Field Notice: FN - 70610 - Cisco Identity Services Engine MAC Address Lookup Might Fail with Android 10, Android 11, and Apple iOS 14 Devices Due to the Use of MAC Randomization on the Mobile Client Devices - Workaround Provided
Available Languages
Notice
THIS FIELD NOTICE IS PROVIDED ON AN "AS IS" BASIS AND DOES NOT IMPLY ANY KIND OF GUARANTEE OR WARRANTY, INCLUDING THE WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY. YOUR USE OF THE INFORMATION ON THE FIELD NOTICE OR MATERIALS LINKED FROM THE FIELD NOTICE IS AT YOUR OWN RISK. CISCO RESERVES THE RIGHT TO CHANGE OR UPDATE THIS FIELD NOTICE AT ANY TIME.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
15-Sep-20 |
Initial Release |
1.1 |
16-Sep-20 |
Updated the Workaround/Solution Section |
1.2 |
18-Sep-20 |
Updated the Products Affected Section |
1.3 |
23-Sep-20 |
Updated the Problem Description, Background, Problem Symptom, and Additional Information Sections |
Products Affected
| Affected OS Type | Affected Software Product | Affected Release | Affected Release Number | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
NON-IOS |
Identity Services Engine System Software |
1 |
1.0, 1.0 MR, 1.1, 1.1.1, 1.1.2, 1.1.3, 1.1.4, 1.2, 1.2.1, 1.3, 1.4 |
All versions of ISE are affected |
NON-IOS |
Identity Services Engine System Software |
2 |
2.0, 2.0.1, 2.1.0, 2.2.0, 2.2.1, 2.3.0, 2.4.0, 2.6.0, 2.7.0 |
All versions of ISE are affected |
NON-IOS |
Identity Services Engine System Software |
3 |
3.0.0 |
All versions of ISE are affected |
Defect Information
| Defect ID | Headline |
|---|---|
| CSCvv71694 | IOS 14 and Android 10 Mac randomization may disrupt BYOD, profiler, and MDM flows |
Problem Description
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) services that use MAC address lookup might fail with Android 10, Android 11, and Apple iOS 14 devices due to the use of MAC address randomization on the mobile client devices, which could result in unexpected network connectivity disruption for these devices.
Background
Android 10, Android 11, and Apple iOS 14 devices use randomized MAC addresses when connecting to wireless networks to provide privacy for users. Within ISE and many network components, the MAC address is considered to be the unique identifier for a given endpoint. Due to the MAC address randomization, this one-to-one mapping is no longer true and a single endpoint could end up generating multiple endpoint entries within the ISE database (DB).
The next sections show how MAC address randomization is implemented on mobile endpoints:
Google Android 10 and Android 11
- Randomization is enabled by default.
- When a user upgrades from a previous version of Android to Android 10 or Android 11, the saved Service Set Identifiers (SSIDs) will stay configured without randomization.
- Randomization can be set up per network profile (SSID).
- Once a random MAC address is used for a given network profile, the mobile device will continue to use the same random MAC address even after the user deletes the network profile and recreates the SSID/network profile.
- For more information on Android MAC randomization, see Privacy: MAC Randomization.
Apple iOS 14, iPad OS 14, and watchOS 7
- Randomization is enabled by default.
- When a user upgrades from a previous version of iOS to iOS 14, the randomization will be enabled for all of the existing SSIDs.
- Randomization can be set up per network profile (SSID).
- Once a random MAC address is used for a given network profile, the mobile device will continue to use the same random MAC address even after the user deletes the network profile and recreates the SSID/network profile.
- For more information on iOS MAC randomization, see Use private Wi-Fi addresses in iOS 14, iPadOS 14, and watchOS 7.
Problem Symptom
Without preparing policies for MAC address randomization, previously provisioned mobile devices and the policies configured based on profiling identity groups might be incorrectly matched after the new MAC address randomization behavior takes effect. This could result in network connectivity disruption for these mobile devices.
MAC address randomization impacts these ISE services that rely on mapping of a single MAC address for a given device:
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) - The MAC address of the client at the time of BYOD onboarding is embedded in the certificate that is returned to the client. Due to this, a dual-SSID flow using MAC-in-SAN or BYOD_is_Registered condition will fail as the MAC address between the onboarding SSID and the secured SSID is different. This is also true for single-SSID flows for devices that are upgraded from a previous version of Apple iOS to iOS 14 (single-SSID flows for devices upgraded to Android 10 or Android 11 are unaffected) as the MAC address randomization is enabled by default on all SSIDs on the device.
- Profiling - Certain profiling policies rely on vendor Organizationally Unique Identifiers (OUIs) which will no longer match. Randomized MAC addresses utilize a custom range for OUIs that is not unique to specific vendors.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) - MAC address lookup to MDM providers will fail as the MAC addresses that ISE has learned from RADIUS are only applicable to a specific SSID.
- ISE Endpoint DB - The endpoint DB will grow over time as random MAC addresses populate the DB. ISE is limited to 2.5M endpoints in the DB with a fully distributed deployment. If this limit is exceeded, ISE system performance might be affected.
Workaround/Solution
There is currently no large scale solution for the issues introduced by third-party MAC address randomization, only workarounds are available.
Note: It is possible to disable MAC address randomization at a per-device level. In order to do so, see the manufacturer's documentation for the respective end user device.
BYOD
As a workaround for the BYOD flow, the MAC_in_SAN condition and BYOD_is_registered condition from the Employee_EAP-TLS authorization rule can be removed so that the MAC address is not compared when the device connects to the SSID with the certificate as shown in this image.

For more information on BYOD, see the Additional Information section.
Profiling and MDM
For Profiling and MDM services, end users can be instructed to disable MAC address randomization on the device before obtaining intended network access. In order to do so, users can be redirected to a modified hotspot page that provides instructions to disable MAC address randomization when the device uses a random MAC address to connect to the network. Once MAC address randomization is disabled, the user can connect normally. For additional details, see Using Hotspot Portal to Instruct Users on Disabling MAC Address Randomization.
ISE Endpoint Database (Optional)
The ISE endpoint DB might end up with unused random MAC addresses over time. An ISE endpoint purge policy can be created in order to remove random MAC addresses periodically to prevent the ISE DB from being consumed with random MAC addresses.
- Navigate to Administration > Identity management > Settings.
- Choose Endpoint Purge.
- In the Purge section, from the drop-down list (next to Edit) for any existing rule, choose Insert New Rule ….
- Type RandomMAC as the rule name and choose these conditions:
- Radius:Calling-Station-ID MATCHES ^.[26AEae].*
- ENDPOINTPURGE:InactiveDays GREATERTHAN 7
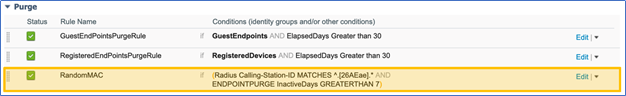
- Click Save.
Note: If the ISE deployment is set up to permit random MAC addresses for certain use cases, the previous purge rule will remove all random MAC addresses that have not been connected to the network in the past seven days. In order to avoid purging legitimate random MAC devices, create a Never Purge rule to exempt those devices from the purge rule.
Additional Information
BYOD
Even though the Android 10, Android 11, and Apple iOS 14 devices are set up to use randomized MAC addresses, when a wireless profile is created on the device the MAC address is always generated with the same random MAC address for the given wireless profile. This is true even when the wireless profile is deleted and recreated. However, when the dual-SSID BYOD flow is used, different MAC addresses will be generated for the onboarding SSID and the secured SSID. This causes a policy mismatch when using the precreated ISE BYOD Employee_EAP-TLS authorization rule.
This also impacts the single-SSID BYOD flow for devices that have been onboarded while running a previous version of iOS. Prior to iOS 14, the device uses a real MAC address for wireless access. However, upon upgrade to iOS 14, all existing wireless profiles will be updated to use random MAC addresses. Since the MAC address used during the previous version of iOS and after iOS 14 is different, authentication might fail if MAC address related conditions are used in conjunction with BYOD.
For More Information
If you require further assistance, or if you have any further questions regarding this field notice, please contact the Cisco Systems Technical Assistance Center (TAC) by one of the following methods:
Receive Email Notification For New Field Notices
My Notifications—Set up a profile to receive email updates about reliability, safety, network security, and end-of-sale issues for the Cisco products you specify.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
This Document Applies to These Products
Unleash the Power of TAC's Virtual Assistance
 Feedback
Feedback