Introduction
This document describes a configuration for Secure Client (AnyConnect) Remote Access VPN on Secure Firewall Threat Defense.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Basic VPN, TLS, and IKEv2 knowledge
- Basic Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) and RADIUS knowledge
- Experience with Secure Firewall Management Center
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- Secure Firewall Threat Defense (SFTD) 7.2.5
- Secure Firewall Management Center (SFMC) 7.2.9
- Secure Client (AnyConnect) 5.1.6
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
This document provides a configuration example for Secure Firewall Threat Defense (FTD) version 7.2.5 and later, that allows remote access VPN to use Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2). As a client, Secure Client (AnyConnect) can be used, which is supported on multiple platforms.
Configuration
1. Prerequisites
In order to go through Remote Access wizard in Secure Firewall Management Center:
- Create a certificate used for server authentication.
- Configure RADIUS or LDAP server for user authentication.
- Create pool of addresses for VPN users.
- Upload AnyConnect images for different platforms.
a) Import the SSL Certificate
Certificates are essential when you configure Secure Client. The certificate must have Subject Alternative Name extension with DNS name and/or IP address to avoid errors in web browsers.
Note: Only registered Cisco users have access to internal tools and bug information.
There are limitations for manual certificate enrollment:
- On SFTD, you need the CA certificate before you generate the CSR.
- If the CSR is generated externally, the manual method fails, therefore, a different method must be used (PKCS12).
There are several methods to obtain a certificate on SFTD appliance, but the safe and easy one is to create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), sign it with a Certificate Authority (CA), and then import certificate issued for public key, which was in CSR.
Here is how to do that:
- Navigate to
Objects > Object Management > PKI > Cert Enrollment, click Add Cert Enrollment.
- Select
Enrollment Type and paste Certificate Authority (CA) certificate (the certificate which is used to sign the CSR).
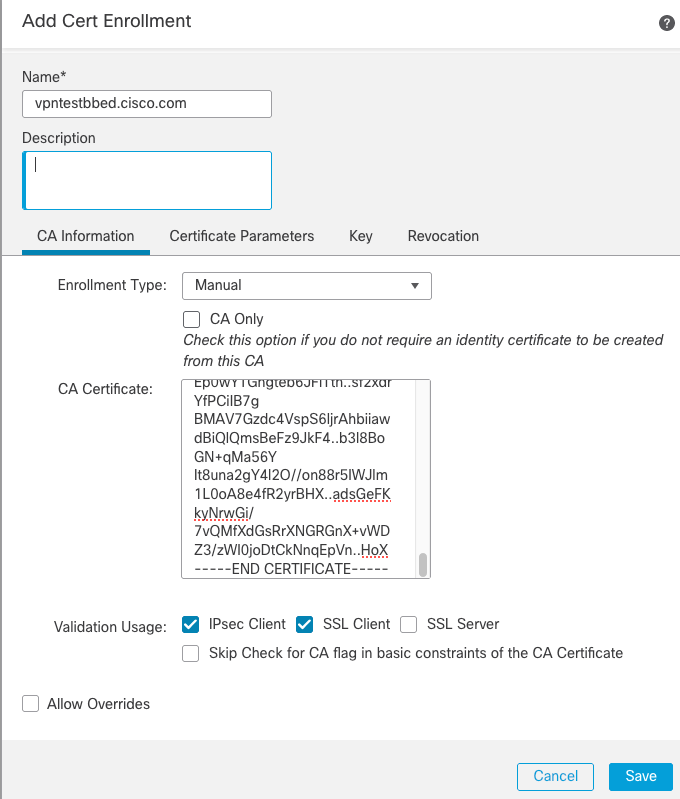
- Then go to second tab and select
Custom FQDN and fill all necessary fields, for example:
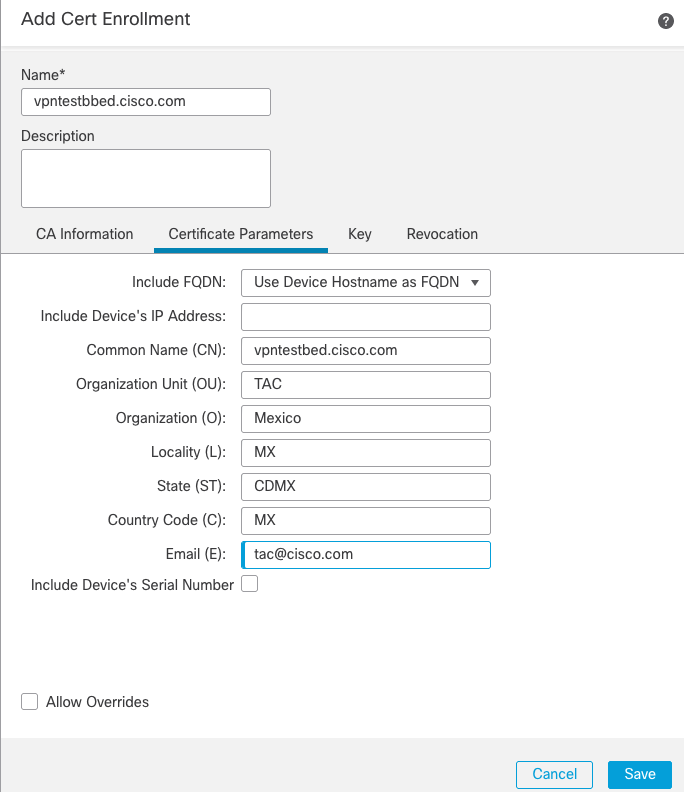
- On the third tab, select
Key Type, choose name and size. For RSA, 2048 bits is minimum.
- Click
Save and navigate to Devices > Certificates > Add.
- Then select
Device, and under Cert Enrollment, select the trustpoint which you just created, and click Add:
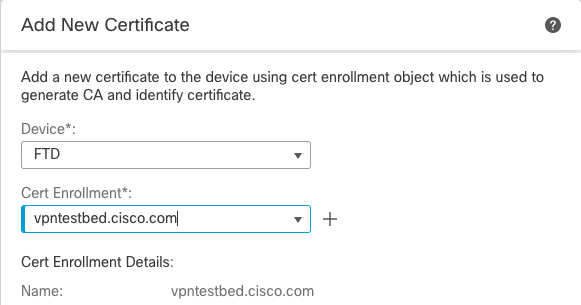
- Later, next to the trustpoint name, click the
 icon, then
icon, then Yes, and after that, copy CSR to CA and sign. Certificate must have attributes the same as a normal HTTPS server.
- After you receive the certificate from CA in base64 format, select
Browse Identity Certificate, select it from the disk and click Import. When this succeeds, you see:

b) Configure RADIUS Server
- Navigate to
Objects > Object Management > RADIUS Server Group > Add RADIUS Server Group > +.
- Fill out the name and add IP address along with shared secret, click
Save:
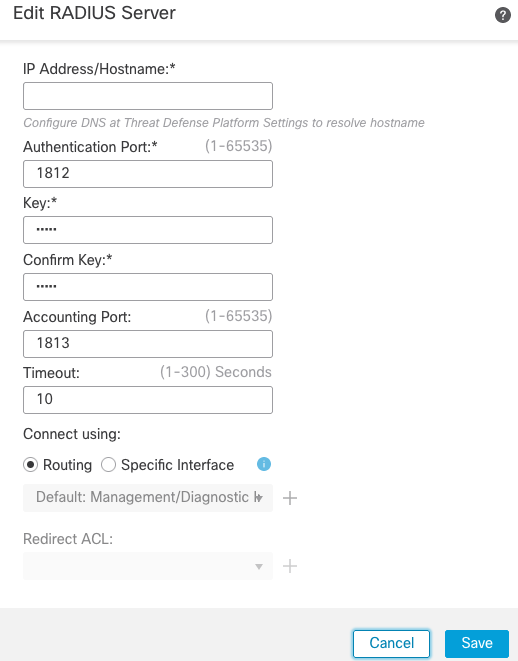
- After that, you see the server on the list:

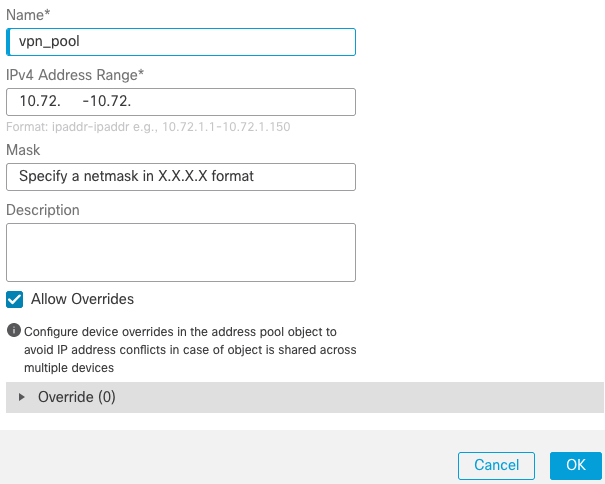
c) Create a Pool of Addresses for VPN Users
- Navigate to
Objects > Object Management > Address Pools > IPv4 Pools > Add IPv4 Pools.
- Enter the name and range, mask is not needed:
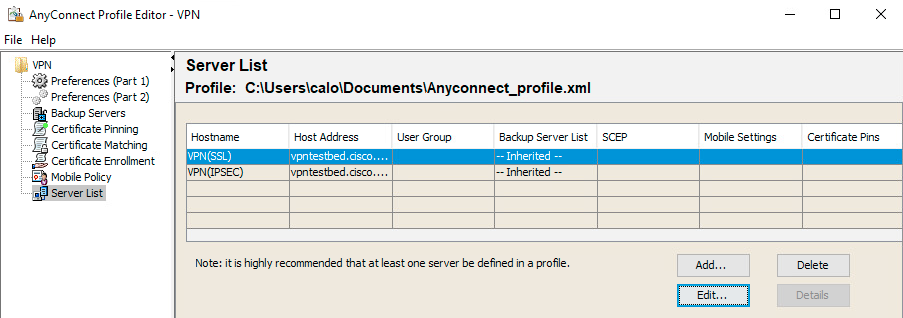
d) Create XML Profile
- Download the Profile Editor from Cisco site and open it.
- Navigate to
Server List > Add...
- Enter Display Name and FQDN. You see entries in Server List:
- Click
OKand File > Save as...
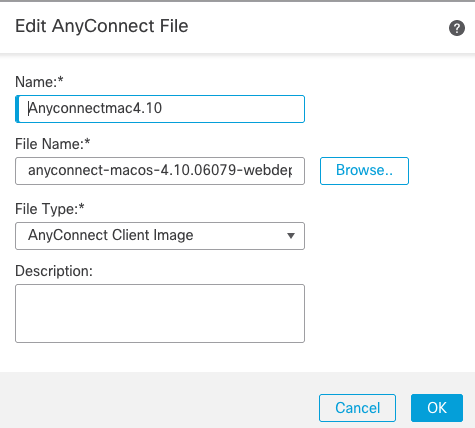
e) Upload AnyConnect Images
- Download pkg images from Cisco site.
- Navigate to
Objects > Object Management > VPN > AnyConnect File > Add AnyConnect File.
- Type the name and select PKG file from disk, click
Save:
- Add more packages based on your own requirements.
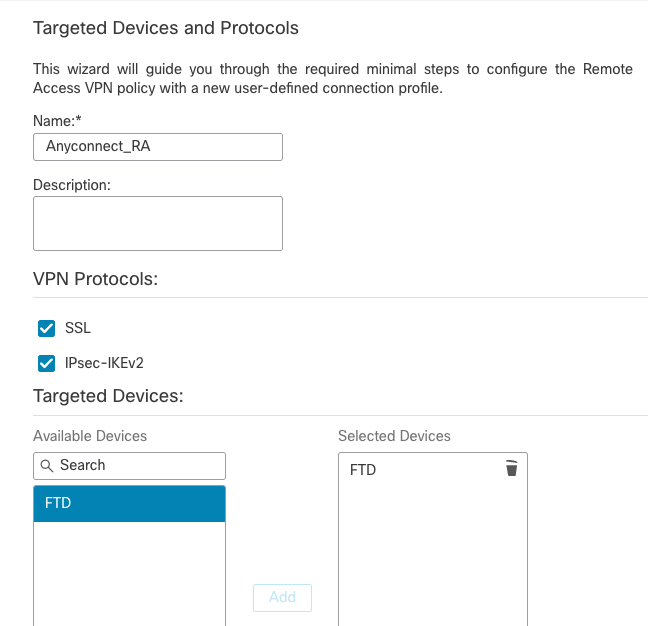
2. Remote Access Wizard
- Navigate to
Devices > VPN > Remote Access > Add a new configuration.
- Name the profile and select FTD device:
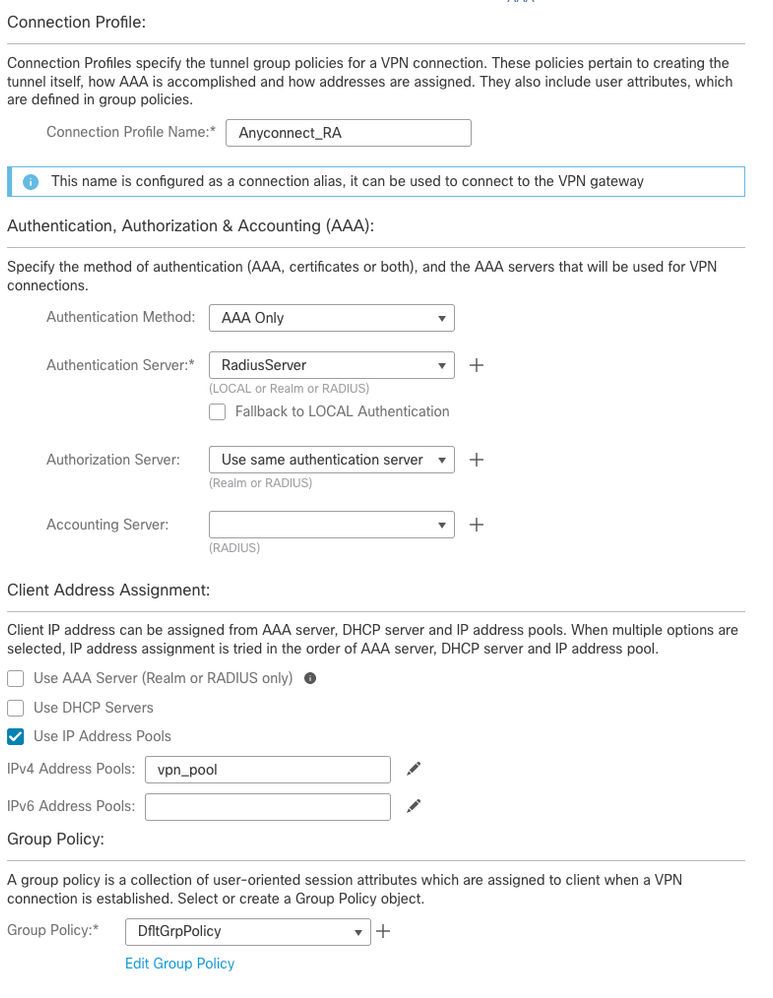
- In Connection Profile step, type
Connection Profile Name, select the Authentication Server and Address Pools that you created earlier:
- Click
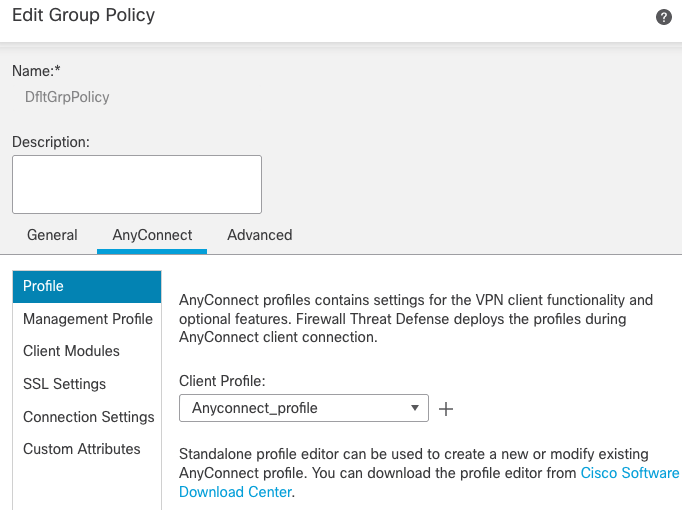
Edit Group Policy and on the tab AnyConnect, select Client Profile, then click Save:
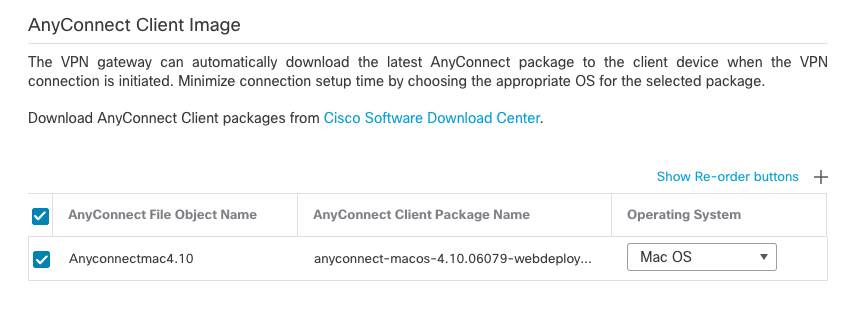
- On the next page, select AnyConnect images and click
Next.
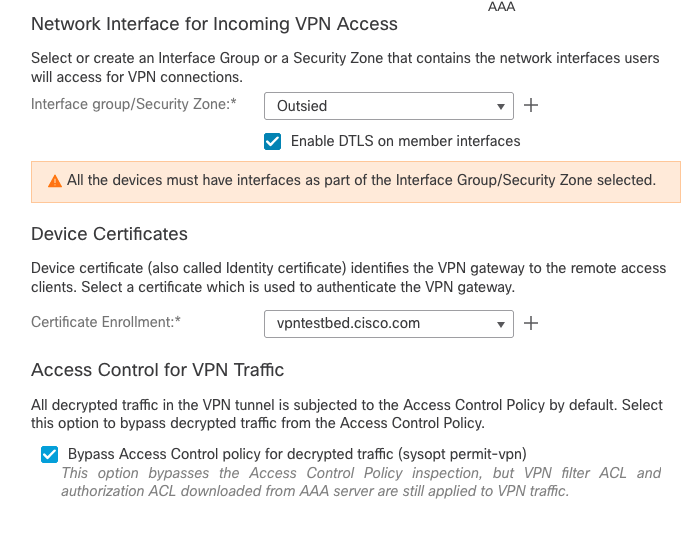
- On the next screen, select
Network Interface and Device Certificates:
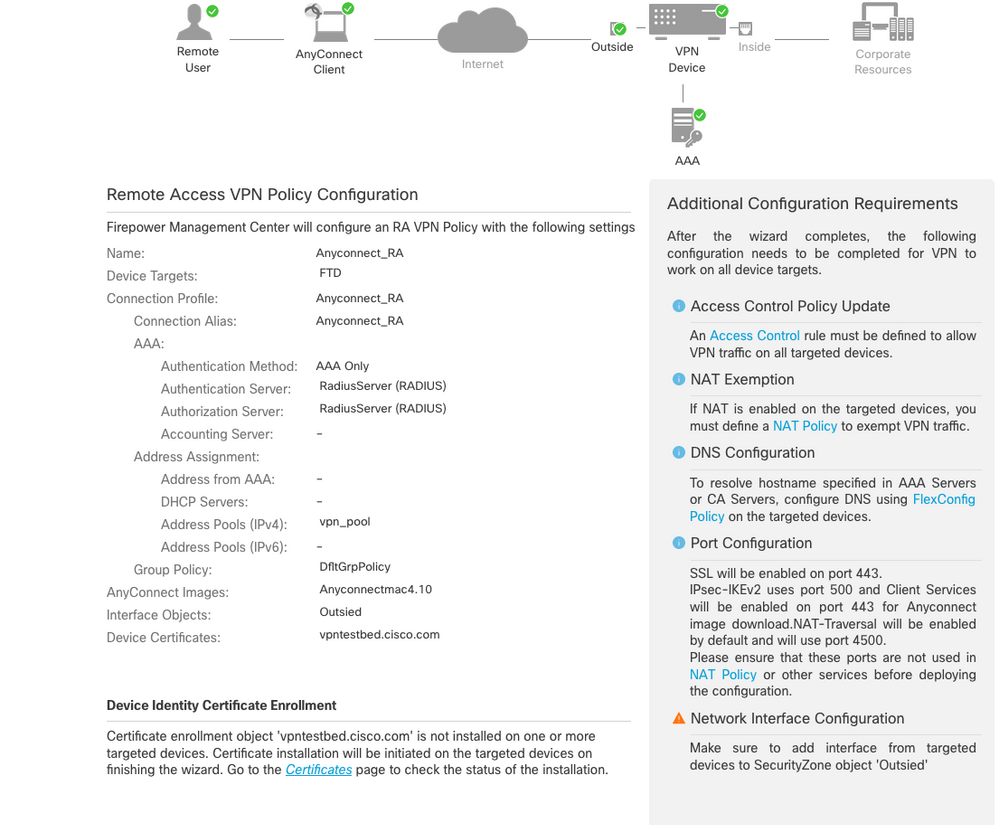
- When everything is configured correctly, you can click
Finish and then Deploy:
- This copies the whole configuration along with certificates and AnyConnect packages to FTD appliance.
Connection
To connect to FTD, you need to open a browser, type DNS name or IP address that points to the outside interface. You then log in with credentials stored in RADIUS server and follow the instructions on the screen. Once AnyConnect installs, you then need to put the same address in AnyConnect window, and click Connect.
Limitations
Currently, unsupported on FTD, but available on ASA:
Security Considerations
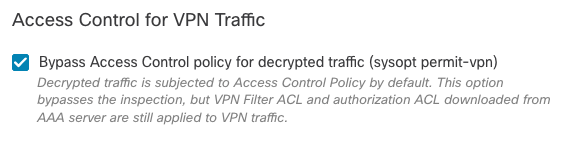
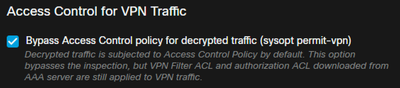
By default, the sysopt connection permit-vpnoption is disabled. This means that you need to allow the traffic that comes from the pool of addresses on outside interface via Access Control Policy. Although the pre-filter or access-control rule is added to allow VPN traffic only, if clear-text traffic happens to match the rule criteria, it is erroneously permitted.
There are two approaches to this problem. First, TAC recommended option is to enable Anti-Spoofing (on ASA it was known as Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding - uRPF) for outside interface, and secondly, is to enable sysopt connection permit-vpn to bypass Snort inspection completely. The first option allows a normal inspection of the traffic that goes to and from VPN users.
a) Enable uRPF
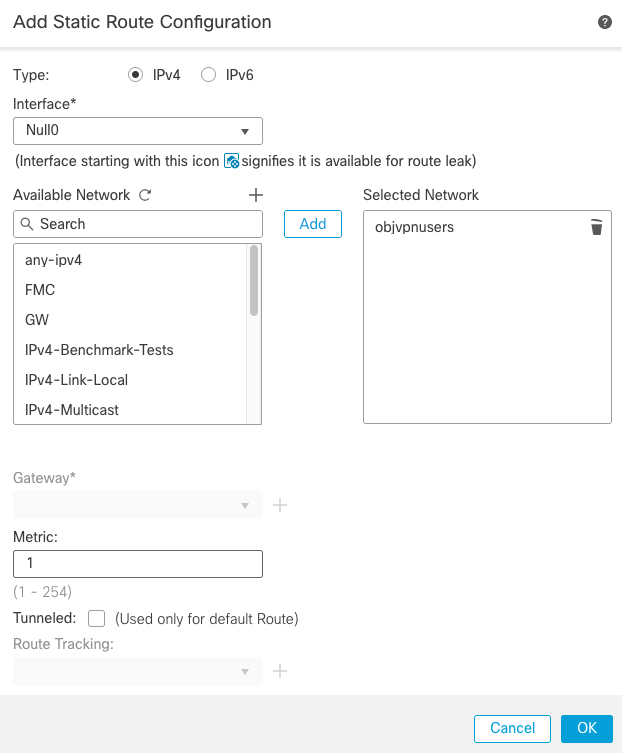
- Create a null route for the network used for remote access users, defined in section C. Navigate to
Devices > Device Management > Edit > Routing > Static Route and select Add route.
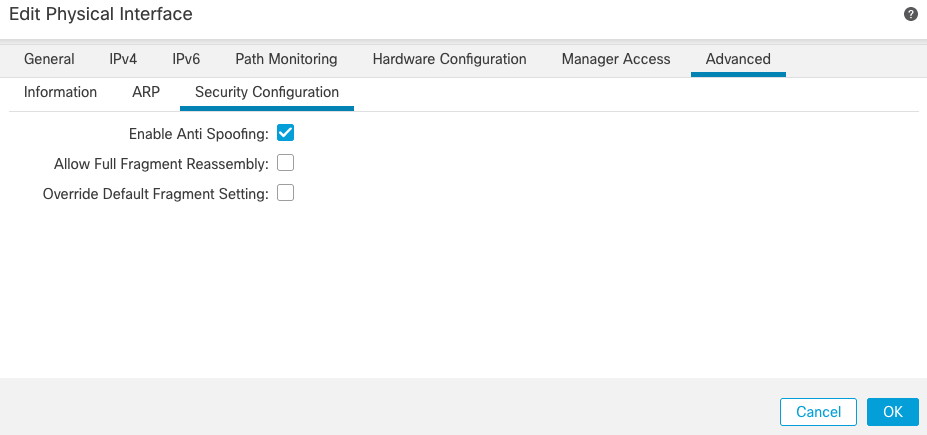
- Next, enable uRPF on the interface where the VPN connections terminate. To find this, navigate to
Devices > Device Management > Edit > Interfaces > Edit > Advanced > Security Configuration > Enable Anti Spoofing.
When a user is connected, the 32-bit route is installed for that user in the routing table. Clear-text traffic sourced from the other, unused IP addresses from the pool is dropped by uRFP. To see a description of Anti-Spoofing refer to Set Security Configuration Parameters on Firewall Threat Defense.
b) Enable sysopt connection permit-vpn Option
- There is an option to do it with the wizard or under
Devices > VPN > Remote Access > VPN Profile > Access Interfaces.
Related Information





















 Feedback
Feedback