Troubleshooting CEF-Related Error Messages
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes the causes of common Cisco Express Forwarding (formerly CEF)-related error messages on platforms that run Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding (formerly dCEF) switching (Cisco 7500 Series Routers and Cisco 12000 Series Internet Routers) and how to troubleshoot them.
Note: Depending on the platform on which Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding is configured, Route Processors (RPs) and Line Cards (LCs) are referred to differently. For the 7500 Series, the RP is called the Route Switch Processor (RSP) and LCs are called Versatile Interface Processors (VIPs). On the 12000 Series, the RP is known as the Gigabit Route Processor (GRP) and LCs are simply referred to as LCs.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
Cisco Express Forwarding switching is a proprietary form of scalable switching intended to tackle the problems associated with demand caching. With Cisco Express Forwarding switching, the information which is conventionally stored in a route cache is split up over several data structures. The Cisco Express Forwarding code is able to maintain these data structures in the RP, and also in slave processors such as VIPs in the Cisco 7500 Series and LCs in the Cisco 12000 Series. The data structures that provide optimized lookup for efficient packet forwarding include:
-
Forwarding Information Base (FIB) table—Cisco Express Forwarding uses a FIB to make IP destination prefix-based switching decisions. The FIB is conceptually similar to a routing table or information base. It maintains a mirror image of the forwarding information contained in the IP routing table. When routing or topology changes occur in the network, the IP routing table is updated, and these changes are reflected in the FIB. The FIB maintains next-hop address information based on the information in the IP routing table.
Because there is a one-to-one correlation between FIB entries and routing table entries, the FIB contains all known routes and eliminates the need for route cache maintenance that is associated with switching paths such as fast switching and optimum switching.
-
Adjacency table—Nodes in the network are said to be adjacent if they can reach each other with a single hop across a link layer. In addition to the FIB, Cisco Express Forwarding uses adjacency tables to prepend Layer 2 (L2) addressing information. The adjacency table maintains L2 next-hop addresses for all FIB entries.
Cisco Express Forwarding can be enabled in one of two modes:
-
Central Cisco Express Forwarding mode—When Cisco Express Forwarding mode is enabled, the Cisco Express Forwarding FIB and adjacency tables reside on the RP, and the RP performs the express forwarding. You can use Cisco Express Forwarding mode when LCs are not available for Cisco Express Forwarding switching, or when you need to use features not compatible with Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding switching.
-
Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding mode—When Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding is enabled, LCs (such as VIP LCs or Gigabit Switch Router (GSR) LCs), maintain identical copies of the FIB and adjacency tables. The LCs can perform the express forwarding by themselves, relieving the main processor (GRP or RSP) of involvement in the switching operation. This is the only switching method available on the 12000 Series.
Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding uses an Inter-Process Communication (IPC) mechanism to ensure synchronization of FIBs and adjacency tables on the RP and LCs.
Verify Cisco Express Forwarding Status on VIPs and LCs
Note: In the examples below, some of the commands use output modifiers (represented by the | symbol), to simplify the display to only show the needed information. Output modifiers are supported in Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.0 and later. If you are running an older version, issue the main command (the one before the | symbol), and look for the corresponding lines in the complete output.
You can easily verify on which VIP or LC Cisco Express Forwarding has been disabled by issuing the show cef linecard command:
-
On the 7500 Series:
Router#show cef linecard CEF linecard generic information: Slot MsgSent Seq MaxSeq LowQ MedQ HighQ Flags 4 8 6 30 0 0 0 up 5 8 6 30 0 0 0 up Default-table CEF table, version 13, 11 routes Slot CEF-ver CEF-XDR Interface Flags 4 12 5 5 Active, sync 5 12 5 2 Active, sync
-
On the 12000 Series:
Router#show cef linecard CEF table version 694517, 95239 routes Slot CEF-ver MsgSent XdrSent Seq MaxSeq LowQ MedQ HighQ Flags 0 32128 365 33320 362 367 0 0 0 disabled 1 95821 1010 99369 1006 1025 0 0 0 disabled 2 92559 971 6033 967 984 0 0 0 disabled 8 62514 653 65734 649 661 0 0 0 disabled 9 47165 486 48428 483 498 0 0 0 disabled 10 79887 834 83232 830 849 0 0 0 disabled
Because 12000 Series only supports Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding, a disabled status causes the entire LC to be disabled.
External Data Representation (XDR) Overview
In order to understand the following error messages, you need to understand what the XDR messages are, and what they are used for:
-
%FIB-3-NORPXDRQELEMS
-
%FIB-3-FIBBADXDRLEN
-
%FIB-4-FIBXDRLEN
Here is an overview of the XDR architecture:
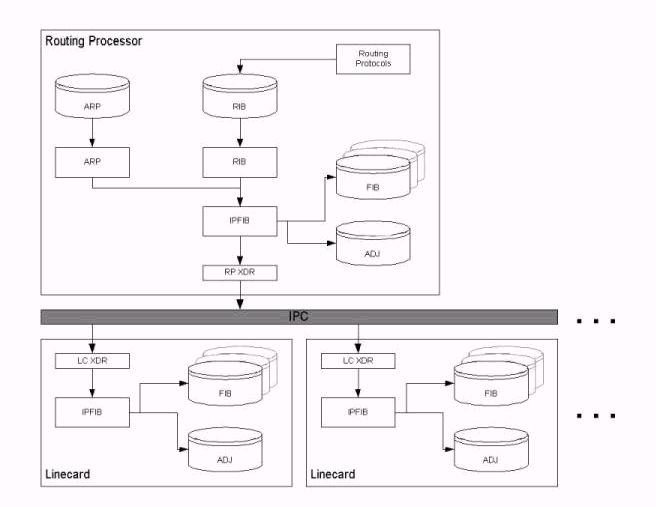
As explained in the Background Information section of this document, IPC messages transport the FIB and adjacency tables from the RP to the LCs. In other words, the IPC mechanism synchronizes both sets of tables on the RP and the LCs. Any data structure used by a feature must be transported to the LC through the FIB IPC, and the statistics must be sent back to the RP. When Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding is enabled, the LC makes the forwarding decision using the locally stored, replicated databases.
XDR is referred to as an IPC overlay mechanism. XDR messages are used exclusively with the Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding implementation.
Statistics as well as data structures to support a Cisco IOS Software feature are carried in XDR messages over the Cisco IOS Software IPC mechanism between the RP and LCs. Specifically, XDR messages carry three sets of information, as listed in the following table:
| Message Type | Message Description | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Control | The RP sends control data in RP feature sub-blocks to be sent to all the mirroring sub-blocks on the LCs that need to know about any changes. | RP to LC |
| Statistics | LCs collect statistics information from the various feature sub-blocks, place the collected information in an XDR buffer, and send an XDR message to the RP. The RP then aggregates these statistics. | LC to RP |
| Asynchronous Event Reporting | LCs report nonroutine events through asynchronous messages that are sent as the condition occurs. | LC to RP |
Issue the show cef line internal command to view information transmitted through XDR messages. A Network Descriptor Block (NDB)/Routing Descriptor Block (RDB) update is one example of an XDR.
Total elements queued: prefix 1877106 adjacency 6011 interface 4084 address 4010 policy routing 3 hw interface 84 state 6 resequence 2 control 24 time 308 subblock 18109 flow features deactivate 3 flow cache config 3 flow export config 3 flow sampling config 3 access-list 213 mpls ttl propogate 3 routemap config 126 mpls stats aggregate 3 dot1q vlan 10109 icmp limit 3
Troubleshoot
This section lists error messages that appear in the router logs, and provides troubleshooting tips.
%FIB-3-FIBDISABLE : Fatal error, slot [#]: no memory and %FIB-3-NOMEM: Malloc Failure, disabling dCEF on line card
These types of error messages are found in the router logs (issue the show logging exec command on your router, or consult your syslog server if you are using one) as follows:
-
On the 7500 Series:
Dec 19 17:58:56 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 0: no memory DEC 19 17:58:58 CET: %IPC-5-SLAVELOG: VIP-SLOT0: 00:03:37: %SYS-2-MALLOCFAIL: Memory allocation of 65524 bytes failed from 0x6009E9E4, pool Processor, alignment 16 -Process= "CEF IPC Background", ipl= 0, pid= 7 -Traceback= 600A141C 600A2B78 6009E9EC 6009F350 60235A34 60221BA4 60225528 6022A46C 60231104 6022FAC4 6022FCCC 6022FDBC 60230334 6009BB74 6009BB60 DEC 19 17:59:06 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 9: no memory DEC 19 17:59:11 CET: %IPC-5-SLAVELOG: VIP-SLOT9: 00:03:47: %SYS-2-MALLOCFAIL: Memory allocation of 65524 bytes failed from 0x6009E9E4, pool Processor, alignment 16 -Process= "CEF IPC Background", ipl= 0, pid= 7 -Traceback= 600A141C 600A2B78 6009E9EC 6009F350 60235A34 60221BA4 60225528 6022A46C 60231104 6022FAC4 6022FCCC 6022FDBC 60230334 6009BB74 6009BB60 DEC 19 17:59:31 CET: %IPC-5-SLAVELOG: VIP-SLOT8: 00:04:11: %SYS-2-MALLOCFAIL: Memory allocation of 3956 bytes failed from 0x602835F0, pool Processor, alignment 32 -Process= "CEF LC Stats", ipl= 0, pid= 21 -Traceback= 600A141C 600A2EC8 602835F8 60283C84 60283C58 60283CE4 60230574 6009BB74 6009BB60 DEC 19 17:59:38 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 8: no memory DEC 19 18:00:29 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 10: no memory ...
-
On the 7500 Series, the error message that appears just after the %IPC-5-SLAVELOG: VIP-SLOT message comes directly from the VIP which is located in the mentioned slot using an IPC mechanism. In this specific example, the %SYS-2-MALLOCFAIL message comes from the VIP card.
Jun 27 04:58:56 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 1: no memory Jun 27 04:59:07 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 2: no memory Jun 27 04:59:36 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 4: no memory Jun 27 04:59:45 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 0: no memory SLOT 2:Jun 27 04:23:00: %SYS-2-MALLOCFAIL: Memory allocation of 65524 bytes failed from 0x4009D9E4, pool Processor, alignment 32 -Process= "CEF IPC Background", ipl= 0, pid= 38 -Traceback= 400A0BFC 400A2358 4009D9EC 4009E338 403168BC 40316B68 40316EBC 4031C318 40321234 4032858C 40326CD4 40326EF4 40326FE4 403275CC 4009BC74 4009BC60 SLOT 2:Jun 27 04:23:00: %FIB-3-NOMEM: Malloc Failure, disabling DCEF on linecard ...
Note: Messages starting with "SLOT #:" are generated by the LC itself.
These messages indicate that Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding has been disabled on the VIP (for the 7500 Series) or LC (for the 12000 Series) because there was not enough memory on it to download the Cisco Express Forwarding FIB and adjacency tables from the main board. Because the 12000 Series only supports Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding switching, disabling Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding also disables the card.
When running full Internet Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routes, it is recommended to have at least 128MB on the VIP or LC.
Because the VIP2-40 on the 7500 Series can only have a maximum of 64 MB, an upgrade to VIP2-50 or even VIP4-80 is recommended if you want to use Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding with full Internet BGP routes. Thirty-two MB is definitely not sufficient to run Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding.
A VIP2-50 or higher with at least 128MB of memory is recommended, depending on the size of the routing table.
If your router accepts the full Internet routing table (or close to it), BGP needs a large amount of memory temporarily during the convergence phase after a router is reloaded or a BGP link changes status. During such convergence, the processor memory pool may reach a very low value, as reflected in the output of the show memory summary command. During the brief low-memory condition, other processes may be affected if they need memory. For example, issuing the telnet command to contact a router requires memory to maintain the TCP session.
Another transient user of processor memory is the Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) in Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) networks.
Cisco Express Forwarding produces the FIBDISABLE error only when the router completely runs out of processor memory. There is no low-water mark for FIBDISABLE. Once Cisco Express Forwarding disables itself, it frees all its memory. Thus, capturing the output of the show memory summary command after the disabling shows that sufficient free memory is available, but this output is misleading. Only captures of show memory summary command before Cisco Express Forwarding disables itself reveals data about the low-memory condition.
In addition, a FIBDISABLE condition may be a side-effect of running out of IPC buffers. Cisco IOS Software does not dynamically allocate more IPC buffers as they are needed. Running out of IPC buffers does not generate FIB NOMEM error messages, but other IPC error messages such as IPC-3-NOBUFF may be seen. Running out of IPC buffers does not cause a FIBDISABLE error; Cisco Express Forwarding simply requeues any failed message and tries again later. However, if IPC buffers are depleted and Cisco Express Forwarding cannot get an IPC buffer, it may queue messages to LCs until it eventually runs out of memory.
A frequent question to the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) is how to plan for or determine whether a BGP-connected router has sufficient memory to run BGP. The answer depends on the configuration. Here are some considerations:
-
Are you planning to use Internal Border Gateway Protocol (iBGP) and External Border Gateway Protocol (eBGP) peers? How many peers? BGP peer groups may help. More peers means a longer convergence time.
-
How many routes are exchanged in each direction for each peer? Ensure that the proper distinction is made between routes and paths. Routes count the number of prefixes in the BGP routing information base. Paths count the number of BGP prefixes advertised to a neighboring peer. For example, if five BGP peers send the full routing table, then each peer is sending the same routes. Assuming the peers have 90 percent overlap in their routes, then the receiving router has a route table of about 150,000 routes with five paths for most routes.
-
Other factors to consider include the following:
-
There is an LC engine on the 12000 Series.
-
The number of Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) routes.
-
The number of adjacencies.
-
Load balancing—The number of paths to the same destination.
-
Use of MPLS Virtual Private Network (VPN) and the number of Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) instances and the number of routes per VRF.
-
Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0(18)S and later releases officially require 128MB on all LCs. Because newer Cisco IOS Software releases occupy more processor memory, up to 256MB is recommended to support future scalability for routers accepting the full Internet routing table. Previously, the 12000 Series was available with 64MB on LCs. Such LCs should be upgraded.
Check which cards are affected (refer to the Verifying Cisco Express Forwarding Status on VIPs and LCs section of this document), and issue the following commands to display the different types of cards present in your router, and their respective amounts of memory:
-
On the 7500 Series:
Router#show diag | i (Slot | controller) Slot 0: EIP controller, HW rev 1.05, board revision B0 Slot database information: Slot 2: Slot 3: Slot 4: VIP2 controller, HW rev 2.11, board revision E0 Slot database information: Controller Memory Size: 64 MBytes DRAM, 2048 KBytes SRAM Slot 5: VIP2 R5K controller, HW rev 2.03, board revision A0 Slot database information: Controller Memory Size: 128 Mbytes DRAM, 8192 Kbytes SRAM Slot 31 (virtual): -
On the 12000 Series:
Router#show diag | i (DRAM|SLOT) SLOT 0 (RP/LC 0 ): 1 Port SONET based SRP OC-12c/STM-4 Single Mode DRAM size: 268435456 bytes FrFab SDRAM size: 134217728 bytes, SDRAM pagesize: 8192 bytes ToFab SDRAM size: 134217728 bytes, SDRAM pagesize: 8192 bytes SLOT 2 (RP/LC 2 ): 12 Port Packet over E3 DRAM size: 67108864 bytes FrFab SDRAM size: 67108864 bytes ToFab SDRAM size: 67108864 bytes SLOT 3 (RP/LC 3 ): 1 Port Gigabit Ethernet DRAM size: 134217728 bytes FrFab SDRAM size: 134217728 bytes, SDRAM pagesize: 8192 bytes ToFab SDRAM size: 134217728 bytes, SDRAM pagesize: 8192 bytes SLOT 5 (RP/LC 5 ): Route Processor DRAM size: 268435456 bytes
Adding more memory to the affected cards should prevent the messages and re-enable Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding on the cards. If the messages are still present after a memory upgrade, contact your Cisco support representative, and provide the information you collected so far along with a the output of a show tech-support command.
Note: The old Fast Ethernet Interface Processor (FEIP) models (CX-FEIP2-2TX and CX-FEIP2-2TX) do not support distributed switching at all, and generates similar messages if you try to enable Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding on it. Issue the show diag [slot#] command to determine whether your board is a VIP or an FEIP:
Router#show diag 0
Slot 0:
Physical slot 0, ~physical slot 0xF, logical slot 0, CBus 0
Microcode Status 0x4
Master Enable, LED, WCS Loaded
Pending I/O Status: None
EEPROM format version 1
FEIP controller, HW rev 2.01, board revision B0
Serial number: 03696620 Part number: 73-1374-04
Test history: 0x0E RMA number: 203-11-48
Flags: cisco 7000 board; 7500 compatible
If you want to run Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding, you have to replace your old FEIP with a VIP card with Fast Ethernet port adapters.
%FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot [#]: No window message, LC to RP IPC is non-operational
The following messages (on the 7500 and 12000 Series) also indicate that Cisco Express Forwarding has been disabled, this time because the RSP or GRP did not receive a keepalive from the VIP or LC:
DEC 19 18:03:55 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 0: No window message, LC to RP IPC is non-operational DEC 19 18:04:05 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 9: No window message, LC to RP IPC is non-operational DEC 19 18:04:37 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 8: No window message, LC to RP IPC is non-operational DEC 19 18:05:28 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 10: No window message, LC to RP IPC is non-operational DEC 19 18:05:59 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 2: No window message, LC to RP IPC is non-operational DEC 19 18:06:07 CET: %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 1: No window message, LC to RP IPC is non-operational
First, check that you have sufficient memory on your cards.
Then check the CPU utilization on your VIP or LC (issue the show controllers vip [slot#] proc cpu command on the 7500 Series, and the execute-on slot 0 show proc CPU command on the 12000 Series). If the CPU utilization is really high (above 95%), the VIP or LC may be too busy to send the keepalives to the RSP or GRP. The root cause of the problem here is the heavy CPU usage. Refer to Troubleshooting High CPU Utilization on Cisco Routers for troubleshooting tips.
If everything looks all right, then the error messages are most probably caused by a bug in the Cisco IOS Software.
When troubleshooting this error, the first thing you should do is to check the cards that have been affected (refer to the Verifying Cisco Express Forwarding Status on VIPs and LCs section of this document). You can try to restart Cisco Express Forwarding on those cards by issuing the clear cef linecard [slot#] command. On the 7500 Series, it may also be necessary to reset the VIP card by issuing the microcode reload command. This generates a CBUS complex, which causes a traffic interruption of approximately two minutes (refer to What Causes a "%RSP-3-RESTART: cbus complex"? for more information). This procedure should, at least temporarily, restore Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding on the VIP or LC.
Otherwise, upgrading to the latest version of your Cisco IOS Software release train gets rid of all fixed issues causing this type of error. If the problem still occurs after the upgrade, contact your Cisco support representative and provide the information you have collected so far, along with a the output from a show tech-support command.
%FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot [#]: IPC failure
The following error messages are more generic, and may cause other error messages to appear (such as %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot [#]: No window message, LC to RP IPC is nonoperational):
%FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 3: IPC failure %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 0: IPC failure %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 1: IPC failure %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 2: IPC failure %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 4: IPC failure %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 9: IPC failure %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 10: IPC failure
Inter-Process Communication (IPC) is a protocol used by the main processor (RSP or GRP) and the VIP or LC for communication. It ensures the synchronization of FIBs and adjacency tables when Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding is running. There are multiple causes for these IPC error messages, such as:
IPC Failures
The commands below can be used to analyze the actual IPC status. The output for these commands sometimes differs between the 7500 Series and the 12000 Series.
-
show ipc status—used to check IPC errors, NACKs, and ipc_output_failures
-
show ipc nodes—used to check the active cards.
-
show ipc queue—used to check the IPC messages waiting for ACK.
On the 7500 Series, the output is as follows:
Router#show ipc status
IPC System Status:
This processor is the IPC master server.
1000 IPC message headers in cache
1591560 messages in, 5884 out, 1587095 delivered to local port,
2757 acknowledgements received, 2764 sent,
0 NACKS received, 0 sent,
0 messages dropped on input, 276 messages dropped on output
0 no local port, 264 destination unknown, 0 no transport
0 missing callback or queue, 0 duplicate ACKs, 5 retries,
1 message timeout.
12 ipc_output failures, 0 mtu failures,
0 msg alloc failed, 0 emer MSG alloc failed, 0 no origs for RPC replies
0 pak alloc failed, 10 memd alloc failed
2 no hwq, 0 failed opens, 0 hardware errors
No regular dropping of IPC output packets for test purposes
Router#show ipc nodes
There are 3 nodes in this IPC realm.
ID Type Name Last Last
Sent Heard
10000 Local IPC Master 0 0
1030000 RSP-CY RSP IPC card slot 3 7 7
1000000 RSP-CY RSP IPC card slot 0 10 10
Router#show ipc queue
There are 0 IPC messages waiting for acknowledgement in the transmit queue.
There are 0 IPC messages waiting for a response.
There are 0 IPC messages waiting for additional fragments.
There are 0 IPC messages currently on the IPC inboundQ.
There are 0 messages currently in use by the system.
On the 12000 Series, the output is as follows:
Router#show ipc status
IPC System Status:
This processor is the IPC master server.
19244592 messages in, 26698 out, 19244448 delivered to local port,
102 acknowledgements received, 4780307 sent,
0 NACKS received, 0 sent,
0 messages dropped on input, 0 messages dropped on output
0 no local port, 0 destination unknown, 0 no transport
0 missing callback or queue, 0 duplicate ACKs, 0 retries,
0 message timeouts.
0 ipc_output failures, 0 mtu failures,
0 MSG alloc failed, 0 emer MSG alloc failed, 0 no origs for RPC replies
0 pak alloc failed, 0 memd alloc failed
0 no hwq, 0 failed opens, 0 hardware errors
Router#show ipc nodes
There are 4 nodes in this IPC realm.
ID Type Name Last Last
10000 Local IPC Master 0 0
1000000 GSR GSR Slot 0 23 47
1010000 GSR GSR Slot 1 23 26
1040000 GSR GSR Slot 4 23 29
Sent Heard
Router#show ipc queue
There are 0 IPC messages waiting for acknowledgement in the transmit queue.
There are 0 messages currently in use by the system.
If the highlighted counters are increasing, IPC is not running properly for the different slots. In that case, you should first try to reseat the corresponding LC, or to reset it by issuing the microcode reload command (for the 7500 Series), or by issuing the hw-module slot [slot#] reload command (for the 12000 Series). If the IPC process does not recover after resetting the LC, try moving the board to another slot. If it still does not work, replace the faulty VIP or LC.
Fabric Problem
On a 12000 Series Internet Router, the fabric itself may be the culprit. If one of the Switching Fabric Cards (SFCs) is bad, you may get similar error messages because the IPC messages can no longer go through the fabric. However, in this case, you should also see other messages pointing to the faulty fabric.
You can check if one of the SFCs is bad by issuing the show controller fia command, as follows:
Router#show controllers fia Fabric configuration: Full bandwidth redundant Master Scheduler: Slot 17 >From Fabric FIA Errors /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html --- redund fifo parity 0 redund overflow 0 cell drops 1 crc32 lkup parity 0 cell parity 0 crc32 0 Switch cards present 0x0017 Slots 16 17 18 20 Switch cards monitored 0x0017 Slots 16 17 18 20 Slot: 16 17 18 19 20 Name: csc0 csc1 sfc0 sfc1 sfc2 /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html los 0 0 0 0 0 state Off Off Off Off Off crc16 0 0 4334 0 0 To Fabric FIA Errors /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html /en/US/docs/net_mgmt/wan_service_administrator/1.1/administrator/guide/getstart.html --- sca not pres 0 req error 0 uni FIFO overflow 0 grant parity 0 multi req 0 uni FIFO undrflow 0 cntrl parity 0 uni req 0 crc32 lkup parity 0 multi FIFO 0 empty dst req 0 handshake error 0 cell parity 0
In this example, sfc0 is probably bad (slot 18), and needs to be replaced.
VIP or LC That does Not Boot Properly or Hangs
If one of the cards does not boot properly, it is unable to communicate with the main processor (GRP or RSP). You can check the log by issuing the show log command; this tells you if something went wrong at bootup. You also need to check the status of the LC.
It is possible to check the actual status of the LCs by issuing the show diag command.
-
On the 7500 Series:
Router#show diag | i (Slot|Board is) Slot 0: Board is analyzed Slot database information: Slot 2: Slot 3: Slot 4: Board is analyzed Slot database information: Slot 5: Board is analyzed Slot database information: Slot 31 (virtual) -
On the 1200 Series:
Router#show diags | i SLOT | State SLOT 0 (RP/LC 0 ): Route Processor Board State is IOS Running (ACTV RP ) SLOT 1 (RP/LC 1 ): 1 port ATM Over SONET OC12c/STM-4c Multi Mode Board State is Line Card Enabled (IOS RUN ) SLOT 2 (RP/LC 2 ): 1 Port Gigabit Ethernet Board State is Line Card Enabled (IOS RUN ) SLOT 3 (RP/LC 3 ): 3 Port Gigabit Ethernet Board State is Line Card Enabled (IOS RUN ) SLOT 4 (RP/LC 4 ): 4 port ATM Over SONET OC-3c/STM-1 Multi Mode Board State is In Reset (IN RSET) SLOT 5 (RP/LC 5 ): 8 Port Fast Ethernet Copper Board State is Line Card Enabled (IOS RUN ) SLOT 6 (RP/LC 6 ): 4 Port Packet Over SONET OC-3c/STM-1 Multi Mode Board State is Line Card Enabled (IOS RUN ) SLOT 7 (RP/LC 7 ): 1 Port E.D. Packet Over SONET OC-48c/STM-16 Single Mode/SR SC-SC connector Board State is Line Card Enabled (IOS RUN ) SLOT 17 (CSC 1 ): Clock Scheduler Card(8) SLOT 18 (SFC 0 ): Switch Fabric Card(8) SLOT 19 (SFC 1 ): Switch Fabric Card(8) SLOT 20 (SFC 2 ): Switch Fabric Card(8) SLOT 24 (PS A1 ): AC Power Supply(8)
The normal status is Line Card Enabled on the 12000 Series, and Board is analyzed on the 7500 Series.
Check whether the card is supported by the Cisco IOS Software and the boot image you are currently running. To do this, you can use the Software Advisor (registered customers only) . If the software is running normally, try reseating the corresponding LC or resetting it by issuing the microcode reload command (for the 7500 Series), or the hw-module slot [slot#] reload command (for the 12000 Series).
If the LC does not come back to life, try swapping the card to another slot to be sure that this particular slot in the chassis is not faulty. If it still does not work, then the VIP or LC probably needs to be replaced.
You may also want to check whether there is enough memory on the LC, and if the memory was purchased directly from Cisco or from a Cisco-approved vendor. An LC does not boot up if the wrong type of memory is used or if there is not enough memory to upload the microcode.
VIP or Line Card With No More Buffers
It may happen that the LC runs short of memory and has no more buffers for the IPC communication to occur. In this case, you should upgrade the memory of the LC.
Cisco IOS Software Bug
If everything else seems in order, then consider the possibility of a bug in the Cisco IOS Software. Upgrading to the latest version of your Cisco IOS Software release train gets rid of all fixed-IPC issues.
In some rare 12000 Series-related cases where access list improvement is configured, you may also get these error messages. A short-term fix is to disable this new feature by issuing the no access-list hardware psa command. For more information, refer to Access List Performance Improvements for Cisco 12000 Gigabit Switch Routers.
If you cannot determine the cause of the messages, or if the problem still appears in the latest Cisco IOS Software release available on CCO for your release train, then you may have encountered a new Cisco IOS Software bug. Contact your Cisco support representative and provide the data you collected so far, along with the output of the show tech-support and show cef linecard commands from that router.
Online Insertion and Removal (OIR) or VIP Crash
After a VIP crash, the RSP packet memory (known as MEMD) is recarved, and IPC connections between the RSP and the VIPs are reset. If the RSP has Cisco Express Forwarding messages queued in the IPC retransmit table during a VIP crash, these messages can timeout and cause Cisco Express Forwarding to disable on other LCs. Cisco bug ID CSCdv87489 (registered customers only) resolves this problem on the RSP by prompting Cisco Express Forwarding to detect an OIR, LC reload, or MEMD recarve, and flush messages in the retransmit queue. Cisco bug ID CSCdu81796 (registered customers only) resolves this problem on the Cisco 10000 Series Router.
Doing an OIR of a VIP or LC can trigger FIBDISABLE error issues on other slots. This situation arises when Cisco Express Forwarding on RP fails to make IPC connection to other VIP cards due to an OIR event on one of the VIPs. Cisco bug ID CSCdv47664 (registered customers only) resolves this problem.
%FIB-4-RPPREFIXINCONST2/1 and %FIB-4-LCPREFIXINCONST2/1
You may also notice the following messages in the router logs:
%FIB-4-RPPREFIXINCONST2: RP missing prefix for 195.74.205.54/32 in FIB table Default-table (present in routing) %FIB-4-RPPREFIXINCONST2: RP missing prefix for 195.74.205.231/32 in FIB table Default-table (present in routing) %FIB-4-RPPREFIXINCONST2: RP missing prefix for 195.74.221.68/32 in FIB table Default-table (present in routing) %FIB-4-RPPREFIXINCONST2: RP missing prefix for 195.74.216.52/32 in FIB table Default-table (present in routing) %FIB-4-RPPREFIXINCONST2: RP missing prefix for 195.74.216.96/32 in FIB table Default-table (present in routing) %FIB-4-RPPREFIXINCONST2: RP missing prefix for 195.74.216.55/32 in FIB table Default-table (present in routing)
or
%FIB-4-LCPREFIXINCONST2: Slot 1 missing prefix entry for 64.0.17.0/32 %FIB-4-LCPREFIXINCONST2: Slot 1 missing prefix entry for 64.0.45.0/32 %FIB-4-LCPREFIXINCONST2: Slot 1 missing prefix entry for 64.0.23.0/32
This issue affects all the hardware running Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding, including the 7500 and 12000 Series. These messages are warnings generated by the Cisco Express Forwarding consistency checker when it discovers inconsistencies between Cisco Express Forwarding tables.
The consistency checker uses different mechanisms to find the inconsistencies :
-
The LC or VIP sends the GRP or RSP any address to which it could not forward packets. If the GRP or RSP detects that it was a relevant entry, then an inconsistency has been detected and an error message is printed on the console.
-
The LCs or VIPs and the GRP or RSP send each other a fixed amount of prefixes (100 by default) every 60 seconds. If an inconsistency is detected, the error message appears.
If the inconsistency is not corrected, this may result in unreachable destinations and dropped packets. When you see those messages, the first thing to do is issue a show ip cef command on the device mentioned in the error message, and verify whether or not the prefix is present. This tells you whether or not the router corrected the inconsistency by itself.
Below are more detailed explanations of each message, and some recommendations for getting rid of them.
-
%FIB-4-RPPREFIXINCONST2—A passive consistency checker has discovered a prefix in the routing table which is not present in the Cisco Express Forwarding forwarding table on the RP. This may be a transient condition.
If the same prefix gives repeated errors, check the prefix in Cisco Express Forwarding and the routing table. Try to disable or enable Cisco Express Forwarding if the prefix is missing.
-
%FIB-4-RPPREFIXINCONST1—A passive consistency checker has discovered a prefix in the forwarding table of the LC which is not present on the RP. This may be a transient condition.
If the same prefix gives repeated errors, check the Cisco Express Forwarding prefix on the RP and linecard. If necessary, issuing the clear cef linecard command downloads a new Cisco Express Forwarding table to the linecard.
-
%FIB-4-LCPREFIXINCONST1—A packet has arrived on the LC, but the lookup of the destination IP address failed to find this prefix in the forwarding table. However, the prefix is present on the RP. This may be a transient condition.
If the same prefix gives repeated errors, check the Cisco Express Forwarding prefix on the RP and LC. If necessary, issuing the clear cef linecard command downloads a new Cisco Express Forwarding table to the LC. You can also try issuing a clear adjacency command to reload the /32 prefixes.
-
%FIB-4-LCPREFIXINCONST2—A passive consistency checker has discovered a prefix missing from the forwarding table of the LC that is present on the RP. This may be a transient condition.
If the same prefix gives repeated errors, check the Cisco Express Forwarding prefix on the RP and LC. If necessary, issuing the clear cef linecard command downloads a new Cisco Express Forwarding table to the LC. You can also try issuing the clear adjacency command to reload the /32 prefixes.
If the message has only appeared once, and the inconsistency was corrected immediately, it might be a transient event and no action is required. However, if you receive many of these messages, or if the router does not correct this situation by itself, then you are probably hitting a software bug in the Cisco Express Forwarding code. A number of these software bugs have been fixed in Cisco IOS Software Releases 12.0(17)S1 and 12.0(17)ST1, so make sure you are running at least this version of Cisco IOS Software.
If the problem still appears after an upgrade to the latest version in your release train, contact your Cisco support representative and provide the output of the show tech, show ip route, and show ip cef commands.
Note: You can turn off the consistency checkers by issuing the no ip cef table consistency-check global configuration command.
For further details and more troubleshooting tips about this error message, refer to Troubleshooting Prefix Inconsistencies with Cisco Express Forwarding.
%FIB-3-NORPXDRQELEMS: Exhausted XDR queuing elements while preparing message for slot [#]
Note: Refer to the External Data Representation (XDR) Overview section of this document to better understand the explanation and recommendations for this error message.
While the RP was preparing to send a message to the LCs in the system, it exhausted the supply of queuing elements needed to enqueue the messages for transmission.
On the Cisco 12000 Series, Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding may be disabled because of a low-memory condition during a large routing update (for example, while booting up). For instance, during routing flaps and reboot, an RP can get malloc failures that disable Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding switching.
As an example, if you clear the ip ospf process with 260 k Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routes on RP, you may get the following error message:
%FIB-3-NORPXDRQELEMS: Exhausted XDR queuing elements while preparing message for slot 2 -Process= "OSPF Router", ipl= 0, pid= 149 -Traceback= 41060B88 40D5C894 403D130C 403A4484 403AB49C 403AAB10 403AB7BC 40736FCC 407384E0 401BE9BC 401BE9A8
Or, if you have a large BGP routing table and if you experience several routing flaps or a reboot of the router, then you see the following:
%FIB-3-NORPXDRQELEMS: Exhausted XDR queuing elements while preparing message for slot 4 -Process= "BGP Router", ipl= 0, pid= 104 -Traceback= 600CDC74 600DC3D0 6038FA90 6036C940 60374510 604A2F30 60753168 604A2FAC 604A9BC0 6018BD8C 6018BD78
Note: These messages may come together with %FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 6: no memory and %FIB-3-NOMEMWARNING: Malloc Failure in DCEF.
While sending 100 k BGP routes, you may see the following:
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 100, Nbr 161.10.1.1 on GigabitEthernet3/1
from LOADING to FULL, Loading Done
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 100, Nbr 161.10.1.1 on GigabitEthernet3/3 from LOADING
to FULL, Loading Done
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 100, Nbr 161.10.1.1 on GigabitEthernet3/2 from LOADING
to FULL, Loading Done
%OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 100, Nbr 161.10.1.1 on GigabitEthernet3/4 from LOADING
to FULL, Loading Done
%BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 161.10.11.1 Up
%FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 6: no memory
%FIB-3-FIBDISABLE: Fatal error, slot 3: no memory
%SYS-2-MALLOCFAIL: Memory allocation of 65540 bytes failed from 0x401C783C,
pool Processor, alignment 0
-Process= "BGP Router", ipl= 0, pid= 120
-Traceback= 401CAB20 401CCF80 401C7844 401C8044 40FD017C 40FD032C 40D65AFC
403D4174 403A7BA4 403AA4D0 40712200 40712EF4 4112E760 40712FE0 406EDD10
401C155C
Queued messages:
%SYS-3-LOGGER_FLUSHING: System pausing to ensure console debugging output.
%FIB-3-NORPXDRQELEMS: Exhausted XDR queuing elements while preparing message for
slot 4
-Process= "BGP Router", ipl= 0, pid= 104
-Traceback= 600CDC74 600DC3D0 6038FA90 6036C940 60374510 604A2F30
60753168 604A2FAC 604A9BC0 6018BD8C 6018BD78
%FIB-3-NOMEMWARNING: Malloc Failure in DCEF
This problem is caused by Cisco Express Forwarding using too much RP memory during large routing updates. What happens is that the RP uses up free memory queuing XDR messages on the Cisco Express Forwarding IPC queues to be forwarded down to the LCs at a fairly slow rate. The Cisco Express Forwarding IPC message rate is currently limited to 25 IPC messages (from any queue) every one-quarter of a second at most. The result of this is that the queues on the RP side grow to a huge size, leaving no free RP memory, so mallocfail occurs and disables Cisco Express Forwarding.
If this is the case, you may reduce the maximum path in BGP to reduce the amount of information that Cisco Express Forwarding has to propagate to the LCs, or reduce the TCP window size to reduce the speed of incoming BGP updates. Refer to Achieve Optimal Routing and Reduce BGP Memory Consumption for additional details.
If you are running a Cisco IOS Software release later than or equal to 12.0(16)S, 12.0(16)ST, 12.1(9), 12.1(8a)E, 12.2(2), or12.2(2)T, you may get favorable results by tuning the parameters of the ip cef linecard ipc memory <0-128000 Kbytes> interface configuration command. The default behavior is to have 25 buffers. However, this value depends on the switching platform. This amount of LC memory is limited to 50 percent of the total available memory. This command:
-
Allows you to allocate a larger amount of LC memory to the queueing for Cisco Express Forwarding routing to update messages.
-
Allows the RP to free memory by releasing Cisco Express Forwarding updates more quickly.
-
Prevents the low-memory condition from occurring on the RP.
If you experience the above error messages, then increasing the LC IPC memory is the solution. It is recommended to issue this command with a parameter of 10000. In most cases, this solves the problem. The command is used as follows:
Router(config)#ip cef linecard ipc mem ? <0-128000> Kbytes of linecard memory (limited to 50% of total) Router(config)#ip cef linecard ipc mem 10000 Router#show cef linecard detail CEF linecard slot number 0, status up, sync Linecard CEF version number 8 Sequence number 3, Maximum sequence number expected 27, Seq Epoch 1 Send failed 0, Out Of Sequence 0, drops 0 Linecard CEF reset 1, reloaded 1 33 elements packed in 4 messages(1030 bytes) sent 1 elements cleared linecard in sync after reloading 0/0/0 xdr elements in LowQ/MediumQ/HighQ 8/9/13 peak elements on LowQ/MediumQ/HighQ Input packets 0, bytes 0 Output packets 0, bytes 0, drops 0
For more information about this command, refer to ip cef linecard ipc memory .
%FIB-3-FIBBADXDRLEN and %FIB-4-FIBXDRLEN
It is suggested that you first read the External Data Representation (XDR) Overview section of this document to better understand the explanation and recommendations for this error message.
You may get the following error message:
%FIB-3-FIBBADXDRLEN: Invalid XDR length. Type/len 6/29479. XDR at 0x622D1F2C -Traceback= 600C786C 601D4B50 602CF7A8 60183454 60183440
The message comes from some message validation code that performs some basic checks on XDR messages. In this case, an XDR message of type 6 has been received whose length field contained the value 29479. This length is bigger than the buffer that contains the data, so the code discards this message.
On the 12000 Series, a hardware fault of the fabric might corrupt some packets, causing the XDR error message to pop up. Check the switching fabric by issuing the show controller fia command to see if there are some Cyclic Redundancy Checks (CRCs) on one of the SFCs. You should also check the log to see if there are some other messages that may provide information to further troubleshoot this error message.
%FIB-3-FIBLC_OOSEQ: Slot [#] disabled - Out of Sequence. Expected [#], received [#]
You get this message if the RP has received an out-of-sequence IPC message from the LC. As a consequence, Cisco Express Forwarding switching has been disabled on the specified slot.
Under some circumstances with a large number of routes or when the RP is reloaded, you may see the error message below displayed on the RP console.
%FIB-3-FIBLC_OOSEQ: Slot 11 disabled - Out of Sequence. Expected 9637, received 9638
This message might come together with the following slot specific message:
SLOT 11:%FIB-3-FIBSEQ: Out of sequence. State 9637 Rcvd 9638
Issue the show cef linecard command to check whether or not Cisco Express Forwarding has been disabled on a slot, as shown below.
router#show cef linecard CEF table version 40975, 47 routes Slot CEF-ver MsgSent XdrSent Seq MaxSeq LowQ HighQ Flags 11 40750 9642 164473 9639 9661 0 0 up, sync, disabled
There are no functional consequences; the FIB table gets reloaded when this event occurs. If you still experience the problem, you can issue the clear cef linecard <slot #> command. After that, check the status of the LC by issuing the show cef linecard command. On the 7500 Series, you can try to disable Cisco Express Forwarding and then re-enable it. If the problem still appears, issuing a microcode reload command to the VIP should solve this issue. On the 12000 Series, the hw-module slot <slot #> reload command issued to the LC solves the problem.
%FIB-4-PUNTINTF: CEF punting packets switched to [int] to next slower path and %FIB-5-NOPUNTINTF: CEF resuming switching packets to [int]
You get the %FIB-4-PUNTINTF message if Cisco Express Forwarding cannot switch some or all packets out this specific interface, given its current configuration. Cisco Express Forwarding punts packets switched to this interface to the next slower switching path. Refer to How to Choose the Best Router Switching Path for Your Network for more information about the different switching paths.
You get the %FIB-5-NOPUNTINTF message if Cisco Express Forwarding has been punting packets switched to this interface to the next slower switching path and the interface configuration has changed such that Cisco Express Forwarding can now resume switching to this interface. This is an informational message only and no action is necessary in most cases.
%FIB-4-PUNTINTF: CEF punting packets switched to POS2/0/0.1 to next slower path
This message might be followed by this one after an interface configuration change:
%FIB-5-NOPUNTINTF: CEF resuming switching packets to POS2/0/0.1
If your Cisco IOS Software release is around 12.1(6) with the ip cef command enabled globally and the no ip route-cache cef command configured on a virtual template, the following messages are displayed when L2F virtual access interfaces become members of Multilink PPP (MP) bundle masters:
-
%FIB-4-PUNTINTF: CEF punting packets switched to Virtual-Access14 to next slower path
-
%FIB-5-NOPUNTINTF: CEF resuming switching packets to Virtual-Access14
-
%FIB-4-PUNTINTF: CEF punting packets switched to Virtual-Access37 to next slower path
-
%FIB-5-NOPUNTINTF: CEF resuming switching packets to Virtual-Access37
A workaround is to set the logging level to such a value that these messages do not appear. Another one is to disable IP Cisco Express Forwarding globally. However, disabling Cisco Express Forwarding should be a temporary workaround since it is the best switching method available on some platforms. On the 7500 and 12000 Series, Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding is the best switching method, then Cisco Express Forwarding, then all the legacy ones.
From the following Cisco IOS Software releases forward—12.1(8), 12.1(08a)E, 12.2(1)S, 12.1(8)AA, 12.0(17)S, 12.0(17)ST, 12.2(1)T, 012.002(2)—messages are not logged when you set or clear the PUNT flag on an interface. It is still possible to issue the show cef interface command or to enable the debug ip cef events command to check whether or not Cisco Express Forwarding is enabled. Consequently, there is no danger of spamming users unnecessarily when an interface is set to punt packets to the next slower path. Routers are not overwhelmed with messages on boot-up or when starting Cisco Express Forwarding, and system logs are not filled up with messages being logged for every call on dial platforms.
If possible, you should configure Cisco Express Forwarding-supported and non-Cisco Express Forwarding-supported features on different subinterfaces. Some encapsulations on ATM interfaces are not supported by Cisco Express Forwarding. You must check the Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for your router to know which encapsulations are supported and which ones are not.
%HW_RES_FAIL-4-LOW_CEF_MEM: SLOT [char] is running low
These messages on the router are part of the Hardware CEF Resiliency feature. Starting in IOS Release 12.0(28)S, the Hardware CEF Resiliency feature is supported on Cisco 12000 Series Engine 2 (E2) and IP Services Engine (ISE) line cards. Hardware CEF resiliency is a protection mechanism for CEF hardware memory and ASIC-forwarding resources. Hardware CEF resiliency prevents CEF from being disabled and packet forwarding from being impacted in case of resource exhaustion or an error condition, such as such as low memory or IPC failure. The line card device driver handles resource failures internally without involving upper layers.
When hardware-forwarding memory (PLU or TLU) runs low or fails on a Cisco 12000 Series E2 or ISE line card, the resource monitoring function prints an alarm (error message or warning as the one you have got in your log) on the system console and logs the alarm. When a memory allocation failure starts, a timer-based resource monitoring process is activated in the background. The process checks the percentage of PLU and TLU hardware-forwarding memory used at one-minute intervals. When the percentages of hardware memory exhaustion are exceeded, an alarm is generated. Finally, the memory that the error message is referencing to is TLU memory. This is fixed size memory and cannot be upgraded.
The workaround is to
-
Reduce the number of routes
-
Disable PSA ACLs (no access-list hardware psa)
%FIB-4-FIBCBLK2: Missing cef tableid [dec] during [chars] event for [IP_address][IP_netmask]
Here are some examples of the message as seen in error logs:
%FIB-4-FIBCBLK: Missing cef table for tableid 63 during route update XDR event %FIB-SP-4-FIBCBLK: Missing cef table for tableid 33 during Table removal event %FIB-4-FIBCBLK: Missing cef table for tableid 45 during routing table event
The cause of these messages is due to a delete VRF request being generated before the associated NDB (Network Descriptor Block) updates are distributed and processed by linecards. This causes a temporary issue in the CEF table where a table ID is generated but the table itself is removed. This issue normally resolves itself with no intervention, and there is no impact to traffic or the stability of the router. Cisco bug IDs CSCsg03483 and CSCee26209 describe the similar system messages.
Collect Troubleshooting Information if You Create a TAC Service Request
| If you create a TAC Service Request using the TAC Service Request Tool (registered customers only) , attach the following information to your case for troubleshooting Cisco Express Forwarding-related error messages: |
|---|
Note: Do not manually reload or power-cycle the router before collecting the above information unless required to troubleshoot Cisco Express Forwarding-related error messages.This can cause important information to be lost that is needed for determining the root cause of the problem. |
Other Troubleshooting Resources
For further information on troubleshooting Cisco Express Forwarding, refer to the following documents:
-
Troubleshooting Load Balancing Over Parallel Links Using Cisco Express Forwarding
-
Troubleshooting Prefix Inconsistencies with Cisco Express Forwarding
-
Troubleshooting Incomplete Adjacencies with Cisco Express Forwarding
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
24-Jun-2008 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback