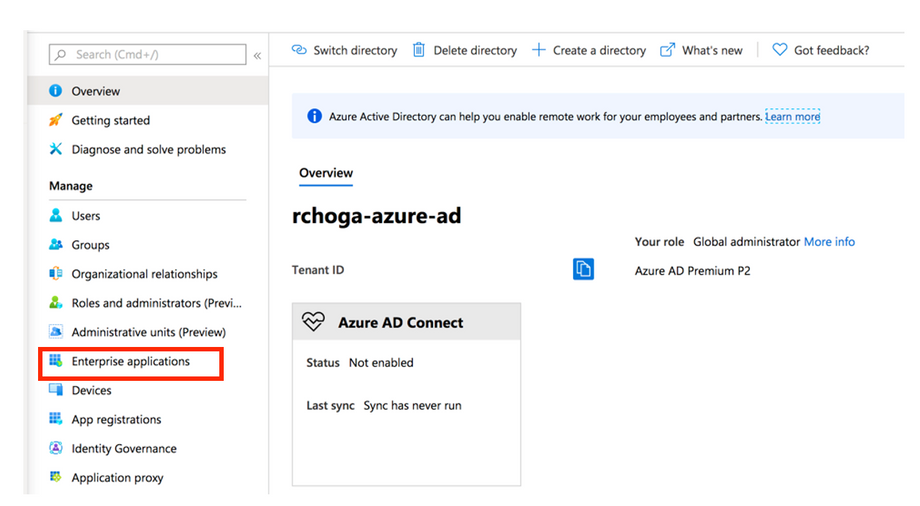
Step 1. Log in to Azure Portal and choose Azure Active Directory.

Step 2. As shown in this image, choose Enterprise Applications.
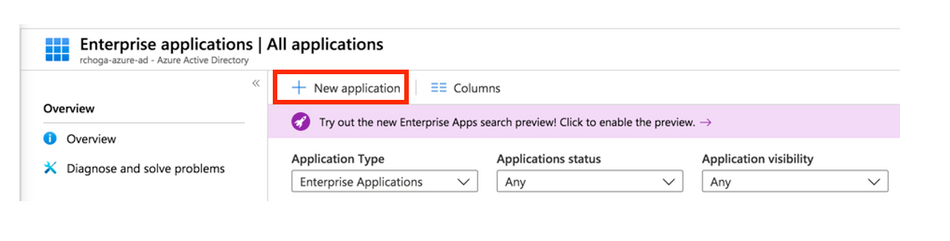
Step 3. Now, choose New Application, as shown in this image.
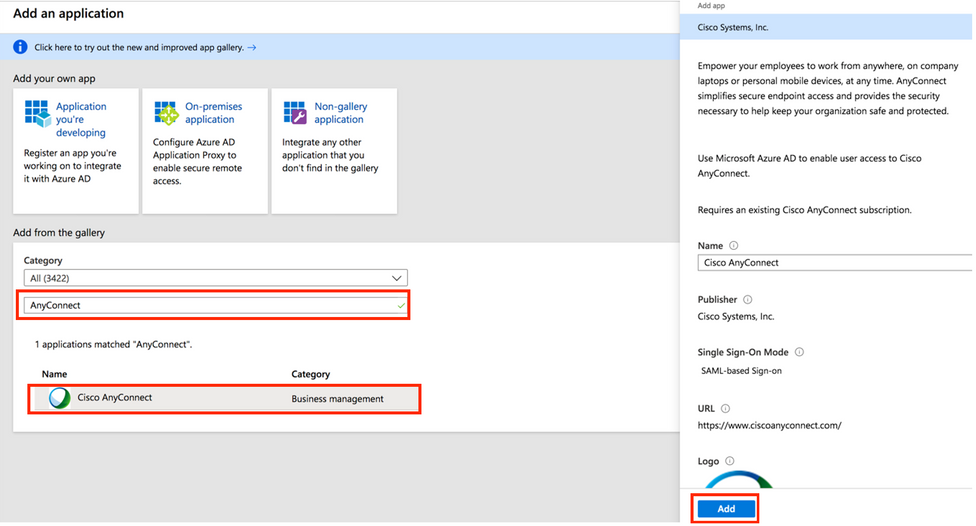
Step 4. In the Add from the gallery section, type AnyConnect in the search box, choose Cisco AnyConnect from the results panel, and then add the app.
Step 5. Choose the Single Sign-on menu item, as shown in this image.
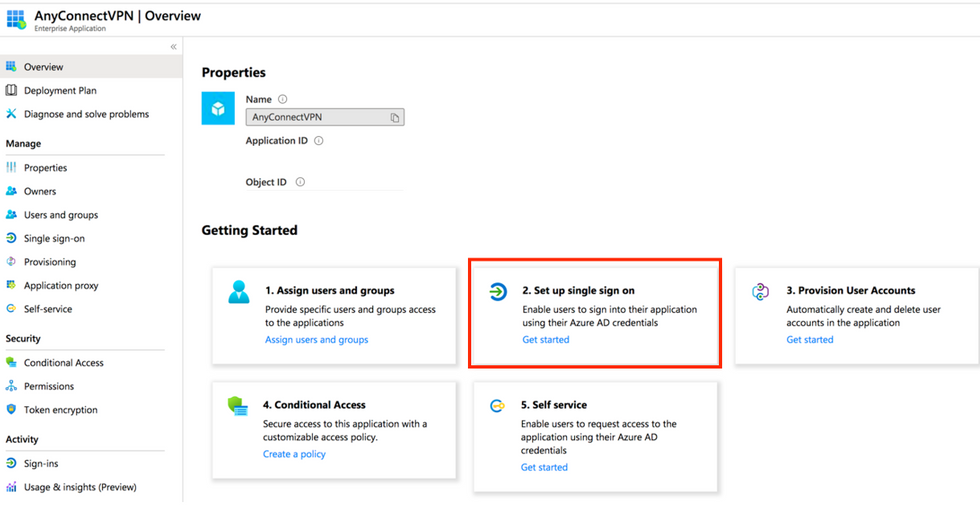
Step 6. Choose SAML, as shown in the image.
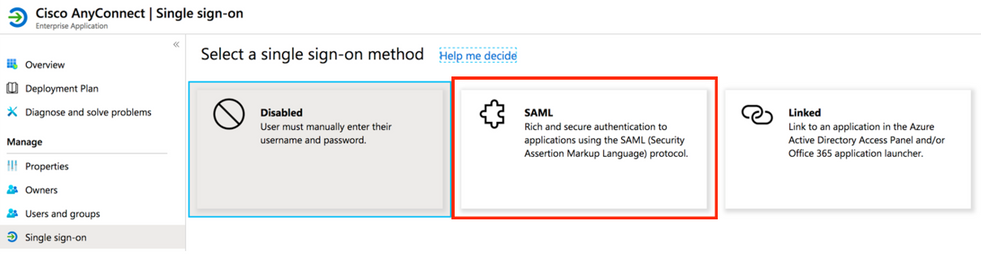
Step 7. Edit Section 1 with these details.
a. Identifier (Entity ID) - https://<VPN URL>/saml/sp/metadata/<TUNNEL-GROUP NAME>
b. Reply URL (Assertion Consumer Service URL) - https://<VPN URL>/+CSCOE+/saml/sp/acs?tgname=<TUNNEL-GROUP NAME>
Example: vpn url called asa.example.com and tunnel-group called AnyConnectVPN-1
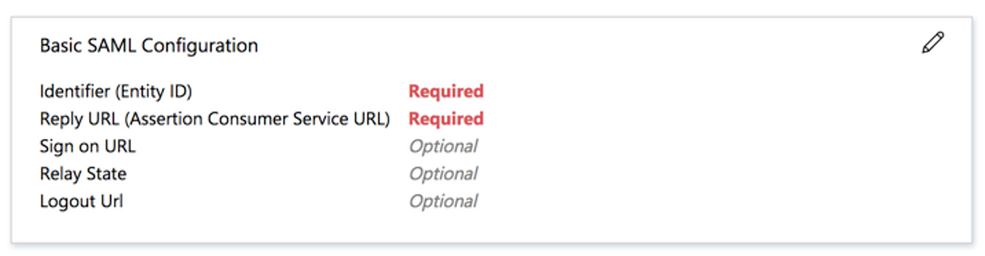
Step 8. In the SAML Signing Certificate section, choose Download to download the certificate file, and save it on your computer.
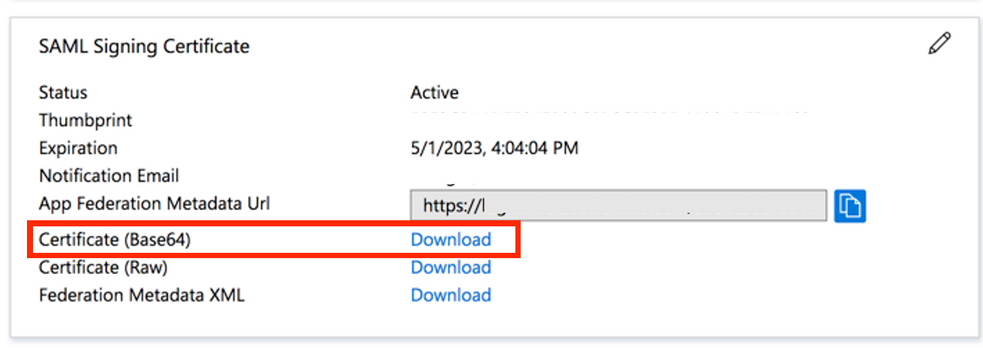
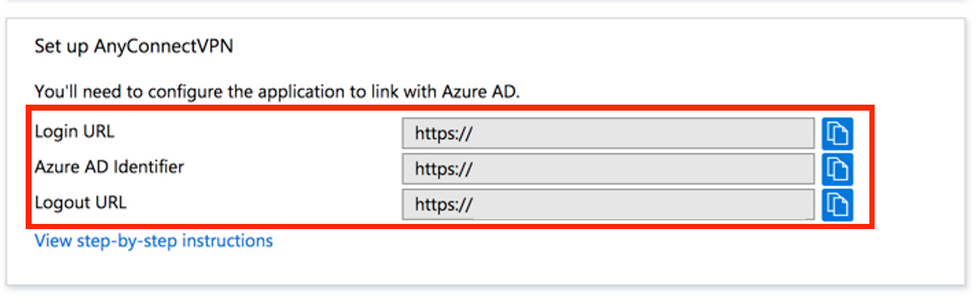
Step 9. This is required for ASA configuration.
- Azure AD Identifier - This is the saml idp in our VPN configuration.
- Login URL - This is the URL sign-in.
- Logout URL - This is the URL sign-out.
Assign Azure AD User to the App
In this section, Test1 is enabled to use Azure single sign-on, as you grant access to the Cisco AnyConnect app.
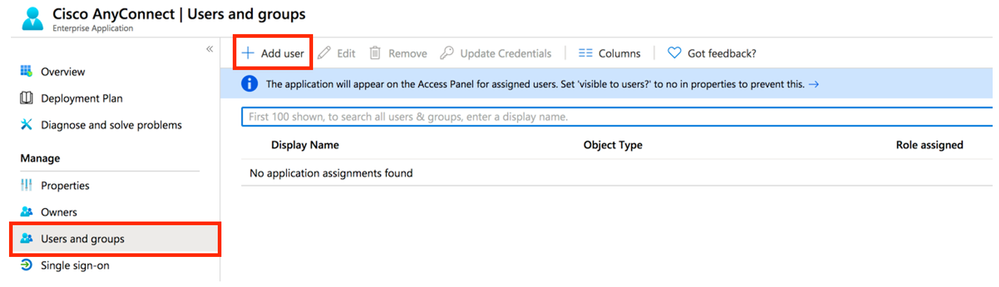
Step 1. In the app's overview page, choose Users and groups, and then Add user.
Step 2. Choose Users and groups in the Add Assignment dialog.
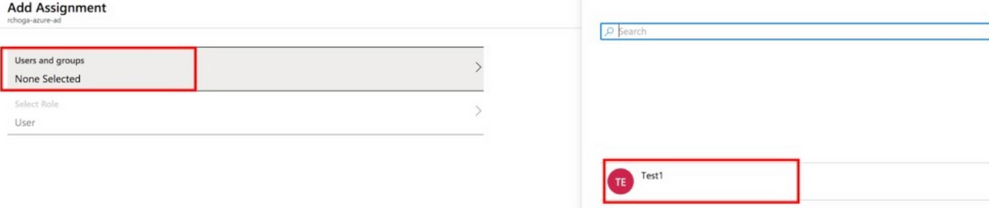
Step 3. In the Add Assignment dialog, click the Assign button.

Configure ASA for SAML via CLI
Step 1. Create a Trustpoint and import your SAML cert.
config t
crypto ca trustpoint AzureAD-AC-SAML
revocation-check none
no id-usage
enrollment terminal
no ca-check
crypto ca authenticate AzureAD-AC-SAML
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
…
PEM Certificate Text you downloaded goes here
…
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
quit
Step 2. These commands provision your SAML IdP.
webvpn
saml idp https://xxx.windows.net/xxxxxxxxxxxxx/ - [Azure AD Identifier]
url sign-in https://login.microsoftonline.com/xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx/saml2 - [Login URL]
url sign-out https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/wsfederation?wa=wsignout1.0 – Logout URL
trustpoint idp AzureAD-AC-SAML - [IdP Trustpoint]
trustpoint sp ASA-EXTERNAL-CERT - [SP Trustpoint]
no force re-authentication
no signature
base-url https://asa.example.com
Step 3. Apply SAML Authentication to a VPN Tunnel Configuration.
tunnel-group AnyConnectVPN-1 webvpn-attributes
saml identity-provider https://xxx.windows.net/xxxxxxxxxxxxx/
authentication saml
end
write memory
Note: If you make changes to the IdP config, you need to remove the saml identity-provider config from your Tunnel Group, and re-apply it for the changes to become effective.
Verify
Test AnyConnect with SAML Auth
Step 1. Connect to your VPN URL and input your log in Azure AD details.
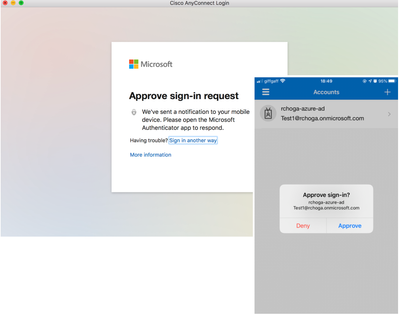
Step 2. Approve sign-in request.
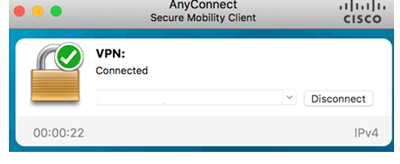
Step 3. AnyConnect is Connected.
Common Issues
Entity ID Mismatch
Debug Example:
[SAML] consume_assertion: The identifier of a provider is unknown to #LassoServer. In order to register a provider in a #LassoServer object, you must use the methods lasso_server_add_provider() or lasso_server_add_provider_from_buffer().
Problem: Generally, means that saml idp [entityID] command under the ASA's webvpn configuration does not match the IdP Entity ID found in the IdP’s metadata.
Solution: Check the entity ID of the IdP’s metadata file and change the saml idp [entity id] command to match this.
Time Mismatch
Debug Example:
[SAML] NotBefore:2017-09-05T23:59:01.896Z NotOnOrAfter:2017-09-06T00:59:01.896Z timeout: 0
[SAML] consume_assertion: assertion is expired or not valid
Problem 1. ASA time not synced with IdP’s time.
Solution 1. Configure ASA with the same NTP server used by IdP.
Problem 2. The assertion is not valid between the specified time.
Solution 2. Modify the timeout value configured on the ASA.
Wrong IdP Signing Certificate Used
Debug Example:
[Lasso] func=xmlSecOpenSSLEvpSignatureVerify:file=signatures.c:line=493:obj=rsa-sha1:subj=EVP_VerifyFinal:error=18:data do not match:signature do not match
[SAML] consume_assertion: The profile cannot verify a signature on the message
Problem: ASA not able to verify the message signed by the IdP or there is no signature for the ASA to verify.
Solution: Check the IdP signing certificate installed on the ASA to make sure it matches what is sent by the IdP. If this is confirmed, make sure that the signature is included in the SAML response.
Invalid Assertion Audience
Debug Example:
[SAML] consume_assertion: assertion audience is invalid
Problem: IdP defines the incorrect audience.
Solution: Correct the Audience configuration on the IdP. It must match the ASA’s Entity ID.
Wrong URL for Assertion Consumer Service
Example Debug: Unable to receive any debugs after the initial authentication request is sent. The user is able to enter credentials at IdP but IdP does not redirect to ASA.
Problem: IdP is configured for the wrong Assertion Consumer Service URL.
Solution(s): Check base URL in configuration and make sure it is correct. Check ASA metadata with show to make sure that the Assertion Consumer Service URL is correct. In order to test it, browse it, If both are correct on the ASA, check the IdP to make sure that the URL is correct.
SAML Configuration Changes That Do Not Take Effect
Example: After a single sign-on URL is modified or changed, the SP certificate, SAML still does not work and sends previous configurations.
Problem: ASA needs to regenerate its metadata when there is a configuration change that affects it. It does not do this automatically.
Solution: After changes are made, under the affected tunnel-group remove and re-apply the saml idp [entity-id] command.
Troubleshoot
Most SAML troubleshoots involve a misconfiguration that can be found when the SAML configuration is checked, or debugs are run. debug webvpn saml 255 can be used to troubleshoot most issues, however, in scenarios where this debug does not provide useful information, additional debugs can be run:
debug webvpn saml 255
debug webvpn 255
debug webvpn session 255
debug webvpn request 255
Related Information

















 Feedback
Feedback