Introduction
This document describes how to troubleshoot common issues with Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, see the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Background Information
This document provides flowcharts for several options to troubleshoot BGP issues.
If you have the output of a show ip bgp , show ip bgp neighbors , show ip bgp summary , or show tech-support command from your Cisco device, you can use Cisco CLI Analyzer to display potential issues and fixes. To use Cisco CLI Analyzer, you must be a registered Cisco user.
Note: Only registered Cisco users can access internal tools and information.
Main Troubleshoot Flowchart
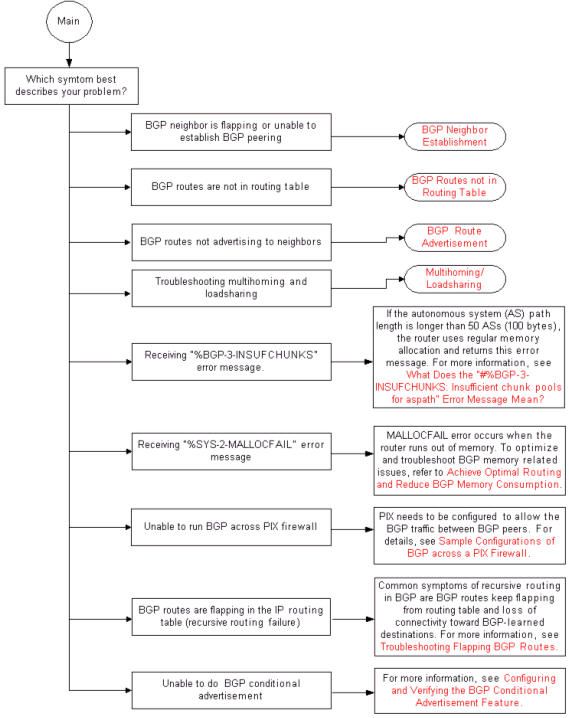 BGP Main Flowchart
BGP Main Flowchart
Troubleshoot BGP Neighbor Establishment
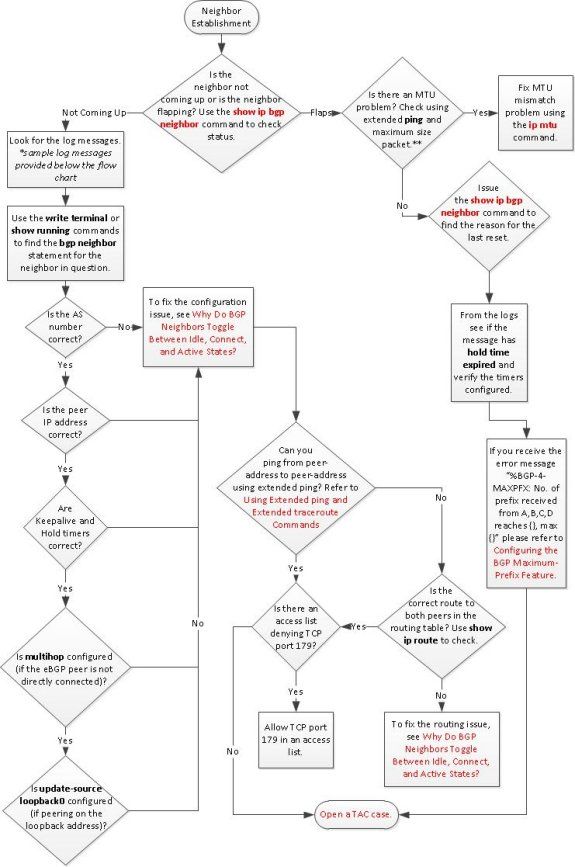
This is a sample log message that must be checked when the neighbor does not come up:
BGP_SESSION-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor[ip address] IPv4 Unicast topology base removed
from session Peer closed the session
BGP_SESSION-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor[ip address] IPv4 Unicast topology base removed
from session Unknown path error
This is an example of ping with packet size and enable does not contain fragment bit in the IP header:
Router#ping 10.10.10.2 size 1400 df-bit
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 1400-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.10.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with the DF bit set
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/37/84 ms
Note: You need to check the duplex settings of the interface.
Note: If the reset has occurred due to interface flapping, disable the eBGP fast failover with the no bgp fast-external-fallover command. By default, BGP resets the neighborship if the link used in order to reach the neighbor goes down. Disable this feature under BGP Configuration in order to keep BGP stable and prevent the interface from flapping.
If flapping occurs due to high CPU, refer to Troubleshooting High CPU Utilization on Cisco Routers.
Troubleshoot Routes Missing from the Routing Table
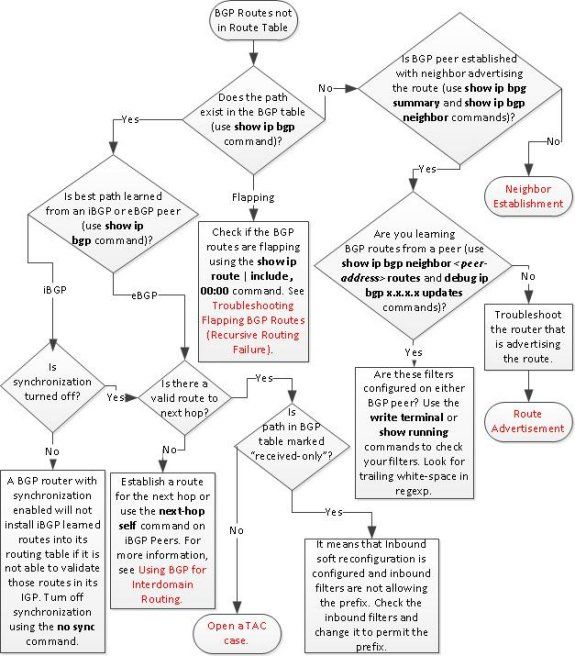
Note: If the BGP routes are not in the routing table, verify if the network statement under the BGP configuration is correct.
Note: In the debug ip bgp x.x.x.x updates command, x.x.x.x is the neighbor to which the route must be advertised.
Troubleshoot Multihoming Inbound
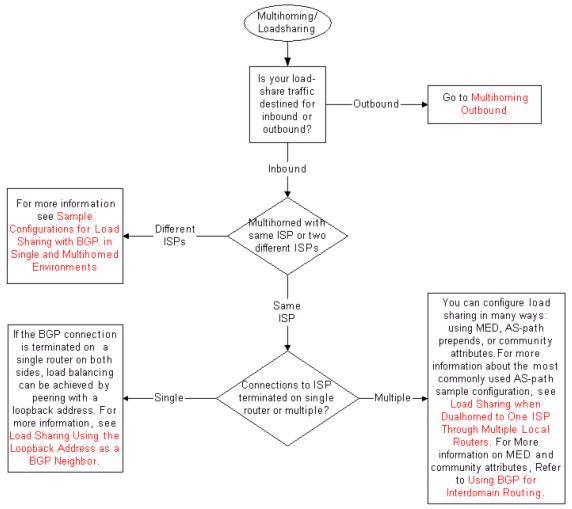
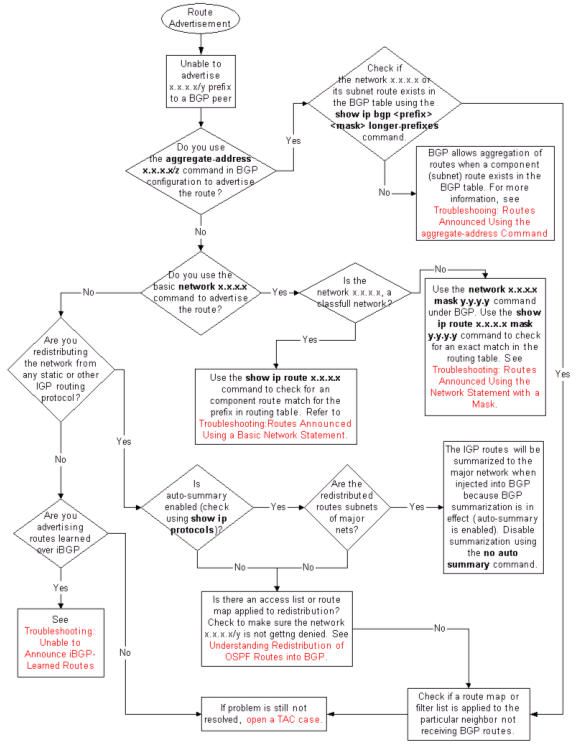
Troubleshoot BGP Route Advertisement
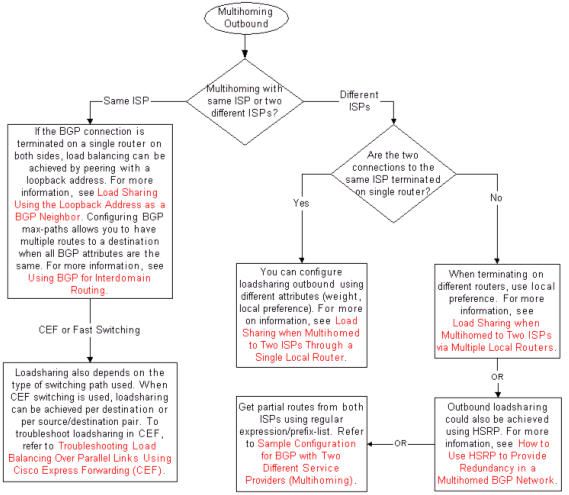
Troubleshoot Multihoming Outbound
Related Information






 Feedback
Feedback