Introduction
This document describes how to configure Wide-Area Network (WAN) or ISP redundancies, wherein multiple WAN links terminate on the same end router.
Prerequisites
Requirements
A basic understanding how to create an Internet Protocol (IP) Service Level Agreement (SLA) and Static Routing and Configuration of an IP SLA must be supported on the device and platform.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions. It applies to all Cisco routers that run Cisco IOS® and where IP SLA and Track can be configured.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
This document also provides instructions on how to configure Network Address Translation (NAT) when you need seamless failover from multiple ISPs, that is, when the primary ISP fails, the secondary ISP takes over via the correct NAT with the use of the secondary ISPs public IP address.
Configure
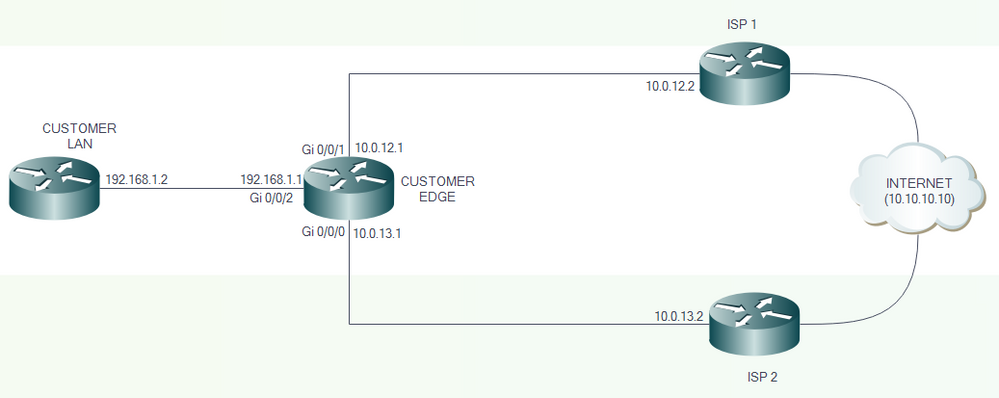
Network Diagram
Configurations
ISP 1 and ISP 2 directly connect to the Internet. For test purposes, use the IP address 10.10.10.10 as a reference to the Internet.
Customer Edge Router Configurations
Interface Configurations:
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
description PRIMARY LINK TO ISP 1
ip address 10.0.12.1 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
negotiation auto
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
description BACKUP LINK TO ISP 2
ip address 10.0.13.1 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
negotiation auto
Track, IP SLA, and Default Route Configurations:
track 8 ip sla 1 reachability
ip sla 1
icmp-echo 10.0.12.2 source-ip 10.0.12.1
ip sla schedule 1 life forever start-time now
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.12.2 track 8
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.13.2 10
When Track 8 is UP, the traffic to the Internet flows through ISP 1.
CustomerEdge#sh ip route static
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
Gateway of last resort is 10.0.12.2 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.0.12.2
When Track 8 is DOWN, the traffic to the Internet flows through ISP 2.
CustomerEdge#sh ip route static
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
Gateway of last resort is 10.0.13.2 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [10/0] via 10.0.13.2
Cisco Recommendations
Note: Cisco recommends these default values when you configure the IP SLA:
1. Threshold (millisecs): 5000
2. Timeout (millisecs): 5000
3. Frequency (secs): 60
Additional configurations for NAT Failover:
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2
description TOWARDS CUSTOMER LAN
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
negotiation auto
!
ip access-list extended 101
permit ip 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 any
!
!
route-map NAT_ISP2 permit 10
match ip address 101
match interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
!
route-map NAT_ISP1 permit 10
match ip address 101
match interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
!
The route maps are created to match the IP address defined by access-list 101 and also match the exit interface.
ip nat inside source route-map NAT_ISP1 interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 overload
ip nat inside source route-map NAT_ISP2 interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 overload
These commands enable Port Address Translation (PAT), where the IP addresses to be translated are defined by the route map. The IP address to be translated into is defined after the interface keyword.
Verify
Use this section in order to confirm that your configuration works properly.
Track status can be verified with the use of the show track command.
CustomerEdge#show track
Track 8
IP SLA 1 reachability
Reachability is Up
7 changes, last change 00:00:17
Latest operation return code: OK
Latest RTT (millisecs) 1
Tracked by:
Static IP Routing 0
When the primary ISP link is UP, the traffic flows through it.
CustomerEdge#traceroute 10.10.10.10
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 10.10.10.10
VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id)
1 10.0.12.2 1 msec * 0 msec
When the primary ISP link is DOWN, the secondary link fails over.
CustomerEdge#traceroute 10.10.10.10
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 10.10.10.10
VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id)
1 10.0.13.2 1 msec * 1 msec
Once the link to the primary ISP link comes back up, the traffic automatically starts to flow through it.
Similarly, for NAT Failover:
CustomerLAN#ping 10.10.10.10
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.10.10, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
CustomerLAN#sh ip route 10.10.10.10
Routing entry for 10.10.10.10/32
Known via "static", distance 1, metric 0
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 192.168.1.1
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
When the primary ISP link is UP, the NAT translation occurs via the Primary ISP link.
CustomerEdge#sh ip nat translations
Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global
icmp 10.0.12.1:1 192.168.1.2:12 10.10.10.10:12 10.10.10.10:1
Total number of translations: 1
When the primary ISP link is DOWN, the NAT translation occurs via the Secondary ISP link.
CustomerEdge#sh ip nat translations
Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global
icmp 10.0.13.1:1 192.168.1.2:13 10.10.10.10:13 10.10.10.10:1
Total number of translations: 1
When the primary ISP link comes back UP, the NAT translation occurs via the Primary ISP link.
Troubleshoot
This section provides the information you can use in order to troubleshoot your configuration.
Troubleshooting must be done mainly from static routing, IP SLA, and Track configuration perspectives.
Primarily, in such scenarios, troubleshooting starts when you analyze the cause of the failure of the primary link.


 Feedback
Feedback