Konfiguration und Fehlerbehebung bei Multicast Service Reflection auf Catalyst 8000
Inklusive Sprache
In dem Dokumentationssatz für dieses Produkt wird die Verwendung inklusiver Sprache angestrebt. Für die Zwecke dieses Dokumentationssatzes wird Sprache als „inklusiv“ verstanden, wenn sie keine Diskriminierung aufgrund von Alter, körperlicher und/oder geistiger Behinderung, Geschlechtszugehörigkeit und -identität, ethnischer Identität, sexueller Orientierung, sozioökonomischem Status und Intersektionalität impliziert. Dennoch können in der Dokumentation stilistische Abweichungen von diesem Bemühen auftreten, wenn Text verwendet wird, der in Benutzeroberflächen der Produktsoftware fest codiert ist, auf RFP-Dokumentation basiert oder von einem genannten Drittanbieterprodukt verwendet wird. Hier erfahren Sie mehr darüber, wie Cisco inklusive Sprache verwendet.
Informationen zu dieser Übersetzung
Cisco hat dieses Dokument maschinell übersetzen und von einem menschlichen Übersetzer editieren und korrigieren lassen, um unseren Benutzern auf der ganzen Welt Support-Inhalte in ihrer eigenen Sprache zu bieten. Bitte beachten Sie, dass selbst die beste maschinelle Übersetzung nicht so genau ist wie eine von einem professionellen Übersetzer angefertigte. Cisco Systems, Inc. übernimmt keine Haftung für die Richtigkeit dieser Übersetzungen und empfiehlt, immer das englische Originaldokument (siehe bereitgestellter Link) heranzuziehen.
Einleitung
In diesem Dokument wird das Verfahren zur Fehlerbehebung bei der Multicast Service Reflection-Funktion auf Catalyst 8000 beschrieben.
Voraussetzungen
Anforderungen
Cisco empfiehlt, dass Sie über Kenntnisse in folgenden Bereichen verfügen:
- Grundlegendes Multicast-Routing
- Kenntnis der Cisco IOS® XE-Befehlszeile
Verwendete Komponenten
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument basierend auf folgenden Software- und Hardware-Versionen:
- Catalyst 8500 Router
- Cisco IOS XE 17.9.4
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument beziehen sich auf Geräte in einer speziell eingerichteten Testumgebung. Alle Geräte, die in diesem Dokument benutzt wurden, begannen mit einer gelöschten (Nichterfüllungs) Konfiguration. Wenn Ihr Netzwerk in Betrieb ist, stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie die möglichen Auswirkungen aller Befehle kennen.
Hintergrundinformationen
In diesem Dokument wird die grundlegende Konfiguration und Fehlerbehebung der Multicast Service Reflection-Funktion erläutert, um ein Multicast-zu-Multicast-Zielumwandlungsszenario mit einem Cisco Catalyst 8000 zu validieren.
Multicast Service Reflection ist eine vielseitige Funktion, die an verschiedenen Punkten in einem Netzwerk bereitgestellt werden kann, um bestimmte Multicast-Anforderungen zu erfüllen. Sie trägt dazu bei, die Effizienz und Zuverlässigkeit von Multicast-Services zu verbessern. in komplexe Netzwerkumgebungen, da Benutzer empfangene Multicast- oder Unicast-Zieladressen in Multicast- oder Unicast-Adressen übersetzen können, die ihrer internen Adressierungsrichtlinie entsprechen.
Multicast Service Reflection bietet die Möglichkeit, beide Quelle und Zieladressen in den IPv4-Header. Identifiziert die Multicast-Datenverkehrsströme (die bestimmten Multicast-Gruppen und -Quellen zugeordnet sind), die umgewandelt werden müssen (anhand der vordefinierten Konfiguration). Wenn der Datenverkehr den Reflexionspunkt erreicht, reflektiert der die Übersetzung durchführende Router diese Pakete selektiv.
Eine der Kernkomponenten dieser Funktion ist die virtuelle Schnittstelle (Virtual Interface, VIF). Diese Vif-Schnittstelle ist eine logische Schnittstelle, die der Gruppe statisch beitreten kann, die gespiegelt werden muss. in um den Multicast-Tree zu erstellen. Mit anderen Worten, diese Vif-Schnittstelle agiert als Multicast-Empfänger für den ursprünglichen Stream und nachdem der Datenverkehr an die Vif-Schnittstelle weitergeleitet wurde, werden die Pakete wiedergegeben, und die Quell-/Zieladressen werden in die neuen gewünschten IPv4-Adressen umgewandelt.

Hinweis: Zur Implementierung dieser Funktion muss auf Ihrem Router mindestens eine Network-Advantage-Lizenz installiert sein, da andernfalls ein Fehler bei der Konfiguration der VIF-Schnittstelle auftritt.
Topologie
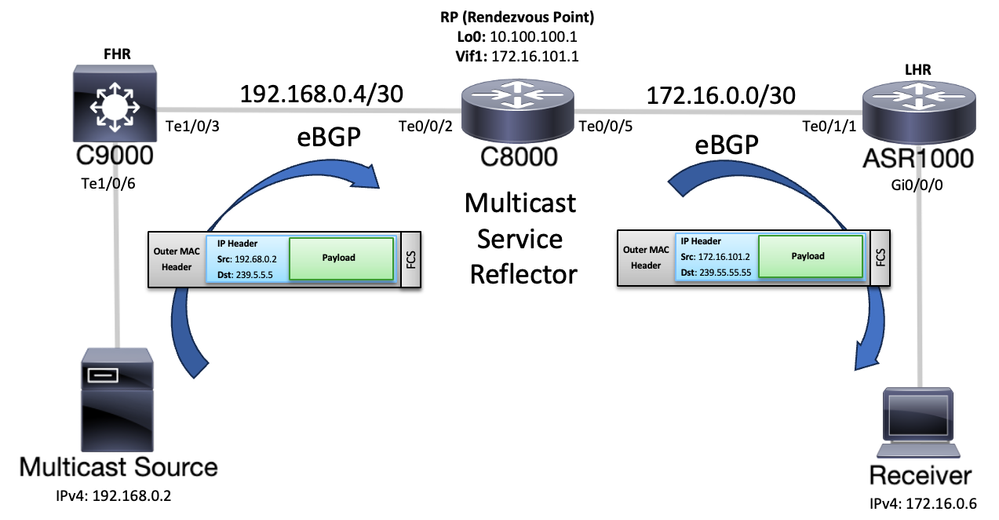 Topologiediagramm
Topologiediagramm
Konfiguration
Um die Funktion in dieser Konfiguration zu konfigurieren, muss Multicast-Routing über den Pfad aktiviert werden. Außerdem ist eine grundlegende IPv4-Verbindung zwischen der Multicast-Quelle und dem Empfänger erforderlich. In diesem Szenario gibt es einen Catalyst 9000-Switch (C9000), der als First Hop Router (FHR) fungiert, dann den Catalyst 8000-Router (C8000), der den Multicast Service Reflector darstellt, sowie den Rendezvous Point (RP) für die verschiedenen Multicast-Gruppen und einen ASR1K-Router (ASR10100000000 00) der Last Hop Router (LHR) ist, an den der Receiver angeschlossen ist. In diesem Beispiel wird das externe Border Gateway Protocol (eBGP) verwendet, um diese Geräte miteinander zu verbinden. Die Implementierung eines bestimmten Routing-Protokolls ist jedoch nicht erforderlich.

Hinweis: In diesem Beispiel wird nur ein RP für die verschiedenen Multicast-Streams verwendet. Weitere Informationen zu Szenarien, in denen unterschiedliche RPs für die Multicast-Domänen verwendet werden, finden Sie im Abschnitt Konfigurationsbeispiele für Multicast-Service-Reflektion aus dem IP Multicast Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE 17.x.
FHR (C900)
Aktivieren Sie zum Starten der Konfiguration im FHR das Multicast-Routing, fügen Sie die RP-IPv4-Adresse hinzu, und konfigurieren Sie Protocol Independent Multicast Sparse Mode (PIM-SM) auf Schnittstellen, die mit der Multicast-Quelle und dem Multicast Service Reflector-Router (C8000) verbunden sind.
C9000#show run | i multicast|rp-address ip multicast-routing class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast-end-station class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast ip pim rp-address 10.100.100.1
C9000#show run interface Ten 1/0/6 Building configuration... Current configuration : 116 bytes ! interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0/6 no switchport ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.252 ip pim sparse-mode end C9000#show run interface Ten 1/0/3 Building configuration... Current configuration : 116 bytes ! interface TenGigabitEthernet1/0/3 no switchport ip address 192.168.0.5 255.255.255.252 ip pim sparse-mode endDer C9000-Switch richtet eine eBGP-Adjacency an den C8000-Router aus, um die verbundenen Routen anzukündigen.
C9000#show run | section router bgp
router bgp 65003
bgp log-neighbor-changes
redistribute connected
neighbor 192.168.0.6 remote-as 65001Multicast Service Reflector Router (C8000)
Fügen Sie auf dem Catalyst 8K-Router für die Erstkonfiguration zur Aktivierung von Multicast-Routing die entsprechende RP-IPv4-Adresse hinzu, und konfigurieren Sie außerdem PIM-SM auf den mit C9000- und ASR1000-Geräten verbundenen Schnittstellen sowie in der Loopback0-Schnittstelle.
Mcast_SR#show run | i multicast|rp-address ip multicast-routing distributed ip pim rp-address 10.100.100.1
Mcast_SR#show run interface Ten 0/0/2 Building configuration... Current configuration : 156 bytes ! interface TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 description to C9000 ip address 192.168.0.6 255.255.255.252 ip pim sparse-mode no negotiation auto cdp enable end Mcast_SR#show run interface Ten 0/0/5 Building configuration... Current configuration : 157 bytes ! interface TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5 description to ASR1000 ip address 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.252 ip pim sparse-mode no negotiation auto cdp enable endMcast_SR#show run interface loopback 0 Building configuration... Current configuration : 88 bytes ! interface Loopback0 ip address 10.100.100.1 255.255.255.255 ip pim sparse-mode end
Dieser Router hat zwei eBGP-Nachbarn. Der Nachbar 192.168.0.5 ist der C9000-Switch, der die Präfixe sendet, um die Multicast-Quelle zu erreichen, und der zweite Nachbar ist der ASR1000-Router, der zum Erreichen des Empfängers verwendet wird. Beachten Sie, dass dieser Router sein lokales Loopback0 ankündigt und auch das Vif-Subnetz ankündigt.
Mcast_SR#show run | section router bgp router bgp 65001 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 10.100.100.1 mask 255.255.255.255 network 172.16.101.0 mask 255.255.255.252 neighbor 172.16.0.2 remote-as 65002 neighbor 192.168.0.5 remote-as 65003
Nun ist es an der Zeit, die Vif-Schnittstelle zu konfigurieren. Diese hilft, die Multicast-Gruppe von 239.5.5.5 in 239.55.55.55 zu übersetzen. Diese logische Schnittstelle muss über eine IP-Adresse verfügen, und dieses Subnetz muss routingfähig sein. Außerdem muss PIM-SM konfiguriert werden. Zum Aktivieren der Multicast Service Reflection-Funktion wird der Befehl ip service mirror <interface_id> destination <destination_ip1> to <destination_ip2> mask-len <subnet_mask_length> source <source_ip> verwendet, wobei interface_id die Schnittstelle ist, die den ursprünglichen Multicast-Datenverkehr empfängt, destination_ip1 die Die IPv4-Adresse, die umgewandelt werden muss (239.5.5.5), und destination_ip2 ist die neue IPv4-Adresse, die nach der Umwandlung erwartet wird (239.55.55.55). Last but not least ist der Befehl ip igmp static-group <group-address> erforderlich, um diese Schnittstelle zu einem statisch verbundenen Mitglied der ursprünglichen Multicast-Gruppe zu machen.
Mcast_SR#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Mcast_SR(config)#interface Vif1
Mcast_SR(config-if)#ip address 172.16.101.1 255.255.255.252
Mcast_SR(config-if)#ip pim sparse-mode
Mcast_SR(config-if)#ip service reflect TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 destination 239.5.5.5 to 239.55.55.55 mask-len 32 source 172.16.101.2
Mcast_SR(config-if)#ip igmp static-group 239.5.5.5
Mcast_SR(config-if)#end
Hinweis: Die Schnittstelle "Vif1" ist eng mit dem standardmäßigen Virtual Route Forwarding (VRF) für die Multicast Service Reflection-Funktion verknüpft. Wenn eine andere Nummer für diese Schnittstelle ausgewählt wird, kann in der Konsole eine Meldung angezeigt werden, die der Meldung ähnelt: "Nur Vif1 kann für Service Reflect in der globalen Tabelle verwendet werden."
Die nächste Ausgabe zeigt die Vif-Schnittstelle, nachdem die Konfiguration angewendet wurde. Beachten Sie, dass der Schnittstellenbetrieb auf "UP/UP" gesetzt wird und die Ausgabefunktion "SERVICE REFLECT" lautet, und zwar mithilfe des Befehls show ip interface <Schnittstelle>:
Mcast_SR#show run interface Vif1 Building configuration... Current configuration : 229 bytes ! interface Vif1 ip address 172.16.101.1 255.255.255.252 ip pim sparse-mode ip service reflect TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 destination 239.5.5.5 to 239.55.55.55 mask-len 32 source 172.16.101.2 ip igmp static-group 239.5.5.5 endMcast_SR#show ip interface vif1 Vif1 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is 172.16.101.1/30 Broadcast address is 255.255.255.255 Address determined by non-volatile memory MTU is 1514 bytes Helper address is not set Directed broadcast forwarding is disabled Multicast reserved groups joined: 224.0.0.1 224.0.0.2 224.0.0.22 224.0.0.13 Outgoing Common access list is not set Outgoing access list is not set Inbound Common access list is not set Inbound access list is not set Proxy ARP is enabled Local Proxy ARP is disabled Security level is default Split horizon is enabled ICMP redirects are always sent ICMP unreachables are always sent ICMP mask replies are never sent IP fast switching is enabled IP Flow switching is disabled IP CEF switching is enabled IP CEF switching turbo vector IP Null turbo vector Associated unicast routing topologies: Topology "base", operation state is UP Associated multicast routing topologies: Topology "base", operation state is UP IP multicast fast switching is enabled IP multicast distributed fast switching is disabled IP route-cache flags are Fast, CEF Router Discovery is disabled IP output packet accounting is disabled IP access violation accounting is disabled TCP/IP header compression is disabled RTP/IP header compression is disabled Probe proxy name replies are disabled Policy routing is disabled Network address translation is disabled BGP Policy Mapping is disabled Input features: MCI Check Output features: SERVICE REFLECT IPv4 WCCP Redirect outbound is disabled IPv4 WCCP Redirect inbound is disabled IPv4 WCCP Redirect exclude is disabled IP Clear Dont Fragment is disabled
LHR (ASR 1000)
Aktivieren Sie auf die gleiche Weise für die Konfiguration im LHR Multicast-Routing und PIM-SM an den Schnittstellen, die mit dem Multicast Service Reflector-Router und zum Receiver verbunden sind, und stellen Sie außerdem sicher, dass die IPv4-Adresse des RP konfiguriert ist:
ASR1000#show run | i multicast|rp-address ip multicast-routing distributed ip pim rp-address 10.100.100.1
ASR1000#show run interface Ten 0/1/1 Building configuration... Current configuration : 133 bytes ! interface TenGigabitEthernet0/1/1 ip address 172.16.0.2 255.255.255.252 ip pim sparse-mode no negotiation auto cdp enable end ASR1000#show run interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 Building configuration... Current configuration : 127 bytes ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 172.16.0.5 255.255.255.252 ip pim sparse-mode negotiation auto cdp enable end
Für die IP-Verbindung verwendet dieser Router außerdem BGP, um die verbundenen Präfixe auszutauschen:
ASR1000#show run | section router bgp
router bgp 65002
bgp log-neighbor-changes
redistribute connected
neighbor 172.16.0.1 remote-as 65001Anfängliche Überprüfung
Zunächst können Sie die grundlegende IP-Verbindung, den Routenaustausch zwischen Geräten und den PIM-Status überprüfen. Die nächste Ausgabe stammt aus dem Catalyst 9K und zeigt die Routen, die zum Receiver (172.16.0.6), RP Loopback0 (10.100.100.1) und Vif (172.16.101.1) installiert wurden. Es ist auch ersichtlich, dass eine PIM-Adjacency zum C8000-Router besteht und dass die RP-Zuordnung ebenfalls auf die Adresse 10.100.100.1 verweist.
C9000#show ip route 172.16.0.6 Routing entry for 172.16.0.4/30 Known via "bgp 65003", distance 20, metric 0 Tag 65001, type external Last update from 192.168.0.6 2d22h ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 192.168.0.6, from 192.168.0.6, 2d22h ago opaque_ptr 0x7FD797D4BA18 Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1 AS Hops 2 Route tag 65001 MPLS label: none C9000#ping 172.16.0.6 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.0.6, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms C9000#show ip route 10.100.100.1 Routing entry for 10.100.100.1/32 Known via "bgp 65003", distance 20, metric 0 Tag 65001, type external Last update from 192.168.0.6 2d22h ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 192.168.0.6, from 192.168.0.6, 2d22h ago opaque_ptr 0x7FD797D4B8D8 Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1 AS Hops 1 Route tag 65001 MPLS label: none C9000#ping 10.100.100.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.100.100.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms C9000#show ip route 172.16.101.1 Routing entry for 172.16.101.0/30 Known via "bgp 65003", distance 20, metric 0 Tag 65001, type external Last update from 192.168.0.6 2d00h ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 192.168.0.6, from 192.168.0.6, 2d00h ago opaque_ptr 0x7FD797D4B8D8 Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1 AS Hops 1 Route tag 65001 MPLS label: none C9000#ping 172.16.101.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.101.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms C9000#show ip pim neighbor PIM Neighbor Table Mode: B - Bidir Capable, DR - Designated Router, N - Default DR Priority, P - Proxy Capable, S - State Refresh Capable, G - GenID Capable, L - DR Load-balancing Capable Neighbor Interface Uptime/Expires Ver DR Address Prio/Mode 192.168.0.6 TenGigabitEthernet1/0/3 2d22h/00:01:29 v2 1 / DR S P G C9000#show ip pim interface Address Interface Ver/ Nbr Query DR DR Mode Count Intvl Prior 192.168.0.5 TenGigabitEthernet1/0/3 v2/S 1 30 1 192.168.0.6 192.168.0.1 TenGigabitEthernet1/0/6 v2/S 0 30 1 192.168.0.1C9000#show ip pim rp mapping PIM Group-to-RP Mappings Group(s): 224.0.0.0/4, Static RP: 10.100.100.1 (?)
Der Multicast Service Reflector zeigt die beiden Adressen 172.16.101.1 (Vif) und 10.100.100.1 (Loopback0) als direkt verbunden an und leitet sie über BGP an die Quelle und den Empfänger weiter:
Mcast_SR#show ip route 10.100.100.1 Routing entry for 10.100.100.1/32 Known via "connected", distance 0, metric 0 (connected, via interface) Advertised by bgp 65001 Routing Descriptor Blocks: * directly connected, via Loopback0 Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
Mcast_SR#show ip route 172.16.101.1 Routing entry for 172.16.101.1/32 Known via "connected", distance 0, metric 0 (connected) Routing Descriptor Blocks: * directly connected, via Vif1 Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1Mcast_SR#show ip route 172.16.0.6 Routing entry for 172.16.0.4/30 Known via "bgp 65001", distance 20, metric 0 Tag 65002, type external Last update from 172.16.0.2 5d20h ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 172.16.0.2, from 172.16.0.2, 5d20h ago opaque_ptr 0x7F841CBD53D0 Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1 AS Hops 1 Route tag 65002 MPLS label: none
Mcast_SR#show ip route 192.168.0.2 Routing entry for 192.168.0.0/30 Known via "bgp 65001", distance 20, metric 0 Tag 65003, type external Last update from 192.168.0.5 5d20h ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 192.168.0.5, from 192.168.0.5, 5d20h ago opaque_ptr 0x7F841CBD5290 Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1 AS Hops 1 Route tag 65003 MPLS label: none
Router C8000 zeigt auch zwei PIM-Nachbarn mit vier Schnittstellen an, die mit PIM-SM aktiviert wurden (einschließlich Vif und Loopback0). Die richtige RP-Zuordnung wird ebenfalls angezeigt, und mit dem Befehl show ip multicast können Sie die Multicast Service Reflect-Funktionen des Geräts überprüfen:
Mcast_SR#show ip pim neighbor PIM Neighbor Table Mode: B - Bidir Capable, DR - Designated Router, N - Default DR Priority, P - Proxy Capable, S - State Refresh Capable, G - GenID Capable, L - DR Load-balancing Capable Neighbor Interface Uptime/Expires Ver DR Address Prio/Mode 192.168.0.5 TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 5d20h/00:01:34 v2 1 / S P G 172.16.0.2 TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5 5d20h/00:01:15 v2 1 / DR S P G Mcast_SR#show ip pim interface Address Interface Ver/ Nbr Query DR DR Mode Count Intvl Prior 10.100.100.1 Loopback0 v2/S 0 30 1 10.100.100.1 192.168.0.6 TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 v2/S 1 30 1 192.168.0.6 172.16.0.1 TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5 v2/S 1 30 1 172.16.0.2 172.16.101.1 Vif1 v2/S 0 30 1 0.0.0.0 Mcast_SR#show ip pim rp mapping PIM Group-to-RP Mappings Group(s): 224.0.0.0/4, Static RP: 10.100.100.1 (?)Mcast_SR#show ip multicast Multicast Routing: enabled Multicast Multipath: disabled Multicast Route limit: No limit Multicast Fallback group mode: Sparse Number of multicast boundaries configured with filter-autorp option: 0 MoFRR: Disabled Multicast Service-Reflect Capabilities: Multicast to Multicast Unicast to Multicast Multicast to Unicast
Beim LHR sind ähnliche Überprüfungen abgeschlossen. Die nächste Ausgabe des ASR1000 Routers zeigt die Routen, die für die umgewandelte Multicast-Quelle 172.16.101.2 installiert wurden (dies ist wichtig zu beachten, da das Multicast-Stream-Paket zu diesem Zeitpunkt mit einem neuen Quell- und Ziel-IPv4-Header empfangen wird), sowie die RP IPv4-Adresse 10.10000.100.100 1. Beachten Sie, dass LHR auch mit der ursprünglichen Multicast-Quelle 192.168.0.2 erreichbar ist. An dieser Stelle in der Topologie ist es jedoch wichtiger, mit dem Vif-Subnetz (172.16.101.0/30) erreichbar zu sein:
ASR1000#show ip route 10.100.100.1 Routing entry for 10.100.100.1/32 Known via "bgp 65002", distance 20, metric 0 Tag 65001, type external Last update from 172.16.0.1 2d22h ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 172.16.0.1, from 172.16.0.1, 2d22h ago opaque_ptr 0x7F2BFA855B80 Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1 AS Hops 1 Route tag 65001 MPLS label: none ASR1000#ping 10.100.100.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.100.100.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms ASR1000#show ip route 172.16.101.1 Routing entry for 172.16.101.0/30 Known via "bgp 65002", distance 20, metric 0 Tag 65001, type external Last update from 172.16.0.1 2d00h ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 172.16.0.1, from 172.16.0.1, 2d00h ago opaque_ptr 0x7F2BFA855B80 Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1 AS Hops 1 Route tag 65001 MPLS label: none ASR1000#ping 172.16.101.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.101.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms ASR1000#show ip pim neighbor PIM Neighbor Table Mode: B - Bidir Capable, DR - Designated Router, N - Default DR Priority, P - Proxy Capable, S - State Refresh Capable, G - GenID Capable, L - DR Load-balancing Capable Neighbor Interface Uptime/Expires Ver DR Address Prio/Mode 172.16.0.1 TenGigabitEthernet0/1/1 2d22h/00:01:24 v2 1 / S P G ASR1000#show ip pim interface Address Interface Ver/ Nbr Query DR DR Mode Count Intvl Prior 172.16.0.5 GigabitEthernet0/0/0 v2/S 0 30 1 172.16.0.5 172.16.0.2 TenGigabitEthernet0/1/1 v2/S 1 30 1 172.16.0.2ASR1000#show ip route 192.168.0.2 Routing entry for 192.168.0.0/30 Known via "bgp 65002", distance 20, metric 0 Tag 65001, type external Last update from 172.16.0.1 5d21h ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 172.16.0.1, from 172.16.0.1, 5d21h ago opaque_ptr 0x7F2BFA855E00 Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1 AS Hops 2 Route tag 65001 MPLS label: none ASR1000#ping 192.168.0.2 source 172.16.0.5 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.0.2, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 172.16.0.5 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
Fehlerbehebung
Nachdem die Multicast-Quelle mit dem Senden des Streams für die Gruppe 239.5.5.5 begonnen hat und gleichzeitig debug ip pim auf den verschiedenen Geräten in der Topologie aktiviert wurde, kann bestätigt werden, dass der FHR die Multicast-Quelle 192.168.0.2 beim RP registriert und die Schnittstelle TenGigabitEthernet1/0/3 der Ausgangs- going Interface List (OIL)
C9000#
*Oct 16 16:23:01.817: PIM(0)[default]: Re-check RP 10.100.100.1 into the (*, 239.5.5.5) entry
*Oct 16 16:23:01.817: PIM(0)[default]: Building Triggered (*,G) Join / (S,G,RP-bit) Prune message for 239.5.5.5
*Oct 16 16:23:01.817: PIM(0)[default]: Adding register encap tunnel (Tunnel0) as forwarding interface of (192.168.0.2, 239.5.5.5).
*Oct 16 16:23:01.839: PIM(0)[default]: Received v2 Join/Prune on TenGigabitEthernet1/0/3 from 192.168.0.6, to us
*Oct 16 16:23:01.839: PIM(0)[default]: Join-list: (192.168.0.2/32, 239.5.5.5), S-bit set
*Oct 16 16:23:01.839: PIM(0)[default]: MIDB Add TenGigabitEthernet1/0/3/192.168.0.6 to (192.168.0.2, 239.5.5.5), Forward state, by PIM SG Join
*Oct 16 16:23:01.839: PIM(0)[default]: Join to 0.0.0.0 on TenGigabitEthernet1/0/6 for (192.168.0.2, 239.5.5.5), Ignored.
*Oct 16 16:23:03.869: PIM(0)[default]: Received v2 Join/Prune on TenGigabitEthernet1/0/3 from 192.168.0.6, to us
*Oct 16 16:23:03.869: PIM(0)[default]: Join-list: (192.168.0.2/32, 239.5.5.5), S-bit set
*Oct 16 16:23:03.869: PIM(0)[default]: MIDB Update TenGigabitEthernet1/0/3/192.168.0.6 to (192.168.0.2, 239.5.5.5), Forward state, by PIM SG Join
*Oct 16 16:23:05.818: PIM(0)[default]: Received v2 Register-Stop on TenGigabitEthernet1/0/3 from 10.100.100.1 *Oct 16 16:23:05.818: PIM(0)[default]: for source 192.168.0.2, group 239.5.5.5
*Oct 16 16:23:05.818: PIM(0)[default]: Removing register encap tunnel (Tunnel0) as forwarding interface of (192.168.0.2, 239.5.5.5).
*Oct 16 16:23:05.818: PIM(0)[default]: Clear Registering flag to 10.100.100.1 for (192.168.0.2/32, 239.5.5.5)
*Oct 16 16:23:11.997: PIM(0)[default]: Send v2 join/prune to 192.168.0.6 (TenGigabitEthernet1/0/3)
C9000#show ip mroute 239.5.5.5 IP Multicast Routing Table Flags: D - Dense, S - Sparse, B - Bidir Group, s - SSM Group, C - Connected, L - Local, P - Pruned, R - RP-bit set, F - Register flag, T - SPT-bit set, J - Join SPT, M - MSDP created entry, E - Extranet, X - Proxy Join Timer Running, A - Candidate for MSDP Advertisement, U - URD, I - Received Source Specific Host Report, Z - Multicast Tunnel, z - MDT-data group sender, Y - Joined MDT-data group, y - Sending to MDT-data group, G - Received BGP C-Mroute, g - Sent BGP C-Mroute, N - Received BGP Shared-Tree Prune, n - BGP C-Mroute suppressed, Q - Received BGP S-A Route, q - Sent BGP S-A Route, V - RD & Vector, v - Vector, p - PIM Joins on route, x - VxLAN group, c - PFP-SA cache created entry, * - determined by Assert, # - iif-starg configured on rpf intf, e - encap-helper tunnel flag, l - LISP decap ref count contributor Outgoing interface flags: H - Hardware switched, A - Assert winner, p - PIM Join t - LISP transit group Timers: Uptime/Expires Interface state: Interface, Next-Hop or VCD, State/Mode (*, 239.5.5.5), 00:24:22/stopped, RP 10.100.100.1, flags: SPF Incoming interface: TenGigabitEthernet1/0/3, RPF nbr 192.168.0.6 Outgoing interface list: Null (192.168.0.2, 239.5.5.5), 00:24:22/00:03:11, flags: FT Incoming interface: TenGigabitEthernet1/0/6, RPF nbr 0.0.0.0 Outgoing interface list: TenGigabitEthernet1/0/3, Forward/Sparse, 00:24:22/00:02:47, flags: Gleichzeitig erhält der Multicast Service Reflector-Router (d. h. der RP für beide Gruppen) die Registrierung für S,G (192.168.0.2, 239.5.5.5) und erkennt sofort, dass diese Gruppe unter die zuvor definierte Reflexionsregel fällt. Anschließend wird das TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 als eingehende Schnittstelle für den 239.5.5.5-Stream hinzugefügt, und später wird das neue S,G (172.16.101.2, 239.55.55.55) registriert. Der Router fügt Vif1 als eingehende Schnittstelle für den Datenstrom 239.55.55.55 hinzu und platziert TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5 (Verbindung mit ASR1000) im OIL, wie im Debugging und der Ausgabe des Befehls show ip mroute dargestellt:
Mcast_SR#
*Oct 16 15:46:11.758: PIM(0)[default]: Received v2 Register on TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 from 192.168.0.5 *Oct 16 15:46:11.758: for 192.168.0.2, group 239.5.5.5
*Oct 16 15:46:11.758: PIM(0)[default]: Adding register decap tunnel (Tunnel1) as accepting interface of (192.168.0.2, 239.5.5.5). *Oct 16 15:46:11.758: MSR(0)[default]: Add 239.5.5.5 to all the SR rules *Oct 16 15:46:11.758: MSR: Found Grp idx 553648130 for rule 239.5.5.5->239.55.55.55 *Oct 16 15:46:11.758: MSR: Found Grp idx 553648130 for rule 239.5.5.5->239.55.55.55
*Oct 16 15:46:11.758: PIM(0)[default]: Insert (192.168.0.2,239.5.5.5) join in nbr 192.168.0.5's queue
*Oct 16 15:46:11.758: PIM(0)[default]: Building Join/Prune packet for nbr 192.168.0.5
*Oct 16 15:46:11.758: PIM(0)[default]: Adding v2 (192.168.0.2/32, 239.5.5.5), S-bit Join
*Oct 16 15:46:11.758: PIM(0)[default]: Send v2 join/prune to 192.168.0.5 (TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2)
*Oct 16 15:46:12.929: PIM(0)[default]: Building Periodic (*,G) Join / (S,G,RP-bit) Prune message for 239.55.55.55
*Oct 16 15:46:12.929: PIM(0)[default]: rp our address for group 239.55.55.55
*Oct 16 15:46:13.251: PIM(0)[default]: Received v2 Join/Prune on TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5 from 172.16.0.2, to us
*Oct 16 15:46:13.251: PIM(0)[default]: Join-list: (*, 239.55.55.55), RPT-bit set, WC-bit set, S-bit set
*Oct 16 15:46:13.252: PIM(0)[default]: MIDB Update TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5/172.16.0.2 to (*, 239.55.55.55), Forward state, by PIM *G Join
*Oct 16 15:46:13.732: PIM(0)[default]: Received v2 Register on TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 from 192.168.0.5
*Oct 16 15:46:13.732: for 192.168.0.2, group 239.5.5.5
*Oct 16 15:46:13.732: PIM(0)[default]: Removing register decap tunnel (Tunnel1) as accepting interface of (192.168.0.2, 239.5.5.5).
*Oct 16 15:46:13.732: PIM(0)[default]: Installing TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 as accepting interface for (192.168.0.2, 239.5.5.5).
*Oct 16 15:46:13.732: PIM(0)[default]: Prune to 0.0.0.0 on for (192.168.0.2, 239.5.5.5), Ignored.
*Oct 16 15:46:13.773: PIM(0)[default]: Adding register decap tunnel (Tunnel1) as accepting interface of (172.16.101.2, 239.55.55.55). *Oct 16 15:46:13.773: PIM(0)[default]: Adding register encap tunnel (Tunnel0) as forwarding interface of (172.16.101.2, 239.55.55.55).
*Oct 16 15:46:13.773: PIM(0)[default]: Removing register decap tunnel (Tunnel1) as accepting interface of (172.16.101.2, 239.55.55.55).
*Oct 16 15:46:13.773: PIM(0)[default]: Installing Vif1 as accepting interface for (172.16.101.2, 239.55.55.55).
*Oct 16 15:46:13.788: PIM(0)[default]: Insert (192.168.0.2,239.5.5.5) join in nbr 192.168.0.5's queue
*Oct 16 15:46:13.788: PIM(0)[default]: Building Join/Prune packet for nbr 192.168.0.5
*Oct 16 15:46:13.788: PIM(0)[default]: Adding v2 (192.168.0.2/32, 239.5.5.5), S-bit Join
*Oct 16 15:46:13.788: PIM(0)[default]: Send v2 join/prune to 192.168.0.5 (TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2)
*Oct 16 15:46:13.794: PIM(0)[default]: Received v2 Register on Vif1 from 10.100.100.1
*Oct 16 15:46:13.794: for 172.16.101.2, group 239.55.55.55
*Oct 16 15:46:13.794: PIM(0)[default]: Send v2 Register-Stop to 10.100.100.1 for 172.16.101.2, group 239.55.55.55
*Oct 16 15:46:13.794: PIM(0)[default]: Received v2 Register-Stop on Loopback0 from 10.100.100.1
*Oct 16 15:46:13.794: PIM(0)[default]: for source 172.16.101.2, group 239.55.55.55
*Oct 16 15:46:13.794: PIM(0)[default]: Removing register encap tunnel (Tunnel0) as forwarding interface of (172.16.101.2, 239.55.55.55).
*Oct 16 15:46:13.794: PIM(0)[default]: Clear Registering flag to 10.100.100.1 for (172.16.101.2/32, 239.55.55.55)
*Oct 16 15:46:13.809: PIM(0)[default]: Received v2 Join/Prune on TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5 from 172.16.0.2, to us
*Oct 16 15:46:13.809: PIM(0)[default]: Join-list: (172.16.101.2/32, 239.55.55.55), S-bit set
*Oct 16 15:46:13.809: PIM(0)[default]: MIDB Update TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5/172.16.0.2 to (172.16.101.2, 239.55.55.55), Forward state, by PIM SG Join
Mcast_SR#show ip mroute IP Multicast Routing Table Flags: D - Dense, S - Sparse, B - Bidir Group, s - SSM Group, C - Connected, L - Local, P - Pruned, R - RP-bit set, F - Register flag, T - SPT-bit set, J - Join SPT, M - MSDP created entry, E - Extranet, X - Proxy Join Timer Running, A - Candidate for MSDP Advertisement, U - URD, I - Received Source Specific Host Report, Z - Multicast Tunnel, z - MDT-data group sender, Y - Joined MDT-data group, y - Sending to MDT-data group, G - Received BGP C-Mroute, g - Sent BGP C-Mroute, N - Received BGP Shared-Tree Prune, n - BGP C-Mroute suppressed, Q - Received BGP S-A Route, q - Sent BGP S-A Route, V - RD & Vector, v - Vector, p - PIM Joins on route, x - VxLAN group, c - PFP-SA cache created entry, * - determined by Assert, # - iif-starg configured on rpf intf, e - encap-helper tunnel flag, l - LISP decap ref count contributor Outgoing interface flags: H - Hardware switched, A - Assert winner, p - PIM Join t - LISP transit group Timers: Uptime/Expires Interface state: Interface, Next-Hop or VCD, State/Mode (*, 239.5.5.5), 00:50:36/stopped, RP 10.100.100.1, flags: SJC Incoming interface: Null, RPF nbr 0.0.0.0 Outgoing interface list: Vif1, Forward/Sparse, 00:50:36/00:00:23, flags: (192.168.0.2, 239.5.5.5), 00:10:08/00:02:36, flags: T Incoming interface: TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2, RPF nbr 192.168.0.5 Outgoing interface list: Vif1, Forward/Sparse, 00:10:08/00:01:51, flags: (*, 239.55.55.55), 00:50:21/00:03:11, RP 10.100.100.1, flags: SF Incoming interface: Null, RPF nbr 0.0.0.0 Outgoing interface list: TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5, Forward/Sparse, 00:50:21/00:03:11, flags: (172.16.101.2, 239.55.55.55), 00:10:06/00:03:23, flags: FT Incoming interface: Vif1, RPF nbr 0.0.0.0 Outgoing interface list: TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5, Forward/Sparse, 00:10:06/00:03:16, flags: (*, 224.0.1.40), 00:50:36/00:03:28, RP 10.100.100.1, flags: SJCL Incoming interface: Null, RPF nbr 0.0.0.0 Outgoing interface list: TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2, Forward/Sparse, 00:50:13/00:03:28, flags: TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5, Forward/Sparse, 00:50:28/00:03:10, flags: Loopback0, Forward/Sparse, 00:50:36/00:02:17, flags: 
Hinweis: Beachten Sie, dass debug ip multicast service-mirror aktiviert werden muss, um die in der Debugausgabe verwendeten Multicast Service Reflection-Regeln beobachten zu können. Beachten Sie, dass dieses spezielle Debugging in Version 17.9.1a von Cisco IOS-XE eingeführt wurde. Weitere Informationen finden Sie im Abschnitt Feature Information for Multicast Service Reflection im IP Multicast Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE 17.x.
Aus der vorherigen Ausgabe von show ip mroute geht hervor, dass es *,G- und S,G-Einträge für die ursprüngliche und die neue Multicast-Gruppe gibt. Zusätzlich kann die Verwendung des Befehls show ip mroute <group> count einen Eindruck von den Paketen geben, die für jeden Multicast-Stream empfangen und weitergeleitet werden. Diese Ausgabe ist ebenfalls nützlich, da sie dazu beiträgt, die Weiterleitung des Datenverkehrs durch die Bestätigung der inkrementierenden Zähler zu identifizieren:
Mcast_SR#show ip mroute 239.5.5.5 count
Use "show ip mfib count" to get better response time for a large number of mroutes.
IP Multicast Statistics
5 routes using 5796 bytes of memory
3 groups, 0.66 average sources per group
Forwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kilobits per second
Other counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops(OIF-null, rate-limit etc)
Group: 239.5.5.5, Source count: 1, Packets forwarded: 4053, Packets received: 4056
RP-tree: Forwarding: 11/0/100/0, Other: 12/1/0
Source: 192.168.0.2/32, Forwarding: 4042/0/113/0, Other: 4044/2/0
Mcast_SR#show ip mroute 239.5.5.5 count
Use "show ip mfib count" to get better response time for a large number of mroutes.
IP Multicast Statistics
5 routes using 5796 bytes of memory
3 groups, 0.66 average sources per group
Forwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kilobits per second
Other counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops(OIF-null, rate-limit etc)
Group: 239.5.5.5, Source count: 1, Packets forwarded: 4058, Packets received: 4061
RP-tree: Forwarding: 11/0/100/0, Other: 12/1/0
Source: 192.168.0.2/32, Forwarding: 4047/0/113/0, Other: 4049/2/0
Mcast_SR#show ip mroute 239.55.55.55 count
Use "show ip mfib count" to get better response time for a large number of mroutes.
IP Multicast Statistics
5 routes using 5796 bytes of memory
3 groups, 0.66 average sources per group
Forwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kilobits per second
Other counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops(OIF-null, rate-limit etc)
Group: 239.55.55.55, Source count: 1, Packets forwarded: 4046, Packets received: 4046
RP-tree: Forwarding: 0/0/0/0, Other: 0/0/0
Source: 172.16.101.2/32, Forwarding: 4046/0/114/0, Other: 4046/0/0
Mcast_SR#show ip mroute 239.55.55.55 count
Use "show ip mfib count" to get better response time for a large number of mroutes.
IP Multicast Statistics
5 routes using 5796 bytes of memory
3 groups, 0.66 average sources per group
Forwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kilobits per second
Other counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops(OIF-null, rate-limit etc)
Group: 239.55.55.55, Source count: 1, Packets forwarded: 4051, Packets received: 4051
RP-tree: Forwarding: 0/0/0/0, Other: 0/0/0
Source: 172.16.101.2/32, Forwarding: 4051/0/114/0, Other: 4051/0/0Wenn die S,G-Einträge nicht erstellt werden, muss festgestellt werden, ob die Multicast-Pakete an der erwarteten Schnittstelle empfangen werden. Eine Reihe von Optionen, um diese Situation zu bestätigen, sind Embedded Packet Capture (EPC) oder Packet Trace. In der nächsten Ausgabe wurde ein EPC in den eingehenden (Te0/0/2) und ausgehenden (Te0/0/5) Schnittstellen des C8000-Routers erstellt. In diesem Arbeitsszenario können Sie beobachten, wie der ursprüngliche Multicast-Stream 239.5.5.5 eingeht und der neue Stream 239.55.55.55 den Router verlässt:
Mcast_SR#monitor capture msr buffer size 10 match any interface tenGigabitEthernet 0/0/2 in
Mcast_SR#monitor capture msr start
Started capture point : msr
*Oct 16 17:59:06.986: %BUFCAP-6-ENABLE: Capture Point msr enabled.
Mcast_SR#monitor capture msr stop
Stopped capture point : msr
Mcast_SR#s
*Oct 16 17:59:25.699: %BUFCAP-6-DISABLE: Capture Point msr disabled
Mcast_SR#show monitor capture msr buffer brief
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# size timestamp source destination dscp protocol
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 114 0.000000 192.168.0.2 -> 239.5.5.5 0 BE ICMP
1 114 2.000000 192.168.0.2 -> 239.5.5.5 0 BE ICMP
2 68 2.979961 192.168.0.5 -> 224.0.0.13 48 CS6 PIM
3 114 4.000000 192.168.0.2 -> 239.5.5.5 0 BE ICMP
4 114 6.000000 192.168.0.2 -> 239.5.5.5 0 BE ICMP
5 114 8.000000 192.168.0.2 -> 239.5.5.5 0 BE ICMP
6 114 10.000000 192.168.0.2 -> 239.5.5.5 0 BE ICMP
7 114 12.000000 192.168.0.2 -> 239.5.5.5 0 BE ICMP
8 114 14.001007 192.168.0.2 -> 239.5.5.5 0 BE ICMP
9 114 16.001999 192.168.0.2 -> 239.5.5.5 0 BE ICMP
10 114 18.001007 192.168.0.2 -> 239.5.5.5 0 BE ICMP
Mcast_SR#monitor capture msr buffer size 10 match any interface tenGigabitEthernet0/0/5 out
Mcast_SR#monitor capture msr start
Started capture point : msr
*Oct 16 18:07:26.846: %BUFCAP-6-ENABLE: Capture Point msr enabled.
Mcast_SR#monitor capture msr stop
Stopped capture point : msr
*Oct 16 18:07:50.360: %BUFCAP-6-DISABLE: Capture Point msr disabled.
Mcast_SR#show monitor capture msr buffer brief
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# size timestamp source destination dscp protocol
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 73 0.000000 172.16.0.1 -> 172.16.0.2 48 CS6 TCP
1 114 0.172040 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP 2 114 2.173047 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
3 114 4.172040 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
4 114 6.173047 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
5 114 8.172040 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
6 114 10.172040 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
7 114 12.173047 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
8 114 14.175046 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
9 114 16.176038 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
10 114 18.176038 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
11 46 19.318029 172.16.0.1 -> 224.0.0.1 48 CS6 IGMP
12 114 20.177045 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
13 72 20.629017 172.16.0.1 -> 224.0.0.13 48 CS6 PIM
14 114 22.178037 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
15 430 23.273033 90:77:EE:3C:80:05 -> 01:00:0C:CC:CC:CC -- LLCAußerdem wurde ein Packet Trace mit erweiterter ACL-Filterung (Access Control List) auf dem 239.5.5.5 implementiert. Vom nächsten Ausgang aus ist zu beobachten, dass die Pakete an der Schnittstelle Te0/0/2 empfangen und zunächst intern verbraucht und kopiert werden, um später als Eingangspakete in die Vif1-Schnittstelle verwendet zu werden und dann über die Schnittstelle Te0/0/5 übersetzt weitergeleitet zu werden:
Mcast_SR#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Mcast_SR(config)#ip access-list extended original-mcast Mcast_SR(config-ext-nacl)#permit ip any host 239.5.5.5 Mcast_SR(config-ext-nacl)#end Mcast_SR# *Oct 16 18:31:49.187: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console Mcast_SR#debug platform packet-trace packet 16 Please remember to turn on 'debug platform condition start' for packet-trace to work Mcast_SR#debug platform condition ipv4 access-list original-mcast ingress Mcast_SR#debug platform condition start Mcast_SR#show platform packet-trace packet all Packet: 0 CBUG ID: 0 Summary Input : TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 Output :State : CONS Packet Consumed Silently Timestamp Start : 521286121898055 ns (10/16/2023 18:33:39.36879 UTC) Stop : 521286122522268 ns (10/16/2023 18:33:39.37503 UTC) Path Trace Feature: IPV4(Input) Input : TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 Output : Source : 192.168.0.2 Destination : 239.5.5.5 Protocol : 1 (ICMP) Packet: 1 CBUG ID: 0 Summary Input : TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 Output : State : CONS Packet Consumed Silently Timestamp Start : 521286121980895 ns (10/16/2023 18:33:39.36962 UTC) Stop : 521286122618968 ns (10/16/2023 18:33:39.37600 UTC) Path Trace Feature: PACKET_COPY Original packet number: 0 Feature: IPV4(Input) Input : TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 Output : Source : 192.168.0.2 Destination : 239.5.5.5 Protocol : 1 (ICMP) Packet: 2 CBUG ID: 0 Summary Input : Vif1 Output : TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5 State : FWD Timestamp Start : 521286122038938 ns (10/16/2023 18:33:39.37020 UTC) Stop : 521286122694795 ns (10/16/2023 18:33:39.37676 UTC) Path Trace Feature: PACKET_COPY Original packet number: 1 Feature: IPV4(Input) Input : Vif1 Output : Source : 172.16.101.2 Destination : 239.55.55.55 Protocol : 1 (ICMP)
Außerdem sollten die Multicast Routing Information Base (MRIB) und die Multicast Forwarding Information Base (MFIB) am Catalyst 8000 überprüft werden. Beachten Sie die Hardware-Installations- (HW)-Flags sowie die Zähler für die Hardware-Weiterleitung, die inkrementell ansteigen, wobei im Idealfall nur sehr wenige Fehler oder Auslassungen bei Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) auftreten. Beachten Sie auch das mit der Ausgangsschnittstelle (Te0/0/5) zum ASR1000-Router verbundene Vorwärts-Flag (F):
Mcast_SR#show ip mrib route IP Multicast Routing Information Base Entry flags: L - Domain-Local Source, E - External Source to the Domain, C - Directly-Connected Check, S - Signal, IA - Inherit Accept, D - Drop ET - Data Rate Exceeds Threshold,K - Keepalive,DDE - Data Driven Event ME - MoFRR ECMP Flow based, MNE - MoFRR Non-ECMP Flow based, MP - Primary MoFRR Non-ECMP Flow based entry, e - Encap helper tunnel flag Interface flags: F - Forward, A - Accept, IC - Internal Copy, NS - Negate Signal, DP - Don't Preserve, SP - Signal Present, II - Internal Interest, ID - Internal Disinterest, LI - Local Interest, LD - Local Disinterest, MD - mCAC Denied, MI - mLDP Interest A2 - MoFRR ECMP Backup Accept (*,224.0.0.0/4) Flags: C (*,224.0.1.40) RPF nbr: 0.0.0.0 Flags: C TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 Flags: F NS TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5 Flags: F NS Loopback0 Flags: F IC NS Tunnel1 Flags: A (*,239.5.5.5) RPF nbr: 0.0.0.0 Flags: C Vif1 Flags: F NS SR(172.16.101.2, 239.55.55.55) Index(2, 2) Tunnel1 Flags: A (*,239.55.55.55) RPF nbr: 0.0.0.0 Flags: C TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5 Flags: F NS Tunnel1 Flags: A (172.16.101.2,239.55.55.55) RPF nbr: 0.0.0.0 Flags: Vif1 Flags: A TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5 Flags: F NS (192.168.0.2,239.5.5.5) RPF nbr: 192.168.0.5 Flags: TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 Flags: A NS Vif1 Flags: F NS SR(172.16.101.2, 239.55.55.55) Index(2, 2) Mcast_SR#show ip mfib 192.168.0.2 239.5.5.5 Entry Flags: C - Directly Connected, S - Signal, IA - Inherit A flag, ET - Data Rate Exceeds Threshold, K - Keepalive DDE - Data Driven Event, HW - Hardware Installed ME - MoFRR ECMP entry, MNE - MoFRR Non-ECMP entry, MP - MFIB MoFRR Primary, RP - MRIB MoFRR Primary, P - MoFRR Primary MS - MoFRR Entry in Sync, MC - MoFRR entry in MoFRR Client, e - Encap helper tunnel flag. I/O Item Flags: IC - Internal Copy, NP - Not platform switched, NS - Negate Signalling, SP - Signal Present, A - Accept, F - Forward, RA - MRIB Accept, RF - MRIB Forward, MA - MFIB Accept, A2 - Accept backup, RA2 - MRIB Accept backup, MA2 - MFIB Accept backup Forwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kbits per second Other counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops I/O Item Counts: HW Pkt Count/FS Pkt Count/PS Pkt Count Egress Rate in pps Default (192.168.0.2,239.5.5.5) Flags: HW SW Forwarding: 1/0/100/0, Other: 0/0/0 HW Forwarding: 6530/0/114/0, Other: 2/2/0 TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2 Flags: A Vif1, SR/(172.16.101.2,239.55.55.55):553648130 Flags: F NS Pkts: 0/0/1 Rate: 0 pps Mcast_SR#show ip mfib 172.16.101.2 239.55.55.55 Entry Flags: C - Directly Connected, S - Signal, IA - Inherit A flag, ET - Data Rate Exceeds Threshold, K - Keepalive DDE - Data Driven Event, HW - Hardware Installed ME - MoFRR ECMP entry, MNE - MoFRR Non-ECMP entry, MP - MFIB MoFRR Primary, RP - MRIB MoFRR Primary, P - MoFRR Primary MS - MoFRR Entry in Sync, MC - MoFRR entry in MoFRR Client, e - Encap helper tunnel flag. I/O Item Flags: IC - Internal Copy, NP - Not platform switched, NS - Negate Signalling, SP - Signal Present, A - Accept, F - Forward, RA - MRIB Accept, RF - MRIB Forward, MA - MFIB Accept, A2 - Accept backup, RA2 - MRIB Accept backup, MA2 - MFIB Accept backup Forwarding Counts: Pkt Count/Pkts per second/Avg Pkt Size/Kbits per second Other counts: Total/RPF failed/Other drops I/O Item Counts: HW Pkt Count/FS Pkt Count/PS Pkt Count Egress Rate in pps Default (172.16.101.2,239.55.55.55) Flags: HW SW Forwarding: 0/0/0/0, Other: 0/0/0 HW Forwarding: 6550/0/114/0, Other: 0/0/0 Vif1 Flags: A TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5 Flags: F NS Pkts: 0/0/0 Rate: 0 pps Mcast_SR#show adjacency vif1 detail Protocol Interface Address IP Vif1 point2point(8) 13270 packets, 657502 bytes epoch 0 sourced in sev-epoch 0 empty encap string P2P-ADJMcast_SR#show platform software ip rp active mfib group 239.5.5.5/32 Route flags: S - Signal; C - Directly connected; IA - Inherit A Flag; L - Local; BR - Bidir route *, 239.5.5.5/32 --> OBJ_INTF_LIST (0x15) Obj id: 0x15, Flags: C OM handle: 0x3480200a50 Mcast_SR#show platform software ip rp active mfib group 239.55.55.55/32 Route flags: S - Signal; C - Directly connected; IA - Inherit A Flag; L - Local; BR - Bidir route *, 239.55.55.55/32 --> OBJ_INTF_LIST (0x36) Obj id: 0x36, Flags: C OM handle: 0x34801fa988 Mcast_SR#show platform software mlist rp active index 0x15 Multicast List entries OCE Flags: NS - Negate Signalling; IC - Internal copy; A - Accept; F - Forward; OCE Type OCE Flags Interface -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0xf8000029 OBJ_ADJACENCY NS, F Vif1 0xf8000186 OBJ_ADJACENCY A Tunnel1 Mcast_SR#show platform software mlist rp active index 0x36 Multicast List entries OCE Flags: NS - Negate Signalling; IC - Internal copy; A - Accept; F - Forward; OCE Type OCE Flags Interface -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0xf80000d1 OBJ_ADJACENCY NS, F TenGigabitEthernet0/0/5 0xf8000186 OBJ_ADJACENCY A Tunnel1
Für die RPF-Prüfung ist es wichtig, dies auf den verschiedenen Geräten im Multicast-Pfad zu überprüfen.
C9000#show ip rpf 192.168.0.2
RPF information for ? (192.168.0.2)
RPF interface: TenGigabitEthernet1/0/6
RPF neighbor: ? (192.168.0.2) - directly connected
RPF route/mask: 192.168.0.0/30
RPF type: multicast (connected)
Doing distance-preferred lookups across tables
RPF topology: ipv4 multicast base
Mcast_SR#show ip rpf 192.168.0.2
RPF information for ? (192.168.0.2)
RPF interface: TenGigabitEthernet0/0/2
RPF neighbor: ? (192.168.0.5)
RPF route/mask: 192.168.0.0/30
RPF type: unicast (bgp 65001)
Doing distance-preferred lookups across tables
RPF topology: ipv4 multicast base, originated from ipv4 unicast base
Mcast_SR#show ip rpf 172.16.101.2
RPF information for ? (172.16.101.2)
RPF interface: Vif1
RPF neighbor: ? (172.16.101.2) - directly connected
RPF route/mask: 172.16.101.0/30
RPF type: multicast (connected)
Doing distance-preferred lookups across tables
RPF topology: ipv4 multicast base
ASR1000#show ip rpf 172.16.101.2
RPF information for ? (172.16.101.2)
RPF interface: TenGigabitEthernet0/1/1
RPF neighbor: ? (172.16.0.1)
RPF route/mask: 172.16.101.0/30
RPF type: unicast (bgp 65002)
Doing distance-preferred lookups across tables
RPF topology: ipv4 multicast base, originated from ipv4 unicast baseSchließlich können Sie den am LHR empfangenen und weitergeleiteten Datenverkehr bestätigen. Die erste Erfassung zeigt, wie ASR1000 die Pakete vom neuen Stream (172.16.101.2, 239.55.55.55) empfangen hat, in den die IPv4-Adressen wie erwartet übertragen wurden. Die zweite Erfassung zeigt den Datenverkehr, der an den Receiver weitergeleitet wird.
ASR1000#monitor capture LHR buffer size 10 match any interface TenGigabitEthernet 0/1/1 in
ASR1000#monitor capture LHR start
Started capture point : LHR
*Oct 17 15:16:06.192: %BUFCAP-6-ENABLE: Capture Point LHR enabled.show moni
ASR1000#show monitor capture LHR buffer brief
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# size timestamp source destination dscp protocol
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 73 0.000000 172.16.0.1 -> 172.16.0.2 48 CS6 TCP
1 114 0.050992 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP 2 114 2.051984 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
3 54 2.896993 172.16.0.1 -> 172.16.0.2 48 CS6 TCP
4 114 4.051984 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
5 72 4.967989 172.16.0.1 -> 224.0.0.13 48 CS6 PIM
6 114 6.052991 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
7 114 8.053983 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
8 114 10.053983 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
9 114 12.053983 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
10 114 14.055997 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
11 114 16.056989 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
12 114 18.055997 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
ASR1000#monitor capture LHR stop
Stopped capture point : LHR
ASR1000#
*Oct 17 15:16:32.029: %BUFCAP-6-DISABLE: Capture Point LHR disabled.
ASR1000#monitor capture TO_RECEIVER buffer size 10 match any interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0 out
ASR1000#monitor capture TO_RECEIVER start
Started capture point : TO_RECEIVER
*Oct 17 15:19:00.309: %BUFCAP-6-ENABLE: Capture Point TO_RECEIVER enabled.ni
ASR1000#show monitor capture TO_RECEIVER buffer brief
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# size timestamp source destination dscp protocol
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 114 0.000000 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
1 46 0.276994 172.16.0.5 -> 224.0.0.1 48 CS6 IGMP
2 114 1.999009 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP 3 114 4.000000 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
4 46 5.550027 172.16.0.5 -> 224.0.1.40 48 CS6 IGMP
5 114 5.999009 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
6 114 8.000000 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
7 114 10.001007 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
8 114 12.001999 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
9 114 14.003006 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
10 114 16.003998 172.16.101.2 -> 239.55.55.55 0 BE ICMP
ASR1000#monitor capture TO_RECEIVER stop
Stopped capture point : TO_RECEIVER
*Oct 17 15:19:24.938: %BUFCAP-6-DISABLE: Capture Point TO_RECEIVER disabled. Wenn die *,G irgendwann fehlen, können Sie den IGMP-Status (Internet Group Management Protocol) mit den Befehlen show ip igmp mitgliedschaft <group> und show ip igmp groups <group> überprüfen. In diesem Szenario wird ein Eintrag für die übersetzte Multicast-Gruppe 239.55.55.55 erwartet.
ASR1000#show ip igmp membership 239.55.55.55
Flags: A - aggregate, T - tracked
L - Local, S - static, V - virtual, R - Reported through v3
I - v3lite, U - Urd, M - SSM (S,G) channel
1,2,3 - The version of IGMP, the group is in
Channel/Group-Flags:
/ - Filtering entry (Exclude mode (S,G), Include mode (G))
Reporter:
- last reporter if group is not explicitly tracked
/
-
reporter in include mode,
reporter in exclude Channel/Group Reporter Uptime Exp. Flags Interface
*,239.55.55.55 172.16.0.6 1w0d 02:40 2A Gi0/0/0
ASR1000#show ip igmp groups 239.55.55.55 IGMP Connected Group Membership Group Address Interface Uptime Expires Last Reporter Group Accounted 239.55.55.55 GigabitEthernet0/0/0 01:11:56 00:02:49 172.16.0.6
Zusätzlich kann bei der LHR eine Verifikation der mroute verwendet werden, um zu bestätigen, dass die Schnittstelle zum Empfänger in das OIL eingefügt wird und die Verwendung von mtrace, um den Rückweg zu beiden Quellen zu bestätigen.
ASR1000#show ip mroute 239.55.55.55
IP Multicast Routing Table
Flags: D - Dense, S - Sparse, B - Bidir Group, s - SSM Group, C - Connected,
L - Local, P - Pruned, R - RP-bit set, F - Register flag,
T - SPT-bit set, J - Join SPT, M - MSDP created entry, E - Extranet,
X - Proxy Join Timer Running, A - Candidate for MSDP Advertisement,
U - URD, I - Received Source Specific Host Report,
Z - Multicast Tunnel, z - MDT-data group sender,
Y - Joined MDT-data group, y - Sending to MDT-data group,
G - Received BGP C-Mroute, g - Sent BGP C-Mroute,
N - Received BGP Shared-Tree Prune, n - BGP C-Mroute suppressed,
Q - Received BGP S-A Route, q - Sent BGP S-A Route,
V - RD & Vector, v - Vector, p - PIM Joins on route,
x - VxLAN group, c - PFP-SA cache created entry,
* - determined by Assert, # - iif-starg configured on rpf intf,
e - encap-helper tunnel flag, l - LISP Decap Refcnt Contributor
Outgoing interface flags: H - Hardware switched, A - Assert winner, p - PIM Join
Timers: Uptime/Expires
Interface state: Interface, Next-Hop or VCD, State/Mode
(*, 239.55.55.55), 23:28:12/stopped, RP 10.100.100.1, flags: SJC
Incoming interface: TenGigabitEthernet0/1/1, RPF nbr 172.16.0.1
Outgoing interface list:
GigabitEthernet0/0/0, Forward/Sparse, 00:01:52/00:02:48
(172.16.101.2, 239.55.55.55), 00:10:11/00:02:40, flags: JT
Incoming interface: TenGigabitEthernet0/1/1, RPF nbr 172.16.0.1
Outgoing interface list:
GigabitEthernet0/0/0, Forward/Sparse, 00:01:52/00:02:48
ASR1000#mtrace 172.16.101.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Mtrace from 172.16.101.2 to 172.16.0.2 via RPF From source (?) to destination (?) Querying full reverse path... 0 172.16.0.2 -1 172.16.0.2 ==> 172.16.0.2 PIM/MBGP [172.16.101.0/30] -2 172.16.0.1 ==> 172.16.101.1 PIM_MT [172.16.101.0/30] -3 172.16.101.2
ASR1000#mtrace 192.168.0.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Mtrace from 192.168.0.2 to 172.16.0.2 via RPF From source (?) to destination (?) Querying full reverse path... 0 172.16.0.2 -1 172.16.0.2 ==> 172.16.0.2 PIM/MBGP [192.168.0.0/30] -2 172.16.0.1 ==> 192.168.0.6 PIM/MBGP [192.168.0.0/30] -3 192.168.0.5 ==> 192.168.0.1 PIM_MT [192.168.0.0/30] -4 192.168.0.2Zugehörige Informationen
Revisionsverlauf
| Überarbeitung | Veröffentlichungsdatum | Kommentare |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
20-Oct-2023 |
Erstveröffentlichung |
Beiträge von Cisco Ingenieuren
- Julio Jimenez
- Juan Rangel
Cisco kontaktieren
- Eine Supportanfrage öffnen

- (Erfordert einen Cisco Servicevertrag)
 Feedback
Feedback