Anyconnect Client to ASA with Use of DHCP for Address Assignment
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to configure the Cisco 5500-X Series Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) to make the DHCP server provide the client IP address to all the Anyconnect clients with the use of the Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) or CLI.
Prerequisites
Requirements
This document assumes that the ASA is fully operational and configured to allow the Cisco ASDM or CLI to make configuration changes.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
Cisco ASA 5500-X Next Generation Firewall Version 9.2(1)
Adaptive Security Device Manager Version 7.1(6)
Cisco Anyconnect Secure Mobility Client 3.1.05152
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Related Products
This configuration can also be used with Cisco ASA Security Appliance 5500 Series Version 7.x and later.
Background Information
Remote access VPNs address the requirement of the mobile workforce to securely connect to the organization's network. Mobile users are able to set up a secure connection using the Cisco Anyconnect Secure Mobility Client software. The Cisco Anyconnect Secure Mobility Client initiates a connection to a central site device configured to accept these requests. In this example, the central site device is an ASA 5500-X Series Adaptive Security Appliance that uses dynamic crypto maps.
In security appliance address management, you have to configure IP addresses that connect a client with a resource on the private network, through the tunnel, and let the client function as if it were directly connected to the private network.
Furthermore, you are dealing only with the private IP addresses that are assigned to clients. The IP addresses assigned to other resources on your private network are part of your network administration responsibilities, not part of VPN management. Therefore, when IP addresses are discussed here, Cisco means those IP addresses available in your private network addressing scheme that let the client function as a tunnel endpoint.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
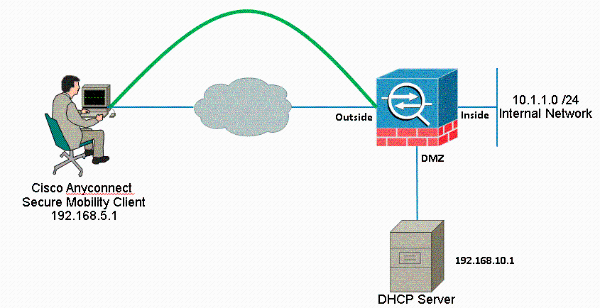
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
Configure Cisco Anyconnect Secure Mobility Client
ASDM Procedure
Complete these steps in order to configure the remote access VPN:
- Enable WebVPN.
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > SSL VPN Connection Profiles and under Access Interfaces, click the check boxes Allow Access and Enable DTLS for the outside interface. Also, check the Enable Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client or legacy SSL VPN Client access on the interface selected in this table check box in order to enable SSL VPN on the outside interface.
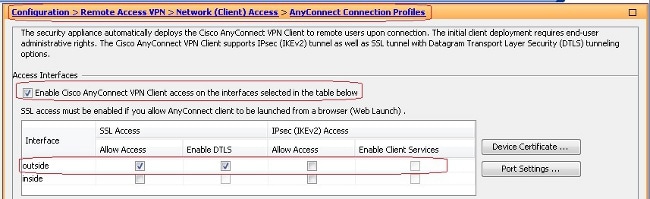
- Click Apply.
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Anyconnect Client Software > Add in order to add the Cisco AnyConnect VPN client image from the flash memory of ASA as shown.
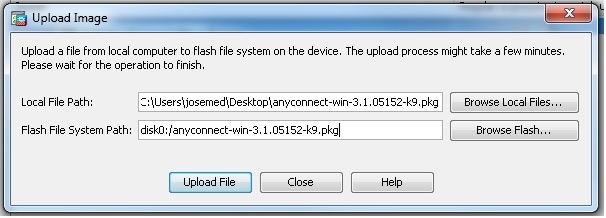
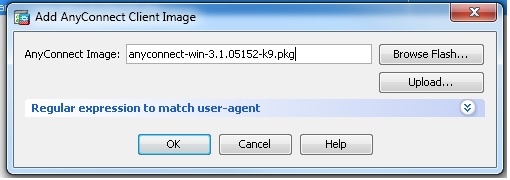
Equivalent CLI Configuration:ciscoasa(config)#webvpn
ciscoasa(config-webvpn)#enable outside
ciscoasa(config-webvpn)#anyconnect image disk0:/anyconnect-win-3.1.05152-k9.pkg 1
ciscoasa(config-webvpn)#tunnel-group-list enable
ciscoasa(config-webvpn)#anyconnect enable
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > SSL VPN Connection Profiles and under Access Interfaces, click the check boxes Allow Access and Enable DTLS for the outside interface. Also, check the Enable Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client or legacy SSL VPN Client access on the interface selected in this table check box in order to enable SSL VPN on the outside interface.
- Configure Group Policy.
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Group Policies in order to create an internal group policy clientgroup. Under the General tab, select the SSL VPN Client check box in order to enable the SSL as tunneling protocol.
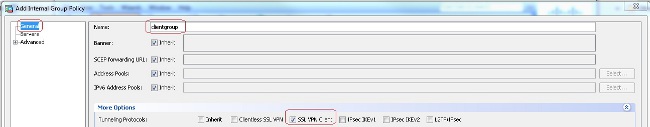
- Configure the DHCP Network-Scope in the Servers tab, choose More Options in order to configure the DHCP Scope for the users to be assigned automatically.

Equivalent CLI Configuration:ciscoasa(config)#group-policy clientgroup internal
ciscoasa(config)#group-policy clientgroup attributes
ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#vpn-tunnel-protocol ssl-client
ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Group Policies in order to create an internal group policy clientgroup. Under the General tab, select the SSL VPN Client check box in order to enable the SSL as tunneling protocol.
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > AAA/Local Users > Local Users > Add in order to create a new user account ssluser1. Click OK and then Apply.
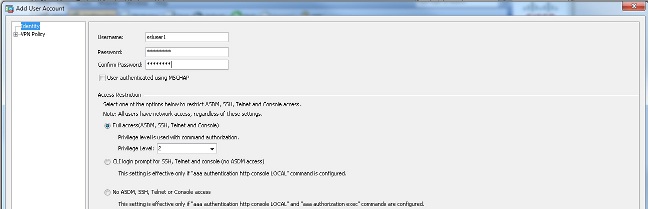
Equivalent CLI Configuration:
ciscoasa(config)#username ssluser1 password asdmASA
- Configure Tunnel Group.
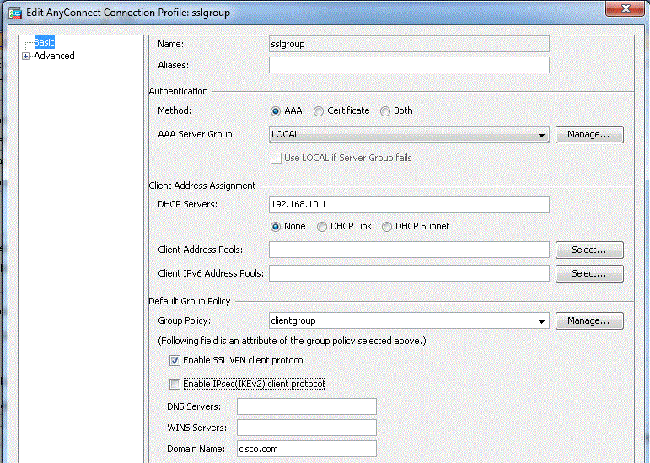
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Anyconnect Connection Profiles > Add in order to create a new tunnel group sslgroup.
- In the Basic tab, you can perform the list of configurations as shown:
- Name the Tunnel group as sslgroup.
- Provide the DHCP server IP address in the space provided for DHCP Servers.
- Under Default Group Policy, choose the group policy clientgroup from the Group Policy drop-down list.
- Configure DHCP Link or DHCP Subnet.
- Under the Advanced > Group Alias/Group URL tab, specify the group alias name as sslgroup_users and click OK.
Equivalent CLI Configuration:ciscoasa(config)#tunnel-group sslgroup type remote-access
ciscoasa(config)#tunnel-group sslgroup general-attributes
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#dhcp-server 192.168.10.1
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#default-group-policy clientgroup
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#exit
ciscoasa(config)#tunnel-group sslgroup webvpn-attributes
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-webvpn)#group-alias sslgroup_users enable
- Choose Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Anyconnect Connection Profiles > Add in order to create a new tunnel group sslgroup.
Subnet-Selection or Link-Selection
DHCP Proxy support for RFC 3011 and RFC 3527 is a feature introduced in the 8.0.5 and 8.2.2 and it has been supported in onward releases.
- RFC 3011 defines a new DHCP option, the subnet selection option, which allows the DHCP client to specify the subnet on which to allocate an address. This option takes precedence over the method that the DHCP server uses to determine the subnet on which to select an address.
- RFC 3527 defines a new DHCP suboption, the link selection suboption, which allows the DHCP client to specify the address to which the DHCP Server should respond.
In terms of the ASA, these RFCs will allow a user to specify a dhcp-network-scope for DHCP Address Assignment that is not local to the ASA, and the DHCP Server will still be able to reply directly to the interface of the ASA. The diagrams below should help to illustrate the new behavior. This will allow the use non-local scopes without having to create a static route for that scope in their network.
When RFC 3011 or RFC 3527 is not enabled, the DHCP Proxy exchange looks similar to this:
With either of these RFCs enabled, the exchange looks similar to this instead, and the VPN client is still assigned an address in the correct subnet:
Configure the ASA with Use of the CLI
Complete these steps in order to configure the DHCP server to provide IP address to the VPN clients from the command line. Refer to Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliances-Command References for more information on each command that is used.
ASA# show run
ASA Version 9.2(1)
!
!--- Specify the hostname for the Security Appliance.
hostname ASA
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
names
!
!--- Configure the outside and inside interfaces.
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
nameif inside
security-level 100
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
nameif DMZ
security-level 50
ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0
!--- Output is suppressed.
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
boot system disk0:/asa802-k8.bin
ftp mode passive
object network obj-10.1.1.0
subnet 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0
object network obj-192.168.5.0
subnet 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0
pager lines 24
logging enable
logging asdm informational
mtu inside 1500
mtu outside 1500
mtu dmz 1500
no failover
icmp unreachable rate-limit 1 burst-size 1
!--- Specify the location of the ASDM image for ASA to fetch the image
for ASDM access.
asdm image disk0:/asdm-716.bin
no asdm history enable
arp timeout 14400
nat (inside,outside) source static obj-10.1.1.0 obj-10.1.1.0 destination static
obj-192.168.5.0 obj-192.168.5.0
!
object network obj-10.1.1.0
nat (inside,outside) dynamic interface
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.2 1
timeout xlate 3:00:00
timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02
timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00 mgcp-pat 0:05:00
timeout sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 sip-invite 0:03:00 sip-disconnect 0:02:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
dynamic-access-policy-record DfltAccessPolicy
http server enable
http 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 inside
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkup linkdown coldstart
telnet timeout 5
ssh timeout 5
console timeout 0
threat-detection basic-threat
threat-detection statistics access-list
!
class-map inspection_default
match default-inspection-traffic
!
!
policy-map type inspect dns preset_dns_map
parameters
message-length maximum 512
policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
inspect dns preset_dns_map
inspect ftp
inspect h323 h225
inspect h323 ras
inspect netbios
inspect rsh
inspect rtsp
inspect skinny
inspect esmtp
inspect sqlnet
inspect sunrpc
inspect tftp
inspect sip
inspect xdmcp
!
service-policy global_policy global
!
!--- Enable webvpn and specify an Anyconnect image
webvpn
enable outside
anyconnect image disk0:/anyconnect-win-3.1.05152-k9.pkg 1
anyconnect enable
tunnel-group-list enable
group-policy clientgroup internal
group-policy clientgroup attributes
!--- define the DHCP network scope in the group policy.This configuration is Optional
dhcp-network-scope 192.168.5.0
!--- In order to identify remote access users to the Security Appliance,
!--- you can also configure usernames and passwords on the device.
username ssluser1 password ffIRPGpDSOJh9YLq encrypted
!--- Create a new tunnel group and set the connection
!--- type to remote-access.
tunnel-group sslgroup type remote-access
!--- Define the DHCP server address to the tunnel group.
tunnel-group sslgroup general-attributes
default-group-policy clientgroup
dhcp-server 192.168.10.1
!--- If the use of RFC 3011 or RFC 3527 is required then the following command will
enable support for them
tunnel-group sslgroup general-attributes
dhcp-server subnet-selection (server ip) (3011)
hcp-server link-selection (server ip) (3527)
!--- Configure a group-alias for the tunnel-group
tunnel-group sslgroup webvpn-attributes
group-alias sslgroup_users enable
prompt hostname context
Cryptochecksum:e0725ca9ccc28af488ded9ee36b7822d
: end
ASA#
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
12-Mar-2015 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)







 Feedback
Feedback