IS-IS Network Types and Frame Relay Interfaces
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
In Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) Protocol, there are two types of networks: point-to-point and broadcast. Unlike Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Protocol, IS-IS does not have other network types like non-broadcast and point-to-multipoint. For each type of network, a different type of IS-IS Hello (IIH) packet is exchanged to establish adjacency. On point-to-point networks, point-to-point IIHs are exchanged; and on broadcast networks (such as LAN), Level 1 or Level 2 LAN IIHs are exchanged. A frame-relay network that is running IS-IS can be configured to belong to one of these network types, depending on the type of connectivity (Fully meshed, Partially meshed, or Hub and Spoke) that is available between the routers through the cloud. This document gives an example of a network type configuration mismatch in such a scenario, and it shows how to diagnose and fix the problem.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Readers of this document should have knowledge of these topics:
-
Configuring Frame Relay
-
Configuring Integrated IS-IS
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
The output shown in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco 2500 Series routers
-
Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.2(27)
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Correct Configuration Example
IS-IS treats multipoint serial interfaces and sub-interfaces in the same way that it treats broadcast interfaces, but it treats a point-to-point sub-interface as if it is attached to a point-to-point network. For example, in the network example topology in this section, the WAN multipoint connection between the three fully meshed routers is treated just like a LAN connection. As on a LAN, Level 1 or Level 2 LAN IIHs are exchanged between them, and a Designated Intermediate System (DIS) is elected.
In this example topology, all three routers are connecting to the Frame Relay cloud on point-to-multipoint interfaces or sub-interface. Main interfaces (like Serial1 on Router E and Serial0 on Router G) are multipoint by default. Routers H and F have a point-to-point connection by way of a point-to-point sub-interface, and they use point-to-point IIHs.
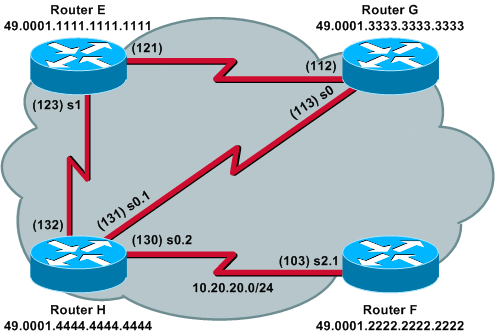
These are the router configurations that are used in this example topology:
| Router E |
|---|
clns routing ! interface Serial1 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 ip router isis encapsulation frame-relay clns router isis frame-relay map clns 123 broadcast frame-relay map clns 121 broadcast frame-relay map ip 10.10.10.3 121 broadcast frame-relay map ip 10.10.10.4 123 broadcast frame-relay lmi-type ansi ! router isis net 49.0001.1111.1111.1111.00 is-type level-1 |
| Router G |
|---|
clns routing ! interface Serial0 ip address 10.10.10.3 255.255.255.0 ip router isis encapsulation frame-relay clns router isis frame-relay map clns 112 broadcast frame-relay map clns 113 broadcast frame-relay map ip 10.10.10.1 112 broadcast frame-relay map ip 10.10.10.4 113 broadcast frame-relay lmi-type ansi ! router isis net 49.0001.3333.3333.3333.00 is-type level-1 |
| Router H |
|---|
clns routing ! interface Serial0 no ip address no ip directed-broadcast no ip mroute-cache encapsulation frame-relay frame-relay lmi-type ansi ! interface Serial0.1 multipoint ip address 10.10.10.4 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis clns router isis frame-relay map clns 132 broadcast frame-relay map clns 131 broadcast frame-relay map ip 10.10.10.1 132 broadcast frame-relay map ip 10.10.10.3 131 broadcast ! interface Serial0.2 point-to-point ip address 10.20.20.4 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis clns router isis frame-relay interface-dlci 130 ! router isis net 49.0001.4444.4444.4444.00 is-type level-1 |
| Router F |
|---|
clns routing ! interface Serial2 no ip address no ip directed-broadcast encapsulation frame-relay frame-relay lmi-type ansi ! interface Serial2.1 point-to-point ip address 10.20.20.2 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis clns router isis frame-relay interface-dlci 103 ! router isis net 49.0001.2222.2222.2222.00 is-type level-1 |
Issue the show clns neighbors, show isis database, and show isis database details commands on any of the routers in the mesh, to observe the effects of the IS-IS configuration on the multipoint WAN connection. This is the output from the show clns neighbors command on all of the routers:
Router_E# show clns neighbors System Id Interface SNPA State Holdtime Type Protocol Router_G Se1 DLCI 121 Up 29 L1 IS-IS Router_H Se1 DLCI 123 Up 7 L1 IS-IS Router_G# show clns neighbors System Id Interface SNPA State Holdtime Type Protocol Router_E Se0 DLCI 112 Up 27 L1 IS-IS Router_H Se0 DLCI 113 Up 7 L1 IS-IS Router_H# show clns neighbors System Id Interface SNPA State Holdtime Type Protocol Router_E Se0.1 DLCI 132 Up 23 L1 IS-IS Router_F Se0.2 DLCI 130 Up 25 L1 IS-IS Router_G Se0.1 DLCI 131 Up 28 L1 IS-IS Router_F# show clns neighbors System Id Interface SNPA State Holdtime Type Protocol Router_H Se2.1 DLCI 103 Up 24 L1 IS-IS
Output from show isis database shows that Router H is the DIS, based on the link-state packet (LSP) ID of the psuedonode:
Router_E# show isis database IS-IS Level-1 Link State Database LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL Router_E.00-00 * 0x00000EA6 0xA415 54 10/0/0 Router_F.00-00 0x00000DD7 0xD76E 46 0/0/0 Router_G.00-00 0x00000DE7 0x780B 40 0/0/0 Router_H.00-00 0x00000DF0 0x4346 37 0/0/0 Router_H.01-00 0x00000DD5 0xFD1F 46 0/0/0 Router_G# show isis database IS-IS Level-1 Link State Database LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL Router_E.00-00 0x00000E8F 0xD2FD 46 10/0/0 Router_F.00-00 0x00000DC0 0x0657 45 0/0/0 Router_G.00-00 * 0x00000DD0 0xA6F3 41 0/0/0 Router_H.00-00 0x00000DDA 0x6F30 42 0/0/0 Router_H.01-00 0x00000DBE 0x2C08 50 0/0/0 Router_H# show isis database IS-IS Level-1 Link State Database LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL Router_E.00-00 0x000001EC 0x1D12 44 10/0/0 Router_F.00-00 0x00000124 0x63A2 54 0/0/0 Router_G.00-00 0x00000130 0x0C3B 33 0/0/0 Router_H.00-00 * 0x0000012F 0xEA6C 42 0/0/0 Router_H.01-00 * 0x00000123 0xBA21 43 0/0/0
You can also examine the details of the LSP for the psuedonode that is generated by the DIS. In this output, the pseudonode LSP Router_H.01-00 represents the fully-meshed WAN, which shows all of the routers that are attached to the mesh (just like the pseudonode LSP does on a LAN):
Router_E# show isis database detail Router_H.01-00 IS-IS Level-1 LSP Router_H.01-00 LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL Router_H.01-00 0x00000DD6 0xFB20 42 0/0/0 Metric: 0 IS Router_H.00 Metric: 0 IS Router_E.00 Metric: 0 IS Router_G.00 Router_G# show isis database detail Router_H.01-00 IS-IS Level-1 LSP Router_H.01-00 LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL Router_H.01-00 0x00000DBE 0x2C08 35 0/0/0 Metric: 0 IS Router_H.00 Metric: 0 IS Router_E.00 Metric: 0 IS Router_G.00 Router_H# show isis database detail Router_H.01-00 IS-IS Level-1 LSP Router_H.01-00 LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL Router_H.01-00 * 0x00000126 0xB424 55 0/0/0 Metric: 0 IS Router_H.00 Metric: 0 IS Router_G.00 Metric: 0 IS Router_E.00
Configuration Mismatch Problem
This section examines a problem due to a configuration mismatch. The Serial2.1 sub-interface of Router F is changed from point-to-point to multipoint, to introduce a problem between Routers F and H. As is shown in the next output, the configuration of Router F has been changed while Router H still connects to Router F via a point-to-point sub-interface.
| Router H |
|---|
clns routing ! interface Serial0 no ip address no ip directed-broadcast no ip mroute-cache encapsulation frame-relay frame-relay lmi-type ansi ! interface Serial0.1 multipoint ip address 10.10.10.4 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis clns router isis frame-relay map clns 132 broadcast frame-relay map clns 131 broadcast frame-relay map ip 10.10.10.1 132 broadcast frame-relay map ip 10.10.10.3 131 broadcast ! interface Serial0.2 point-to-point ip address 10.20.20.4 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis clns router isis frame-relay interface-dlci 130 ! router isis passive-interface Ethernet0 net 49.0001.4444.4444.4444.00 is-type level-1 |
| Router F |
|---|
clns routing ! interface Serial2 no ip address no ip directed-broadcast encapsulation frame-relay frame-relay lmi-type ansi ! interface Serial2.1 multipoint ip address 10.20.20.2 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis clns router isis frame-relay interface-dlci 103 ! router isis net 49.0001.2222.2222.2222.00 is-type level-1 |
Now, Router H no longer sees Router F as an IS-IS neighbor.
Router_H# show clns neighbors System Id Interface SNPA State Holdtime Type Protocol Router_E Se0.1 DLCI 132 Up 23 L1 IS-IS Router_G Se0.1 DLCI 131 Up 22 L1 IS-IS
Router F sees Router H as a neighbor; but the adjacency Type is IS instead of L1, and the Protocol is End System-to-Intermediate System (ES-IS) instead of IS-IS. This means that Router F has an adjacency problem.
Router_F# show clns neighbors System Id Interface SNPA State Holdtime Type Protocol Router_H Se2.1 DLCI 103 Up 272 IS ES-IS
Problem Cause
The problem revolves around the fact that Router F sends LAN IIHs on its multipoint sub-interface and Router H sends serial IIHs on its point-to-point sub-interface. When you activate debug isis adj packets on Router H, you can see that it sends serial IIH over Serial0.2. However, you do not see any IIHs coming via Serial0.2, although Router F is sending LAN IIHs on Serial2.1.
Router_H# debug isis adj-packets IS-IS Adjacency related packets debugging is on *Mar 2 01:11:10.065: ISIS-Adj: Rec L1 IIH from DLCI 131 (Serial0.1), cir type L1, cir id4444.01, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:11.421: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:11.961: ISIS-Adj: Rec L1 IIH from DLCI 132 (Serial0.1), cir type L1, cir id4444.01, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:14.657: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:15.205: ISIS-Adj: Sending serial IIH on Serial0.2, length 1499 *Mar 2 01:11:17.237: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:18.765: ISIS-Adj: Rec L1 IIH from DLCI 131 (Serial0.1), cir type L1, cir id4444.01, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:20.181: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:21.861: ISIS-Adj: Rec L1 IIH from DLCI 132 (Serial0.1), cir type L1, cir id4444.01, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:22.717: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:24.073: ISIS-Adj: Sending serial IIH on Serial0.2, length 1499 *Mar 2 01:11:25.845: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:27.289: ISIS-Adj: Rec L1 IIH from DLCI 131 (Serial0.1), cir type L1, cir id4444.01, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:28.637: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:31.853: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:31.865: ISIS-Adj: Rec L1 IIH from DLCI 132 (Serial0.1), cir type L1, cir id4444.01, length 1500 *Mar 2 01:11:33.181: ISIS-Adj: Sending serial IIH on Serial0.2, length 1499 *Mar 2 01:11:35.165: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500
When you activate the same debug on Router F, you can see that Router F is receiving the serial IIHs from Router H on its Serial2.1 interface, but it is ignoring the Hellos. The LAN IIHs that Router F is trying to send are dropped with encapsulation failures.
Router_F# debug isis adj-packets IS-IS Adjacency related packets debugging is on *Mar 2 01:19:15.113: ISIS-Adj: Rec serial IIH from DLCI 103 (Serial2.1), cir type L1, cir id 00, length 1499 *Mar 2 01:19:15.117: ISIS-Adj: Point-to-point IIH received on multi-point interface: ignored IIH *Mar 2 01:19:17.177: ISIS-Adj: Encapsulation failed for L1 LAN IIH on Serial2.1 *Mar 2 01:19:20.305: ISIS-Adj: Encapsulation failed for L1 LAN IIH on Serial2.1 *Mar 2 01:19:22.813: ISIS-Adj: Rec serial IIH from DLCI 103 (Serial2.1), cir type L1, cir id 00, length 1499 *Mar 2 01:19:22.817: ISIS-Adj: Point-to-point IIH received on multi-point interface: ignored IIH *Mar 2 01:19:23.229: ISIS-Adj: Encapsulation failed for L1 LAN IIH on Serial2.1 *Mar 2 01:19:26.157: ISIS-Adj: Encapsulation failed for L1 LAN IIH on Serial2.1 *Mar 2 01:19:28.825: ISIS-Adj: Encapsulation failed for L1 LAN IIH on Serial2.1 *Mar 2 01:19:30.833: ISIS-Adj: Rec serial IIH from DLCI 103 (Serial2.1), cir type L1, cir id 00, length 1499 *Mar 2 01:19:30.837: ISIS-Adj: Point-to-point IIH received on multi-point interface: ignored IIH *Mar 2 01:19:31.849: ISIS-Adj: Encapsulation failed for L1 LAN IIH on Serial2.1 *Mar 2 01:19:34.929: ISIS-Adj: Encapsulation failed for L1 LAN IIH on Serial2.1 *Mar 2 01:19:38.029: ISIS-Adj: Encapsulation failed for L1 LAN IIH on Serial2.1
This is an analysis of what occurs between Routers F and H when the link types are mismatched:
-
LAN adjacencies utilize a handshake, which results in one of three possible states: DOWN, INIT, or UP.
-
There are encapsulation failures for the Level 1 IIHs outbound from Router F on the Serial2.1 sub-interface, because it does not have—under the multipoint sub-interface—a frame-relay map clns command to forward the IS-IS PDUs.
-
Router H does not receive any LAN IIHs from Router F, because Router F has encapsulation failures when it sends them.
-
Router F does see the serial IIHs that come from Router H, but it ignores the Hellos because it receives point-to-point Hellos on a multipoint sub-interface. Router F does detect that there is something missing or wrong in the IIH from Router H, so Router F creates a LAN adjacency but considers it to be learned through ES-IS, rather than from a L1 type adjacency with IS-IS.
Solution
The solution is to ensure that both sides of a link are either point-to-point or multipoint. In this case, change the Serial2.1 sub-interface of Router F back to point-to-point, to match that which is configured on the Serial0.2 interface of Router H. After the change, flap the interface.
The next debug output shows what happens after you make the change and the Serial2 interface on Router F is flapped. Now Router F is able to send and receive serial IIHs on its Serial2.1 interface.
Router_F# debug isis adj-packets *Mar 2 04:32:37.276: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial2, changed state to administratively down *Mar 2 04:32:38.316: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial2, changed state to down *Mar 2 04:32:45.868: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Serial2, changed state to up *Mar 2 04:32:46.868: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial2, changed state to up *Mar 2 04:33:05.896: ISIS-Adj: Sending serial IIH on Serial2.1, length 1499 *Mar 2 04:33:13.312: ISIS-Adj: Rec serial IIH from DLCI 103 (Serial2.1), cir type L1, cir id 00, length 1499 *Mar 2 04:33:13.316: ISIS-Adj: rcvd state DOWN, old state DOWN, new state INIT *Mar 2 04:33:13.316: ISIS-Adj: Action = GOING UP, new type = L1 *Mar 2 04:33:13.320: ISIS-Adj: New serial adjacency *Mar 2 04:33:13.324: ISIS-Adj: Sending serial IIH on Serial2.1, length 1499 *Mar 2 04:33:14.196: ISIS-Adj: Rec serial IIH from DLCI 103 (Serial2.1), cir type L1, cir id 00, length 1499 *Mar 2 04:33:14.204: ISIS-Adj: rcvd state INIT, old state INIT, new state UP *Mar 2 04:33:14.204: ISIS-Adj: Action = GOING UP, new type = L1 *Mar 2 04:33:14.208: ISIS-Adj: L1 adj count 1 *Mar 2 04:33:14.212: ISIS-Adj: Sending serial IIH on Serial2.1, length 1499 *Mar 2 04:33:15.100: ISIS-Adj: Rec serial IIH from DLCI 103 (Serial2.1), cir type L1, cir id 00, length 1499 *Mar 2 04:33:15.100: ISIS-Adj: rcvd state UP, old state UP, new state UP *Mar 2 04:33:15.104: ISIS-Adj: Action = ACCEPT *Mar 2 04:33:22.924: ISIS-Adj: Rec serial IIH from DLCI 103 (Serial2.1), cir type L1, cir id 00, length 1499 *Mar 2 04:33:22.928: ISIS-Adj: rcvd state UP, old state UP, new state UP *Mar 2 04:33:22.932: ISIS-Adj: Action = ACCEPT
From the perspective of Router H, the configuration is back to normal:
Router_H# show clns neighbors System Id Interface SNPA State Holdtime Type Protocol Router_E Se0.1 DLCI 132 Up 28 L1 IS-IS Router_F Se0.2 DLCI 130 Up 21 L1 IS-IS Router_G Se0.1 DLCI 131 Up 28 L1 IS-IS
The debug isis adj packets command output is also back to normal:
Router_H# debug isis adj-packets *Mar 2 04:40:19.376: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 04:40:21.944: ISIS-Adj: Rec L1 IIH from DLCI 132 (Serial0.1), cir type L1, cir id 4444.4444.01, length 1500 *Mar 2 04:40:22.020: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 04:40:22.428: ISIS-Adj: Rec L1 IIH from DLCI 131 (Serial0.1), cir type L1, cir id 4444.4444.01, length 1500 *Mar 2 04:40:24.740: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 04:40:24.780: ISIS-Adj: Rec serial IIH from DLCI 130 (Serial0.2), cir type L1, cir id 0ngth 1499 *Mar 2 04:40:24.784: ISIS-Adj: rcvd state UP, old state UP, new state UP *Mar 2 04:40:24.784: ISIS-Adj: Action = ACCEPT *Mar 2 04:40:26.068: ISIS-Adj: Sending serial IIH on Serial0.2, length 1499 *Mar 2 04:40:27.516: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 04:40:30.432: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 04:40:31.152: ISIS-Adj: Rec L1 IIH from DLCI 132 (Serial0.1), cir type L1, cir id 4444.4444.01, length 1500 *Mar 2 04:40:31.540: ISIS-Adj: Rec L1 IIH from DLCI 131 (Serial0.1), cir type L1, cir id 4444.4444.01, length 1500 *Mar 2 04:40:33.292: ISIS-Adj: Rec serial IIH from DLCI 130 (Serial0.2), cir type L1, cir id 0ngth 1499 *Mar 2 04:40:33.296: ISIS-Adj: rcvd state UP, old state UP, new state UP *Mar 2 04:40:33.296: ISIS-Adj: Action = ACCEPT *Mar 2 04:40:33.664: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500 *Mar 2 04:40:34.420: ISIS-Adj: Sending serial IIH on Serial0.2, length 1499 *Mar 2 04:40:36.328: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on Serial0.1, length 1500
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
10-Aug-2005 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback