Konfigurieren von vorinstallierten IKE-Schlüsseln mithilfe eines RADIUS-Servers für den Cisco Secure VPN Client
Inhalt
Einführung
In diesem Dokument wird beschrieben, wie der gemeinsame geheime Internet Key Exchange (IKE) mithilfe eines RADIUS-Servers konfiguriert wird. Die IKE-Funktion für gemeinsam genutzte geheime Schlüssel, die einen AAA-Server (Authentication, Authorization, Accounting) verwendet, ermöglicht die Schlüsselsuche vom AAA-Server. Pre-Shared Keys lassen sich nicht gut skalieren, wenn Sie ein groß angelegtes VPN-System ohne Zertifizierungsstelle (CA) bereitstellen. Wenn dynamische IP-Adressen wie DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) oder PPP-Wählverbindungen (Point-to-Point Protocol) verwendet werden, kann die Änderung der IP-Adresse die Schlüsselsuche erschweren oder unmöglich machen, es sei denn, ein vorinstallierter Platzhalter-Schlüssel wird verwendet. Bei der IKE Shared geheim-Funktion, die einen AAA-Server verwendet, wird der Zugriff auf den gemeinsamen geheimen Schlüssel im aggressiven Modus der IKE-Aushandlung über den AAA-Server gewährt. Die ID des Austauschs wird als Benutzername für die Abfrage von AAA verwendet, wenn auf dem Cisco IOS®-Router, mit dem der Benutzer eine Verbindung herstellen möchte, kein lokaler Schlüssel gefunden wird. Dies wurde in Version 12.1.T der Cisco IOS-Software eingeführt. Zur Verwendung dieser Funktion muss auf dem VPN-Client der aggressive Modus aktiviert sein.
Voraussetzungen
Anforderungen
Der aggressive Modus muss auf dem VPN-Client aktiviert sein, und Sie müssen die Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1.T oder höher auf dem Router ausführen.
Verwendete Komponenten
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument basieren auf den folgenden Software- und Hardwareversionen:
-
Cisco Secure ACS für Windows
-
Cisco IOS Softwareversion 12.2.8T
-
Cisco Router der Serie 1700
Die in diesem Dokument enthaltenen Informationen wurden aus Geräten in einer bestimmten Laborumgebung erstellt. Alle in diesem Dokument verwendeten Geräte haben mit einer leeren (Standard-)Konfiguration begonnen. Wenn Sie in einem Live-Netzwerk arbeiten, stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie die potenziellen Auswirkungen eines Befehls verstehen, bevor Sie es verwenden.
Konventionen
Weitere Informationen zu Dokumentkonventionen finden Sie unter Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Konfigurieren
In diesem Dokument werden die unten angegebenen Konfigurationen verwendet.
Hinweis: Um weitere Informationen zu den in diesem Dokument verwendeten Befehlen zu erhalten, verwenden Sie das Command Lookup Tool (nur registrierte Kunden).
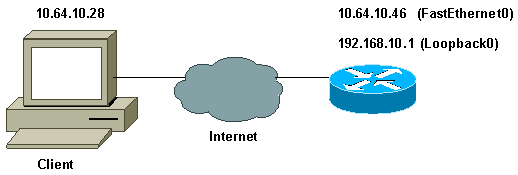
Netzwerkdiagramm
In diesem Dokument wird die folgende Netzwerkeinrichtung verwendet:
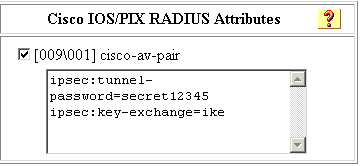
Erstellen eines sicheren Cisco Profils
Dieses Profil wurde mit UNIX erstellt, aber ein ähnliches Profil kann auf Cisco Secure ACS für Windows erstellt werden.
# ./ViewProfile -p 9900 -u haseeb User Profile Information !--- The user name is sent by the VPN Client; !--- look at the client configuration. user = haseeb{ radius=Cisco12.05 { check_items= { !--- This should always be "cisco." 2=cisco } reply_attributes= { 6=5 64=9 65=1 !--- Pre-shared key. 9,1="ipsec:tunnel-password=secret12345" 9,1="ipsec:key-exchange=ike" } } }
Diese Ausgabe zeigt das Skript, das zum Hinzufügen eines Benutzerprofils in Cisco Secure ACS für UNIX verwendet wird.
#!/bin/sh
./DeleteProfile -p 9900 -u haseeb
./AddProfile -p 9900 -u haseeb -a 'radius=Cisco12.05
{ \n check_items = { \n 2="cisco" \n } \n
reply_attributes = { \n 6=5 \n 64=9 \n 65=1 \n
9,1="ipsec:tunnel-password=cisco" \n
9,1="ipsec:key-exchange=ike" \n } \n }'
Befolgen Sie diese Schritte, um das Benutzerprofil auf Cisco Secure ACS für Windows 2.6 über die Benutzeroberfläche zu konfigurieren.
-
Definieren Sie den Benutzernamen, wobei "cisco" als Kennwort dient.

-
Definieren Sie den Schlüsselaustausch als IKE und einen Pre-Shared Key unter dem Cisco Av-Pair.
Konfigurieren des Routers
| Cisco 1751 mit IOS 12.2.8T |
|---|
version 12.2 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname 1751-vpn ! !--- Enable AAA. aaa new-model ! ! aaa authentication login default none !--- Configure authorization. aaa authorization network vpn_users group radius aaa session-id common ! memory-size iomem 15 mmi polling-interval 60 no mmi auto-configure no mmi pvc mmi snmp-timeout 180 ip subnet-zero ! no ip domain-lookup ! !--- Define IKE policy for phase 1 negotiations of the VPN Clients. crypto isakmp policy 10 hash md5 authentication pre-share crypto isakmp client configuration address-pool local mypool ! !--- Define IPSec policies - Phase 2 Policy for actual data encryption. crypto ipsec transform-set myset esp-des esp-md5-hmac ! !--- Create dynamic crypto map. crypto dynamic-map dynmap 10 set transform-set myset ! !--- Configure IKE shared secret using AAA server on this router. crypto map intmap isakmp authorization list vpn_users !--- IKE Mode Configuration - the router will attempt !--- to set IP addresses for each peer. crypto map intmap client configuration address initiate !--- IKE Mode Configuration - the router will accept !--- requests for IP addresses from any requesting peer. crypto map intmap client configuration address respond crypto map intmap 10 ipsec-isakmp dynamic dynmap ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback1 no ip address ! interface Ethernet0/0 no ip address half-duplex ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.64.10.46 255.255.255.224 speed auto !--- Assign crypto map to interface. crypto map intmap ! !--- Configure a local pool of IP addresses to be used when a !--- remote peer connects to a point-to-point interface. ip local pool mypool 10.1.2.1 10.1.2.254 ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.64.10.33 no ip http server ip pim bidir-enable ! !--- Specify the security server protocol and defines security !--- server host IP address and UDP port number. radius-server host 10.64.10.7 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 key cisco123 radius-server retransmit 3 ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! end |
Konfigurieren des Clients
Befolgen Sie diese Schritte, um den Client zu konfigurieren.
-
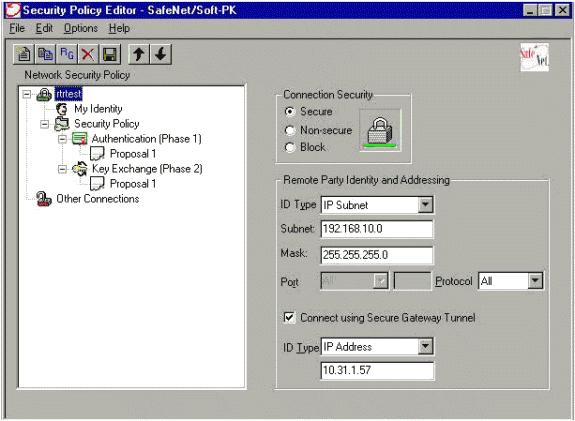
Gehen Sie im Sicherheitsrichtlinien-Editor zu Netzwerksicherheitsrichtlinie > Rettest. Wählen Sie den ID-Typ als E-Mail-Adresse aus, und geben Sie einen Benutzernamen ein, der auf dem RADIUS-Server konfiguriert werden soll. Wenn diese Einstellung als "IP Address" (IP-Adresse) beibehalten wird, entspricht der an den RADIUS-Server gesendete Benutzername der IP-Adresse des Client-PCs.
-
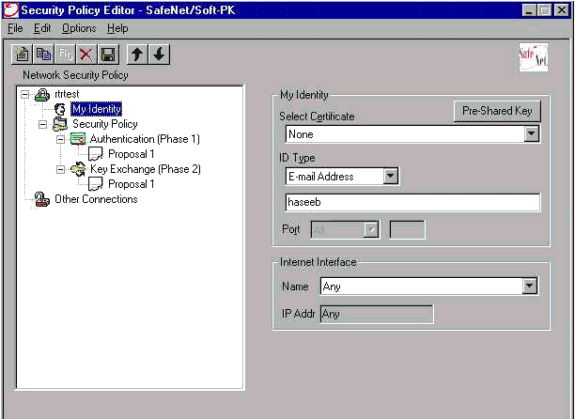
Gehen Sie zu Netzwerksicherheitsrichtlinie > trtest > My Identity, und wählen Sie Aggressive Mode (Aggressiver Modus) aus. Wenn dieser Modus nicht ausgewählt ist, funktioniert das Setup nicht.
Überprüfen
Für diese Konfiguration ist derzeit kein Überprüfungsverfahren verfügbar.
Fehlerbehebung
Dieser Abschnitt enthält Informationen zur Fehlerbehebung in Ihrer Konfiguration.
Diese Ausgabe zeigt gute Debug-Ergebnisse für diese Konfiguration:
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:0): received packet from 10.64.10.28 (N) NEW SA
23:43:41: ISAKMP: local port 500, remote port 500
23:43:41: ISAKMP: Locking CONFIG struct 0x8180BEF4 from
crypto_ikmp_config_initialize_sa, count 2
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): processing SA payload. message ID = 0
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): processing ID payload. message ID = 0
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): processing vendor id payload
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): vendor ID seems Unity/DPD but bad major
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): vendor ID is XAUTH
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): Checking ISAKMP transform 1 against priority 10 policy
23:43:41: ISAKMP: encryption DES-CBC
23:43:41: ISAKMP: hash MD5
23:43:41: ISAKMP: default group 1
23:43:41: ISAKMP: auth pre-share
!--- ISAKMP policy proposed by VPN Client !--- matched the configured ISAKMP policy.
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): atts are acceptable. Next payload is 0
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): processing KE payload. message ID = 0
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): processing NONCE payload. message ID = 0
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): SKEYID state generated
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): processing vendor id payload
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): vendor ID seems Unity/DPD but bad major
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): vendor ID is XAUTH
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): SA is doing pre-shared key authentication
using id type ID_IPV4_ADDR
23:43:41: ISAKMP (3): ID payload
next-payload : 10
type : 1
protocol : 17
port : 500
length : 8
23:43:41: ISAKMP (3): Total payload length: 12
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): sending packet to 10.64.10.28 (R) AG_INIT_EXCH
23:43:41: ISAKMP (0:3): Input = IKE_MESG_FROM_PEER, IKE_AM_EXCH
Old State = IKE_READY New State = IKE_R_AM2
23:43:42: ISAKMP (0:3): received packet from 10.64.10.28 (R) AG_INIT_EXCH
23:43:42: ISAKMP (0:3): processing HASH payload. message ID = 0
23:43:42: ISAKMP (0:3): SA has been authenticated with 10.64.10.28
23:43:42: ISAKMP (0:3): Input = IKE_MESG_FROM_PEER, IKE_AM_EXCH
Old State = IKE_R_AM2 New State = IKE_P1_COMPLETE
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): received packet from 10.64.10.28 (R) QM_IDLE
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): Need config/address
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): Need config/address
23:43:43: ISAKMP: Sending private address: 10.1.2.2
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): initiating peer config to 10.64.10.28.
ID = -1082015193
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): sending packet to 10.64.10.28 (R) CONF_ADDR
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): Input = IKE_MESG_INTERNAL, IKE_PHASE1_COMPLETE
Old State = IKE_P1_COMPLETE New State = IKE_CONFIG_MODE_SET_SENT
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): received packet from 10.64.10.28 (R) CONF_ADDR
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): processing transaction payload from 10.64.10.28.
message ID = -1082015193
23:43:43: ISAKMP: Config payload ACK
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): peer accepted the address!
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): deleting node -1082015193 error FALSE
reason "done with transaction"
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): Input = IKE_MESG_FROM_PEER, IKE_CFG_ACK
Old State = IKE_CONFIG_MODE_SET_SENT New State = IKE_P1_COMPLETE
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): Delaying response to QM request.
23:43:43: ISAKMP (0:3): Input = IKE_MESG_INTERNAL, IKE_PHASE1_COMPLETE
Old State = IKE_P1_COMPLETE New State = IKE_P1_COMPLETE
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): received packet from 10.64.10.28 (R) QM_IDLE
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): processing HASH payload. message ID = -920829332
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): processing SA payload. message ID = -920829332
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): Checking IPSec proposal 1
23:43:44: ISAKMP: transform 1, ESP_DES
23:43:44: ISAKMP: attributes in transform:
23:43:44: ISAKMP: authenticator is HMAC-MD5
23:43:44: ISAKMP: encaps is 1
!--- Proposed Phase 2 transform set !--- matched configured IPSec transform set.
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): atts are acceptable.
23:43:44: IPSEC(validate_proposal_request): proposal part #1,
(key eng. msg.) INBOUND local= 10.64.10.46, remote= 10.64.10.28,
local_proxy= 192.168.10.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
remote_proxy= 10.1.2.2/255.255.255.255/0/0 (type=1),
protocol= ESP, transform= esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 0s and 0kb,
spi= 0x0(0), conn_id= 0, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): processing NONCE payload. message ID = -920829332
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): processing ID payload. message ID = -920829332
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): processing ID payload. message ID = -920829332
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): asking for 1 spis from ipsec
23:43:44: ISAKMP (0:3): Node -920829332,
Input = IKE_MESG_FROM_PEER, IKE_QM_EXCH
Old State = IKE_QM_READY New State = IKE_QM_SPI_STARVE
23:43:44: IPSEC(key_engine): got a queue event...
23:43:44: IPSEC(spi_response): getting spi 2940839732 for SA
from 10.64.10.46 to 10.64.10.28 for prot 3
23:43:44: ISAKMP: received ke message (2/1)
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): sending packet to 10.64.10.28 (R) QM_IDLE
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): Node -920829332,
Input = IKE_MESG_FROM_IPSEC, IKE_SPI_REPLY
Old State = IKE_QM_SPI_STARVE New State = IKE_QM_R_QM2
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): received packet from 10.64.10.28 (R) QM_IDLE
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): Creating IPSec SAs
23:43:45: inbound SA from 10.64.10.28 to 10.64.10.46
(proxy 10.1.2.2 to 192.168.10.0)
23:43:45: has spi 0xAF49A734 and conn_id 200 and flags 4
23:43:45: outbound SA from 10.64.10.46 to 10.64.10.28
(proxy 192.168.10.0 to 10.1.2.2 )
23:43:45: has spi 1531785085 and conn_id 201 and flags C
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): deleting node 1961959105 error FALSE
reason "saved qm no longer needed"
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): deleting node -920829332 error FALSE
reason "quick mode done (await()"
23:43:45: ISAKMP (0:3): Node -920829332,
Input = IKE_MESG_FROM_PEER, IKE_QM_EXCH
Old State = IKE_QM_R_QM2 New State = IKE_QM_PHASE2_COMPLETE
23:43:45: IPSEC(key_engine): got a queue event...
23:43:45: IPSEC(initialize_sas): ,
(key eng. msg.) INBOUND local= 10.64.10.46, remote= 10.64.10.28,
local_proxy= 192.168.10.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
remote_proxy= 10.1.2.2/0.0.0.0/0/0 (type=1),
protocol= ESP, transform= esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 0s and 0kb,
spi= 0xAF49A734(2940839732), conn_id= 200, keysize= 0, flags= 0x4
23:43:45: IPSEC(initialize_sas): ,
(key eng. msg.) OUTBOUND local= 10.64.10.46, remote= 10.64.10.28,
local_proxy= 192.168.10.0/255.255.255.0/0/0 (type=4),
remote_proxy= 10.1.2.2/0.0.0.0/0/0 (type=1),
protocol= ESP, transform= esp-des esp-md5-hmac ,
lifedur= 0s and 0kb,
spi= 0x5B4D2F7D(1531785085), conn_id= 201, keysize= 0, flags= 0xC
!--- IPSec SAs created.
23:43:45: IPSEC(create_sa): sa created, (sa) sa_dest= 10.64.10.46,
sa_prot= 50, sa_spi= 0xAF49A734(2940839732),
sa_trans= esp-des esp-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 200
23:43:45: IPSEC(create_sa): sa created, (sa) sa_dest= 10.64.10.28,
sa_prot= 50, sa_spi= 0x5B4D2F7D(1531785085),
sa_trans= esp-des esp-md5-hmac , sa_conn_id= 201
23:43:45: ISAKMP: received ke message (4/1)
23:43:45: ISAKMP: Locking CONFIG struct 0x8180BEF4
for crypto_ikmp_config_handle_kei_mess, count 3
23:43:50: ISAKMP (0:2): purging node 618568216
23:43:50: ISAKMP (0:2): purging node -497663485
23:44:00: ISAKMP (0:2): purging SA., sa=816B5724, delme=816B5724
23:44:00: ISAKMP: Unlocking CONFIG struct 0x8180BEF4 on
return of attributes, count 2
Zugehörige Informationen
Revisionsverlauf
| Überarbeitung | Veröffentlichungsdatum | Kommentare |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
14-May-2009 |
Erstveröffentlichung |
 Feedback
Feedback