Configuring Cisco Integrated Data Service Unit/Channel Service Unit (DSU/CSU) Modules and WAN Interface Cards
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
These configuration commands apply to the integrated DSU/CSU modules for the Cisco 2524-2525, the WIC-1DSU-56K4 (56/64 Kbps DSU/CSU WAN Interface Card), and the WIC-1DSU-T1 (T1 and fractional T1 DSU/CSU WAN Interface Card).
Prerequisites
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Requirements
There are no specific prerequisites for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
56K Configuration Commands
service-module 56k clock rate
Syntax
service-module 56k clock rate {auto | 2.4 | 4.8 | 9.6 | 19.2 | 38.4 | 56 | 64}
Description
The service-module 56k clock rate command configures the speed of the Digital Data Service (DDS) circuit. When the network-type is set to switched, the clock rate is always 56k, so the service-module 56k clock rate command does not apply (thus it never applies to the two-wire 56k CSU/DSU).
The auto setting determines the clock rate from the line. In order to use auto, the clock source command must be configured as line. If the clock source was **internal** and the clock rate was auto, the CSU/DSU would not know the rate at which to generate clock. The auto setting cannot be used in back-to-back configurations.
The four-wire CSU/DSU cannot be used in back-to-back configurations with a clock rate of 64.
Application
This command applies to the four-wire 56k CSU/DSU. It does not apply to the two-wire 56k CSU/DSU.
Default
56
Example
interface serial 0 service-module 56k clock rate 56
service-module 56k clock source
Syntax
service-module 56k clock source {line | internal}
Description
The service-module 56k clock source command configures the 56k CSU/DSU module to accept the source of clock from the line (or network, in telco terminology) or to generate clocking internally. This command configures the CSU/DSU module, not the Cisco 2524-2525 interface to the CSU/DSU. The 2524-2525 interface is clocked from the CSU/DSU in either setting.
In most applications, the CSU/DSU should be configured with the clock source line. For back-to-back configurations, one CSU/DSU should be configured with clock source internal and the other with clock source line.
Application
This command applies to the four-wire 56k CSU/DSU, but not the two-wire 56k CSU/DSU.
Default
line
Example
interface serial 0 service-module 56k clock source line
service-module 56k data-coding
Syntax
service-module 56k data-coding {normal | scrambled}
Description
The service-module 56k data-coding command is used only when the four-wire 56k CSU/DSU is configured for a data rate of 64kbps. When data-coding is set to scrambled, the CSU/DSU "scrambles" the user data so that it does not contain control codes such as "Out Of Service" (OOS) or "Out Of Frame" (OOF).
The four-wire 56k CSU/DSU cannot be configured for back-to-back operation at 64kbps, so you cannot test data-coding with a cross-over cable.
Application
This command applies to the four-wire 56k CSU/DSU at 64kbps only. It does not apply to the two-wire 56k CSU/DSU.
Default
normal
Example
interface serial 0 service-module 56k data-coding scrambled
service-module 56k network-type
Syntax
service-module 56k network-type {dds | switched}
Description
The service-module 56k network-type command is used to specify whether the four-wire 56k CSU/DSU operates in DDS (leased line) or switched-56 (dial-up) mode. The two-wire 56k CSU/DSU operates in switched-56 mode only, so this command does not apply to the two-wire 56k CSU/DSU.
In switched-56 operation, the 56k CSU/DSUs use V.25bis commands to interface with the router, so the interface must be configured for dialer in-band. Data terminal ready (DTR) dial is not supported.
You can test DDS operation in a back-to-back configuration, but you must use a real switched-56 line to test switched-56 service.
Application
This command applies to the four-wire 56k CSU/DSU. It does not apply to the two-wire 56k CSU/DSU.
Default
dds
Example
interface serial 0 service-module 56k network-type switched dialer in-band
service-module 56k remote-loopback
Syntax
service-module 56k remote-loopback
Description
The service-module 56k remote loopback command controls whether the 56k CSU/DSU responds to loopback codes received on the line. When the Cisco 2524-2525 is configured for no service-module 56k remote loopback, the CSU/DSU will not go into loopback when it receives the loopback code on the line.
The 56k CSU/DSU can still generate loopback codes with the no service-module 56k remote loopback configuration via the loopback remote command. This is different from the T1 CSU/DSU behavior.
Application
This command applies to both the four-wire 56k CSU/DSU and two-wire 56k CSU/DSU.
Default
Remote loopbacks are enabled:
service-module 56k remote-loopback
Example
interface serial 0 no service-module 56k remote-loopback
service-module 56k switched-carrier
Syntax
service-module 56k switched-carrier {att | sprint | other}
Description
The service-module 56k switched carrier command controls whether the 56k CSU/DSU sends an echo cancellation tone on the line when intiating a switched-56 call. When the switched-carrier command is set to sprint, the 56k CSU/DSU sends the echo cancellation tone at the beginning of a connection. When the switched-carrier command is set to att or other, no echo cancellation tone is sent.
Sending the echo cancellation tone increases call set-up time by about eight seconds. Otherwise, having echo cancellation on does not affect data traffic. If an echo canceller is on the circuit and is not disabled, it could "cancel" user data.
This method of configuring echo cancellation was chosen because Sprint is the only major carrier that uses some voice lines to carry switched-56 traffic, thus echo cancellation must be disabled on those circuits.
Application
This command applies to both the four-wire 56k CSU/DSU and the two-wire 56k CSU/DSU.
Default
For the four-wire 56k CSU/DSU: att
For the two-wire 56k CSU/DSU: sprint
Example
interface serial 0 service-module 56k network-type switched service-module 56k switched-carrier other
T1 Configuration Commands
service-module t1 clock source
Syntax
service-module t1 clock source {line | internal}
Description
The service-module t1 clock source command configures the T1 CSU/DSU module to accept the source of clock from the line (or network, in telco terminology) or to generate clocking internally. This command configures the CSU/DSU module, not the Cisco 2524-2525 interface to the CSU/DSU. The 2524-2525 interface is clocked from the CSU/DSU in either setting.
In most applications, the CSU/DSU should be configured with the clock source line. For back-to-back configurations, one CSU/DSU should be configured with clock source internal and the other with clock source line.
Application
This command applies to the T1 CSU/DSU.
Default
line
Example
interface serial 0 service-module t1 clock source line
service-module t1 data-coding
Syntax
service-module t1 data-coding {normal | inverted}
Description
The service-module t1 data-coding command determines whether the user data is inverted by the CSU/DSU. Data inversion makes every one bit in the data stream into a zero and every zero bit into a one. Data inversion is used with bit-oriented protocols like HDLC, PPP, and LAPB to ensure density on a T1 line with Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI) encoding. These bit-oriented protocols perform zero insertions after every five "one" bits in the data stream. This has the effect of ensuring at least one zero in every eight bits. If the data stream is then inverted, it ensures at least one out of every eight bits is a one.
This command cannot be used if the timeslots speed is set to 56.
Application
This command applies to the T1 CSU/DSU. It is the preferred method to ensure density on an AMI line.
Default
normal
Example
interface serial 0 service-module t1 linecode ami service-module t1 data-coding inverted
service-module t1 timeslots
Syntax
service-module t1 timeslots {all | <range>} [speed 56 | 64]
Description
The service-module t1 timeslots command configures which timeslots (DS-0s) are used in fractional T1 operation. It also configures the amount of bandwidth available to the router in each timeslot. In order to use the entire T1 line, set timeslots to all.
For fractional T1, the timeslots are configured as 1-4, 6, 7-10, for example.
When the speed is set to 56, the CSU/DSU takes one out of every eight bits of bandwidth and makes it a one bit. This is not the preferred method of ensuring ones density because of this loss of bandwidth. The preferred methods of ensuring density are service-module t1 linecode b8zs and service-module t1 data-coding inverted .
Application
This command applies to the T1 CSU/DSU.
Default
all speed 64
Example
interface serial 0 service-module t1 timeslots 1-10
service-module t1 fdl
Syntax
[no] service-module t1 fdl {att | ansi}
Description
The service-module t1 fdl command configures the CSU/DSU behavior on the Facilities Data Link (FDL) of the Exented Super Frame (ESF). When configured for att, the CSU/DSU implements AT&T TR 54016. When configured for ansi, it implements ANSI T1.403. When the CSU/DSU is configured with no service-module t1 fdl, it ignores the FDL.
Application
This command applies only to the WIC-1DSU-T1. It does not apply to the SM25-T1 T1 CSU/DSU service module for the Cisco 2524-2525. The SM25-T1 always implements AT&T TR 54016 and ANSI T1.403 simultaneously and cannot be disabled.
Default
no service-module t1 fdl (the FDL is disabled)
Example
interface serial 0 service-module t1 fdl att
service-module t1 framing
Syntax
service-module t1 framing {sf | esf}
Description
The service-module t1 framing command configures the T1 CSU/DSU for operation with D4 Super Frame (sf) or Extended Super Frame (esf).
Application
This command applies to the T1 CSU/DSU.
Default
esf
Example
interface serial 0 service-module t1 framing sf
service-module t1 lbo
Syntax
service-module t1 lbo {none | -7.5db | -15db}
Description
The service-module t1 lbo command is used to configure the Line Build Out (LBO) of the T1 CSU/DSU. The LBO decreases the transmit strength of the signal by -7.5 or -15 decibels. In theory, this might be used in back-to-back configurations, but it is not necessary when connecting two Cisco 2524-2525 CSU/DSU modules back-to-back. It is not likely to be needed on actual T1 lines.
Application
This command applies to the T1 CSU/DSU.
Default
none
Example
interface serial 0 service-module t1 lbo -7.5db
service-module t1 linecode
Syntax
service-module t1 linecode {b8zs | ami}
Description
The service-module t1 linecode command configures the T1 CSU/DSU for operation on Binary 8 Zeroes Substitution (B8ZS) or Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI) T1 lines. B8ZS is a method of ensuring density on a T1 line by substituting intentional bi-polar violations in bit positions 4 and 7 for a sequence of eight zero bits. When the CSU/DSU is configured for AMI, you must guarantee density in your router confgiuration with the service-module t1 data-coding inverted or service-module t1 timeslots [all | <range>] speed 56 command.
Application
This command applies to the T1 CSU/DSU.
Default
b8zs
Example
interface serial 0 service-module t1 linecode ami service-module t1 data-coding inverted
service-module t1 remote-alarm-enable
Syntax
service-module t1 remote-alarm-enable
Description
The service-module t1 remote-alarm-enable command configures whether the T1 CSU/DSU module generates remote alarms (yellow alarms) or detects remote alarms being sent from the opposite CSU/DSU.
The remote alarm is transmitted by a CSU/DSU when it detects an alarm condition: either a red alarm (loss of signal) or a blue alarm (unframed 1s). The receiving CSU/DSU then knows that there is an error condition on the line.
With D4 Super Frame ( service-module t1 framing sf ), a remote alarm condition is transmitted by setting bit 2 of every time slot to zero. This corrupts the user data, which is why the default setting for this command is no service-module t1 remote-alarm-enable.
With Extended Super Frame ( service-module t1 framing esf ), the remote alarm condition is signalled out of band, in the Facility Data Link (FDL). Thus with ESF, it is safe and desirable to enable remote alarms.
You can see whether the T1 CSU/DSU is receiving a remote alarm (yellow alarm) by issuing the show service-module [serial 0|1] command.
The T1 CSU/DSU transmits a blue alarm (unframed 1s) if the interface is shut down. Therefore, the opposite CSU/DSU transmits the remote alarm signal if remote alarms are enabled.
Application
This command applies to the T1 CSU/DSU. It should be used only when the framing is ESF.
Default
no service-module t1 remote-alarm-enable
Example
interface serial 0 service-module t1 remote-alarm-enable
service-module t1 remote-loopback
Syntax
service-module t1 remote-loopback [full | payload] [v54 | alternate]
Description
The service-module t1 remote-loopback command specifies whether the T1 CSU/DSU goes into loopback when it receives a loopback code on the line. The [full | payload] parameter specifies whether the T1 CSU/DSU accepts full loopbacks (CSU loopback) or payload loopbacks (DSU loopback).
The [v54 | alternate] parameter selects the loopback code that the T1 CSU/DSU recognizes or generates with the loopback remote command. The "standard" pattern (specified by omitting the [v54 | alternate]) is used in the United States and consists of a repeating bit pattern "10000". The alternate pattern is used in Canada, and is the inverse of the "standard" code: "01111".
In order to disable remote loopbacks, use no service-module t1 remote-loopback. The T1 module will not generate loopback codes via the loopback remote command if configured for no service-module t1 remote-loopback.
Application
This command applies to the T1 CSU/DSU. V.54 loop codes are not yet implemented in the WIC-1DSU-T1.
Default
By default, this command is enabled for full and payload loopbacks using the "standard" loop patterns.
Example
interface serial 0 no service-module t1 remote-loopback
Exec Commands
clear service-module
Syntax
clear service-module [serial 0|1]
Description
The clear service-module command performs a hardware reset of the CSU/DSU module. After the reset, the router software loads the current configuration onto the CSU/DSU module. The CSU/DSU is also reset at power on and when the module doesn't respond to a command from the router software within three seconds. The clear service-module command cancels all loopbacks, and in the case of a remote loopback, it sends the loop down code to the remote CSU/DSU. The clear service-module command clears all the statistics and counters for the CSU/DSU module. However, if you only want to clear these statistics and counters, you should simply issue the clear counters command instead.
The CSU/DSU module is not reset with the clear interface command or when the router reloads. When the router reloads, the router software downloads the configuration to the CSU/DSU module.
Application
This command applies to the four-wire 56k CSU/DSU, two-wire 56k CSU/DSU, and T1 CSU/DSU.
Example
clear service-module serial 0
debug service-module
Syntax
debug service-module
Description
The debug service-module command enables debugging for the CSU/DSU modules. This command does not take the interface as a parameter, so debugging is enabled for both interfaces. The debug messages are generated in response to alarm interrupts from the CSU/DSU module.
If an alarm has happened, a message like the one shown below will display:
SERVICE_MODULE(1): detects <x>
If an alarm has cleared, a message like the one shown below will display:
SERVICE_MODULE(1): <x> ended after duration 01:00:10
The value of <x> differs for the two module types:
For the T1 module, <x> can be:
-
loss of signal
-
loss of frame
-
AIS alarm
-
remote alarm
-
module access errors
-
loopback test
For the SW56 module, <x> can be:
-
oos/oof
-
loss of signal
-
loss of sealing current
-
loss of frame
-
rate adaptation attempts
-
call connect/disconnect
-
loopback test from telco
-
loopback test from remote module
Application
This command applies to the four-wire 56k CSU/DSU, two-wire 56k CSU/DSU, and T1 CSU/DSU.
Example
debug service-module
show service-module
Syntax
show service-module [serial 0|1] [performance-statistics [<range>]
Description
The show service-module command displays information about the CSU/DSU modules. This is the most important troubleshooting command for the CSU/DSU modules. The performance-statistics parameter displays 15-minute interval statistics for the T1 CSU/DSU.
Application
This command applies to the four-wire 56k CSU/DSU, two-wire 56k CSU/DSU, and T1 CSU/DSU. The performance statistics only apply to the T1 CSU/DSU.
Examples
56k CSU/DSU Example:
show service-module Module type is 4-wire Switched 56 Hardware revision is B, Software revision is X.06, Image checksum is 0x44304635, Protocol revision is 1.0 Connection state: Idle Receiver has no alarms. Current line rate is 56 Kbits/sec Last module self-test (done at startup): Passed Last clearing of alarm counters 0:15:12 oos/oof : 0, loss of signal : 0, loss of frame : 0, rate adaption attempts: 0,
T1 CSU/DSU Example:
show service-module Module type is T1/fractional Hardware revision is A, Software revision is 1.1h, Image checksum is 0x21749B4, Protocol revision is 1.1 Receiver has AIS alarm, Framing is ESF, Line Code is B8ZS, Current clock source is line, Fraction has 24 timeslots (64 Kbits/sec each), Net bandwidth is 1536 Kbits/sec. Last module self-test (done at startup): Passed Last clearing of alarm counters 0:24:11 loss of signal : 0, loss of frame : 0, AIS alarm : 2, current duration 0:24:04 Remote alarm : 0, Module access errors : 0, Total Data (last 1 15 minute intervals): 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 895 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs Data in current interval (553 seconds elapsed): 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 553 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 553 Unavail Secs
T1 CSU/DSU show service-module performance-statistics Example:
boa1#show service-module serial 0 performance-statistics 1-1
Total Data (last 2 15 minute intervals):
1 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations
1 Slip Secs, 1 Fr Loss Secs, 1 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins
1 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 1 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs
Data in current interval (247 seconds elapsed):
0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations
0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins
0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs
Data in Interval 1:
0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations
0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins
0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs
If you have the output of a show service-module serial command from your Cisco device, you can use to display potential issues and fixes. In order to use , you must be a registered customer, be logged in, and have JavaScript enabled.
test service-module
Syntax
test service-module [serial 0|1]
Description
The test service-module command performs a CSU/DSU self-test that consists of these tests:
-
flash checksum
-
eeprom checksum
-
ROM checksum
-
RAM test
-
DTE loopback with internal test pattern
This self-test is performed at power on and by this exec command. The test service-module command cannot be used if a DTE, line, or remote loopback is in progress. You can see the results of the last CSU/DSU self-test with the show service-module command.
Application
This command applies to the four-wire 56k CSU/DSU, two-wire 56k CSU/DSU, and T1 CSU/DSU.
Example
test service-module serial 0
Loopback Commands
loopback dte
Syntax
[no] loopback dte
Description
The loopback remote interface configuration command puts the CSU/DSU module into DTE loopback.
56k CSU/DSU Module:
When the 56k CSU/DSU module is placed into DTE loopback, the traffic generated by the DTE (PING, for example) is looped back to the DTE. The Out Of Service (OOS) signal is sent on the line.
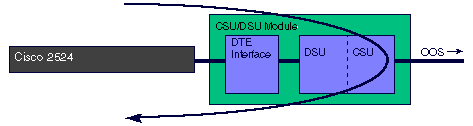
T1 CSU/DSU Module:
When the T1 CSU/DSU module is placed into DTE loopback, the traffic generated by the DTE (PING, for example) is looped back to the DTE.
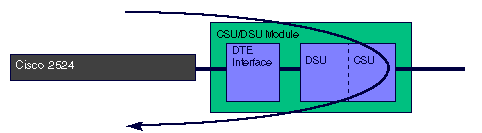
Application
This command applies to the two-wire 56k, four-wire 56k, and T1 CSU/DSUs.
Default
no loopback dte
Example
interface serial 0 loopback dte
loopback line
Syntax
[no] loopback line [payload]
Description
The loopback line interface configuration command puts the CSU/DSU module into line loopback. There are two type of line loopbacks. Without the payload parameter, the line is looped through the CSU portion of the module. In payload loopback, the line is looped through the DSU portion of the module.
56k CSU/DSU Module:
When the 56k CSU/DSU module is placed into loopback line, the CSU/DSU module loops the line through the CSU portion of the module and loops the DTE interface back to the router. The Adtran terminology for this loopback is "DTE and loop." If the CSU/DSU is configured for switched mode, there must be a connection established in order to do a line loopback.
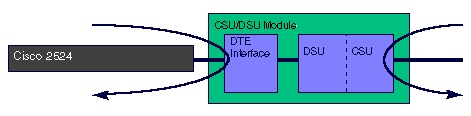
When the 56k CSU/DSU module is placed into loopback line payload, the CSU/DSU module loops the line through the DSU portion of the module. The Adtran terminology for this loopback is "loop only." If the CSU/DSU is configured for switched mode, there must be a connection established in order to do a line loopback.
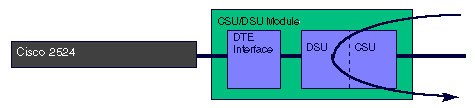
T1 CSU/DSU Module:
When the T1 CSU/DSU module is placed into line loopback, the CSU/DSU does a full bandwidth loopback through the CSU portion of the module. It regenerates the signal back to the line.
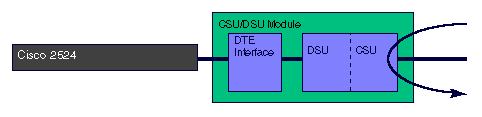
When the T1 CSU/DSU module is placed into line loopback payload, the CSU/DSU does a loopback through the DSU portion of the module. Data is only looped back on the configured timeslots. The line loopback payload command reframes the data link, regenerates the signal, and corrects Bi-Polar Violations (BPV) and Extended Super Frame (ESF) CRC errors.
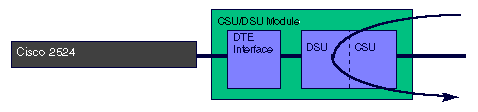
Application
This command applies to the two-wire 56k, four-wire 56k, and T1 CSU/DSUs.
Default
no loopback line
Example
interface serial 0 loopback line
loopback remote
Syntax
56k CSU/DSU:
[no] loopback remote [2047 | 511 | stress-pattern {1-4}]
T1 CSU/DSU:
[no] loopback remote {full | payload | smart-jack}
[qrw | 1in8 | 3in24 | 1in2 | 1in5 | 1in1 | 0in1 | user-pattern value]
Note: value is a 24-bit-binary value
Description
The loopback remote command causes the CSU/DSU to send a loop up code to the remote CSU/DSU. You may optionally specify a test pattern or send user data (a router PING, for example). If the remote interface is already in the loopback state, then the no loopback remote command will not be issued.
56k CSU/DSU Module:
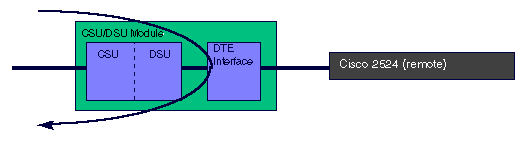
The 56k CSU/DSU will generate a loop up code to the remote CSU/DSU. The stress patterns 1-4 are only available on the 4-wire CSU/DSU. If the remote CSU/DSU does not go into loopback, check to make sure that remote loopbacks are enabled.
56k CSU/DSU loopback remote
T1 CSU/DSU Module:
The T1 CSU/DSU generates the loop up code configured with the service-module t1 remote-loopback command to the remote CSU/DSU. If a test pattern is specified, the CSU/DSU module generates the specified test pattern. When the loopback is terminated, the result of the pattern test is displayed. If you do not specify a test pattern, use the router to send data, such as pinging the router interface, to test the loopback. The T1 CSU/DSU will not generate loop up codes if remote loopbacks are disabled on the local CSU/DSU.
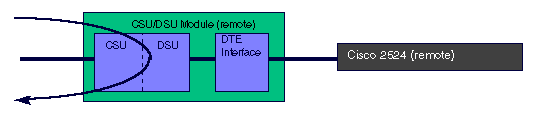
The loopback remote full command sends the loop up code unframed (without the Extended Super Frame or D4 Super Frame) to the remote CSU/DSU. The remote CSU/DSU goes into the equivalent of a loopback line, which is a full bandwidth loopback through the CSU portion of the module.
T1 CSU/DSU loopback remote full
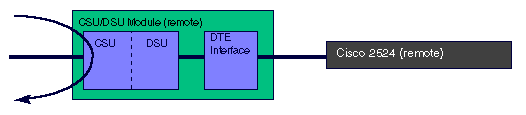
The loopback remote payload command sends the loop up code on the configured timeslots while maintaining the framing (ESF or D4 SF). The remote CSU/DSU goes into the equivalent of a loopback line payload . The remote CSU/DSU loops back only those timeslots on which it received the loop up code. This loopback reframes the data link, regenerates the signal, and corrects Bi-Polar Violations (BPV) and Extended Super Frame (ESF) CRC errors.
T1 CSU/DSU loopback remote payload
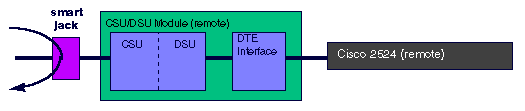
The loopback remote smart-jack command sends a loop up code to the remote smart jack. You cannot put the local smart jack into loopback. The smart-jack loopback does not apply to the WIC-1DSU-T1.
T1 CSU/DSU loopback remote smart-jack
Note: If the T1 CSU/DSU is configured to provide clock (service-module t1 clock source internal), it will no longer generate clock when it is placed into loopback.
Application
This command applies to the two-wire 56k, four-wire 56k and T1 CSU/DSUs.
Default
no loopback remote
Example
interface serial 0 loopback remote payload
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
09-Sep-2005 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback